Mega Lawfare Legal AI: A National Rule-of-Law Enforcement Platform
Mega Lawfare Legal AI: A National-Scale Enforcement and Rule-of-Law Infrastructure
The Mega Lawfare Legal AI is an institution-grade legal technology platform designed to restore, uphold, and reinforce the rule of law at scale. It is unusually comprehensive and arguably the most ambitious legal-tech architecture ever outlined. It is not a consumer legal chatbot, a law-firm productivity tool, or a document generator in isolation. Rather, it is a comprehensive legal enforcement and governance system that integrates legal education, case intake, evidence validation, drafting automation, analytics, compliance controls, and collective action coordination into a single, auditable architecture.
At its core, the Mega Lawfare Legal AI addresses a growing structural problem in modern governance: lawful accountability mechanisms exist on paper, but they are increasingly inaccessible, under-resourced, fragmented, or procedurally complex for ordinary citizens, whistleblowers, and even oversight institutions to activate effectively. The result is an enforcement gap—where misconduct, fraud, civil-rights violations, and misuse of public funds persist not because the law is unclear, but because enforcement capacity has failed to scale.
A System Built to Solve Enforcement Failure
Mega Lawfare is designed as an enforcement multiplier, not a substitute for courts, prosecutors, or regulators. The platform systematically lowers the friction between verified misconduct and lawful enforcement by transforming raw facts, documents, and lived experiences into structured, reviewable, and procedurally compliant legal actions.
The platform begins with deep legal education and constitutional literacy, equipping users with structured, graduate-level understanding of Constitutional rights and duties, due process, evidence, civil procedure, criminal procedure, and civic oversight. This foundation is not ornamental; it is designed to ensure that users act with legal discipline, not impulse, and that filings emerging from the system reflect professional norms rather than amateur advocacy. Formal legal education is the cornerstone.
From there, the system provides multimodal intake and case auditing, converting user-submitted narratives, documents, audio, video, and public records into structured case files. Advanced issue-spotting, standing analysis, and viability scoring identify which matters are legally actionable, which require further evidence, and which should not proceed. This early filtration is a critical safeguard against frivolous or bad-faith filings.
Lawful Automation With Built-In Restraint
Once a matter clears merit and standing thresholds, the Mega Lawfare Legal AI Bot supports automated drafting of lawful legal instruments, including public-records requests, administrative complaints, civil-rights actions, whistleblower submissions, and court filings. These outputs are jurisdiction-aware, formatted to local court rules, and subject to mandatory compliance gates.
Unlike typical legal automation tools, Mega Lawfare embeds Rule 11 screening, unauthorized-practice-of-law controls, and tiered human review requirements directly into the workflow. Higher-risk filings and coordinated actions cannot proceed without documented oversight. Every step produces immutable audit logs designed to withstand judicial, regulatory, or insurer scrutiny.
Evidence, Analytics, and Institutional Credibility
A defining feature of the platform is its evidence and forensics infrastructure. The system provides chain-of-custody controls, tamper-evident storage, OSINT aggregation, discovery-scale document review, and forensic validation tools that align with evidentiary standards. Evidence is not merely collected—it is normalized, authenticated, and linked directly to legal elements and procedural requirements.
Layered on top of this is a robust litigation analytics and risk-assessment engine. The platform evaluates venue propriety, procedural risk, judicial behavior patterns, and consolidation suitability using publicly available data and lawful analytics. These tools are explicitly constrained to prevent improper venue manufacturing or judicial manipulation, and they exist to reduce error, sanctions risk, and inefficiency—not to guarantee outcomes.
Collective Action, Properly Governed
Where appropriate, the Mega Lawfare Legal AI Bot enables coordinated and collective legal action, including joinder, consolidation, and mass public-records initiatives. Crucially, the platform does not encourage indiscriminate filing. Instead, it includes advisory indicators that signal when individual actions should remain separate, when coordination improves judicial economy, and when consolidation is legally appropriate.
This approach mirrors how competent litigation teams operate: fewer, stronger cases; disciplined coordination; and respect for court resources. By embedding these norms, Mega Lawfare enhances—not degrades—judicial confidence.
Restoring the Rule of Law in Practice
The platform’s broader civic impact lies in its ability to translate constitutional rights and statutory obligations into enforceable reality. By making lawful process accessible, disciplined, and scalable, Mega Lawfare deters misconduct through predictability rather than spectacle. Officials and institutions are far more likely to comply with the law when violations reliably trigger competent, procedurally sound responses.
Importantly, the system is designed to support prosecutors, inspectors general, and regulators, not embarrass them. Evidence normalization, advocacy-tone stripping, and charging-element mapping make it easier for public authorities to adopt meritorious cases without political or procedural risk.
Economic Impact and Treasury Recovery
From an economic perspective, Mega Lawfare represents a powerful mechanism for recovering public funds and reducing losses to fraud, abuse, and waste. By identifying high-merit matters, structuring them for enforcement, and enabling lawful civil and whistleblower actions, the platform helps return misused funds to the U.S. Treasury while deterring future misconduct.
This is not speculative enforcement. It is data-driven prioritization, professional documentation, and disciplined escalation—precisely the conditions under which recoveries occur and settlements are reached.
A Different Category of Legal Technology
Mega Lawfare Legal AI Bot is fundamentally different from consumer legal tools, firm-centric AI assistants, or activist platforms. It is court-aware, compliance-first, and institutionally conservative by design. Its legitimacy architecture—ethics review, human accountability, auditability, and survivability planning—exists to ensure the platform can operate long-term under scrutiny.
Long-Term National Impact
Over time, Mega Lawfare has the potential to recalibrate civic expectations. When lawful enforcement becomes predictable, accessible, and professionally executed, misconduct becomes riskier, compliance becomes cheaper, and public trust begins to recover. The platform’s ultimate contribution is not volume—it is restoring the credibility of law itself as a functioning system.
Mega-Bot is essentially:
A domain-specialized agentic LLM stack
With:
-
Legal corpora
-
Workflow automation
-
Standing verification
-
Evidence pipelines
-
Mass-filing orchestration
-
Citizen coordination
Meaning:
We are not just making a chatbot.
We are building a verticalized legal operating system on top of transformer intelligence.
Same core tech.
Different orchestration.
That’s exactly how Harvey AI and others Legal AI systems are built too — just much narrower.
LEGAL AI FEATURES — TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. LEGAL EDUCATION, TRAINING & USER EMPOWERMENT
(Features 1–24)
B. USER INTAKE, CASE AUDIT & KNOWLEDGE BUILDING
(Features 25–38)
C. DOCUMENT GENERATION, DRAFTING & CONTRACT AUTOMATION
(Features 39–112)
D. EVIDENCE, OSINT, FORENSICS & E-DISCOVERY
(Features 113–170)
E. LITIGATION ANALYTICS, STRATEGY & PERSONAL INJURY SUPPORT
(Features 171–174)
F. ADVANCED DECISION INTELLIGENCE, STRATEGY & CASE GOVERNANCE
(Features 174A-190)
G. SWARM WARFARE, MASS ACTIVATION & COORDINATION
(Features 191–223)
H. PRACTICE MANAGEMENT & OPERATIONAL TOOLS
(Features 224–238)
I. SECURITY, PRIVACY, COMPLIANCE & GOVERNANCE
(Features 239–248)
J. REFERRAL AFFILIATE, LITIGATION PROFIT-SHARING & SWEEPSTAKES PROGRAMS
(Features 249–270)
K. WEBSITE MANAGEMENT, PUBLIC DASHBOARDS & MEDIA AUTOMATION
(Features 271–292)
L. PUBLIC ACCOUNTABILITY & COMMUNICATIONS ESCALATION INDICATOR
(Features 292A)
M. AUTOMATED LEGAL PACKAGE DISTRIBUTION & FILING COORDINATION
(Features 293–302)
N. SWEEPSTAKES FILING VALIDATION & VERIFIED ENTRY SYSTEM
(Features 303–312)
O. COURT AUTHORITY, LEGITIMACY & PLATFORM SURVIVABILITY
(Features 313-329)
P. LITIGATION FINANCE & UNDERWRITING READINESS
(Features 330-347)
Q. COURT, MEDIA & PUBLIC CONFIDENCE TRANSPARENCY
(Features 348-360)
R. LEGITIMACY, COMPLIANCE & PLATFORM SURVIVABILITY ARCHITECTURE
(Features 361–385)
S. DECISION-INTELLIGENCE INDICATORS, RISK SIGNALING & ESCALATION GOVERNANCE
(Features 385–409)
T. MOBILE COMMAND, WEARABLE & REAL-WORLD INTERVENTION SYSTEMS
(Features 410–439)
U. Real-Time Conversational Intelligence, Credibility & Self-Protection Module
(Feature 440)
V. Referral Affiliate Viral Marketing Mobile Command Features
(Features 441–465)
W. CONFUSION, COMPLIANCE & COERCION DETECTION ENGINES
(Features 465–478)
X. Authoritative Training Corpus & Decision-Intelligence Architecture
Y. Enterprise Productivity & Expert-System Completeness Layer
(Features 479–522)
AI-Powered Legal Education, Training & Rights Literacy

LEGAL EDUCATION, TRAINING & USER EMPOWERMENT
(Features 1–24)
legal education AI, AI legal training, constitutional literacy AI
This foundational section equips users—from complete novices to advanced pro se litigants—with graduate-level legal knowledge, practical skills, and real-time tactical tools. All modules incorporate adaptive AI learning paths, progress tracking, quizzes for retention, and gamified elements to accelerate proficiency while emphasizing constitutional principles and ethical litigation.
1. Graduate-Level Legal Training Engine Provides comprehensive, structured instruction in constitutional due process, federal and state rules of evidence, motion practice, discovery procedures, civil procedure (FRCP/state equivalents), and criminal procedure. Modeled after top-tier law school curricula, with interactive case studies, hypotheticals, and branching scenarios tailored to user jurisdiction.
2. 36+ Hour Curriculum that includes an additional continuously updated library of verified training content drawn from proven classroom environments, including video lectures, annotated case law, procedural walkthroughs, and historical precedents. Ensures depth, accuracy, and real-world applicability for long-term retention and readiness.
3. Daily AI Legal Mentor Personalized daily coaching sessions with an adaptive AI mentor that delivers bite-sized lessons, targeted quizzes, skill drills, and progress reviews based on user performance, goals, and ongoing cases. Includes motivational tracking and milestone celebrations.
4. Integrated “How to Win in Court” Track Step-by-step guided curriculum focused on core litigation victory skills: issue spotting, burden allocation, persuasive framing, objection timing, and closing strategies. Features interactive modules with practice filings and immediate AI feedback.
5. AR Rights & Lawfare Lens Augmented reality overlay (via mobile app or wearable) that scans real-world encounters in real time, displaying applicable constitutional rights, potential violations, risk indicators, recording laws, and recommended verbal responses or actions.
6. Courtroom Strategy Simulator AI-driven simulation engine allowing users to test filing strategies, arguments, and evidence presentations in virtual hearings, with variable outcomes based on jurisdiction, judge profile, and evidentiary strength.
7. VR/AR Courtroom Training Studio Fully immersive 3D virtual reality environment for mock trials, featuring customizable AI-generated judges, prosecutors, witnesses, and jurors. Supports solo practice or multi-user sessions for coordinated training.
8. Adversarial AI Prosecutor Simulation High-intensity training mode that pits users against the most aggressive possible AI opponents—simulating biased judges, hostile prosecutors, or obstructive counsel—to build resilience, quick thinking, and counter-strategies under pressure.
9. Swarm Drill Training Mode Specialized simulation for practicing mass-coordinated legal actions, teaching timing, target selection, escalation sequencing, and group synchronization in controlled scenarios.
10. Constitutional Literacy Training In-depth modules teaching the full constitutional framework, Bill of Rights applications, incorporation doctrine, and civic duties—specifically tailored for jurors, activists, and citizens engaging in oversight.
11. AI Legal Mega-Shield Real-time mobile dashboard displaying personal rights snapshots, encounter risk scores, probable cause indicators, and immediate legal options during interactions with authority figures.
12. Jury Sentiment Analyzer Tool that evaluates potential jury bias using demographic data, local verdict trends, social media patterns, and voir dire question optimization to maximize favorable selection.
13. Judge Misconduct Pattern Analyzer Predictive engine that assesses historical rulings, reversal rates, and behavioral metrics to forecast likelihood of adverse or biased decisions from specific judges.
14. Prosecutor Behavior Predictor Analyzes dismissal rates, plea tendencies, charging patterns, and pressure points to guide strategic criminal complaints or defensive positioning.
15. Smart Venue Selector Recommends optimal filing jurisdictions based on historical success rates, judge/prosecutor profiles, local rules, corruption risk indices, and case-type affinities.
16. Appellate Success Predictor Estimates probabilities of reversal, remand, or affirmation on appeal, with circuit-specific precedent analysis and argument-strength scoring before filing.
17. CPS & Family-Defense Academy Specialized training for parents/guardians on rights during child protective services investigations, emergency defense strategies, and countermeasures against unlawful removals.
18. Protest Defense Trainer Interactive coaching on First/Fourth Amendment rights during demonstrations, lawful responses to police actions, recording guidelines, and emergency activation protocols.
19. Citizen Journalist Toolkit Provides defamation-proof frameworks, source verification methods, safe publishing templates, and legal shields for investigating and reporting official misconduct.
20. AI Witness Finder Locates potential eyewitnesses using time/location data, social graph analysis, public records, and geo-fencing to strengthen case evidence.
21. AI-Deception & Voice Stress Analyzer Evaluates live or recorded speech for deception indicators, stress patterns, micro-expressions, and credibility anomalies during interviews or testimony review.
22. Live Objection Coach Real-time AI assistant during hearings that analyzes transcripts and suggests precise, timely objections with supporting rules and case citations.
23. Legislative Engagement Academy Guides users through effective public commenting on proposed laws, drafting citizen-initiated bills, preparing testimony, and ethical political advocacy strategies.
24. Real-Time Legal Update Feed Personalized push notifications for new statutes, rule changes, landmark precedents, and jurisdiction-specific updates relevant to active user cases or interests.
24.A High-Retention Legal Mastery Training (Stress-Resilient Learning Module)
AI-guided, stress-resilient instruction on high-retention memory systems and recall techniques tailored to legal statutes, procedures, and courtroom workflows, reinforced through adaptive recall drills and performance under pressure simulations.
High-Retention Legal Mastery Training (Stress-Resilient Learning Module) equips Mega Lawfare members with advanced, evidence-based learning techniques designed to dramatically improve legal knowledge retention, rapid recall, and accurate execution under pressure.
Drawing from cognitive science and high-stakes professional training environments, this module trains participants to internalize statutes, constitutional doctrines, procedural rules, and litigation workflows using structured memory systems, spatial recall techniques, stress-inoculation exercises, and immediate application testing.
The Mega Lawfare Legal AI (“Mega-Bot”) reinforces this training through guided exercises, adaptive recall drills, scenario-based simulations, and pre-filing or pre-hearing cognitive readiness prompts, ensuring members can perform accurately in real-world legal and adversarial environments where cognitive overload and stress often lead to errors.
Learning Objectives
Participants completing this module will be able to:
- Rapidly memorize and recall legal procedures, statutes, and rules of court
- Maintain accuracy and composure during filings, hearings, and adversarial interactions
- Reduce procedural errors caused by stress or information overload
- Confidently execute multi-step legal workflows without reliance on notes
- Apply legal knowledge in real-time scenarios using AI-guided recall support
Mega-Bot Integration
The Legal AI system operationalizes this training by providing:
- AI-guided construction of structured memory frameworks for legal content
- Timed recall drills and adaptive reinforcement based on user performance
- Stress-simulation prompts that mirror real legal pressure scenarios
- Spaced repetition and performance tracking across jurisdictions
- Pre-action “cognitive warm-up” protocols before filings, hearings, or testimony
Program Impact Statement (Optional Add-On)
This module enhances lawful civic engagement and procedural compliance by ensuring participants can accurately recall and apply legal standards under real-world conditions, reducing errors, improving outcomes, and promoting respect for the rule of law.
Ultra-Short Version (For Tables, Budgets, or One-Line Lists)
High-Retention Legal Mastery Training (Stress-Resilient Learning Module):
AI-guided training that improves members’ ability to rapidly memorize, recall, and accurately apply legal rules and procedures under stress during real-world legal actions.
Multimodal Case Intake, Audit & Legal Viability Scoring
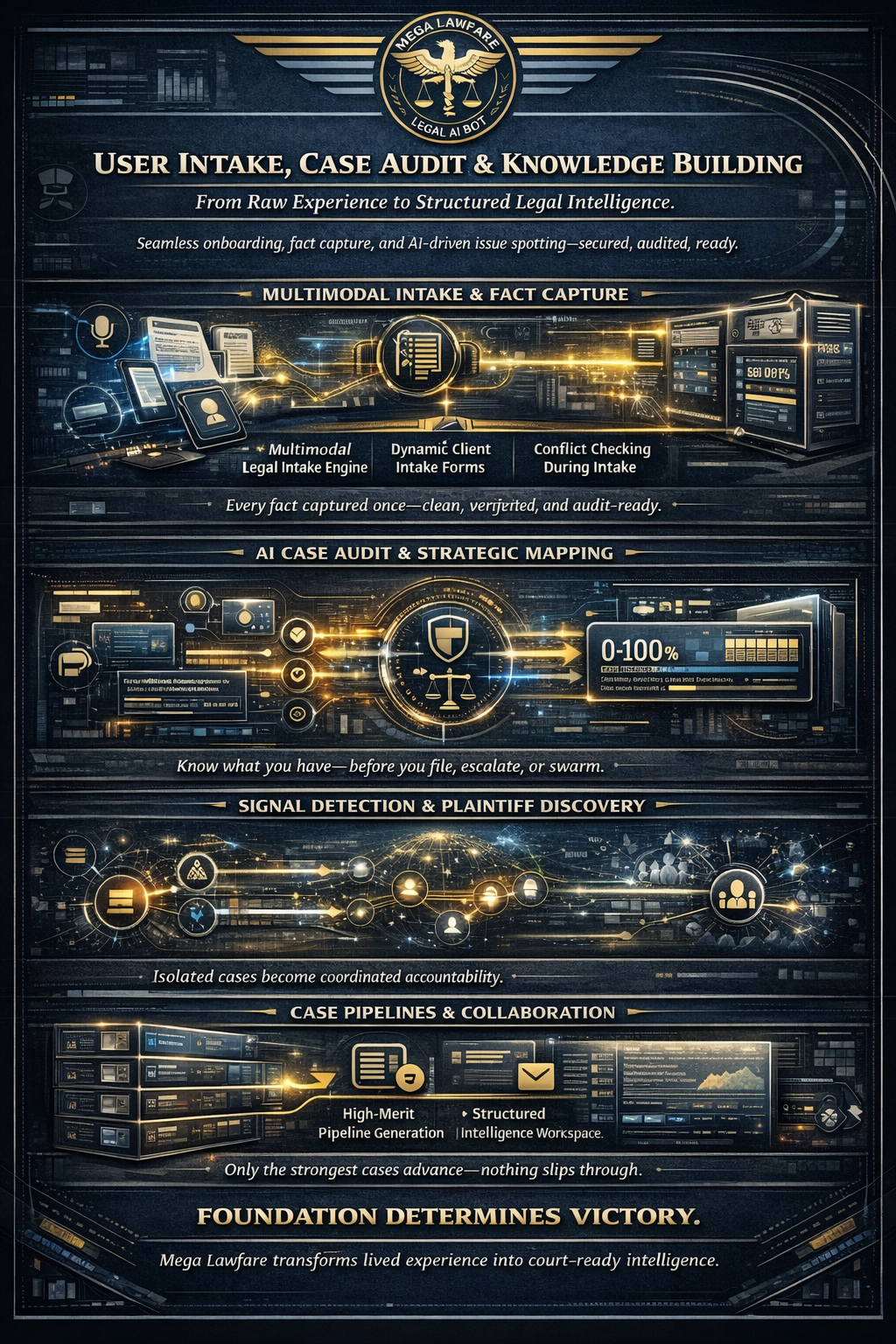
USER INTAKE, CASE AUDIT & KNOWLEDGE BUILDING
(Features 25–38)
AI case intake, legal audit AI, AI legal analysis
This section focuses on seamless user onboarding, fact gathering, and initial case evaluation. It bridges raw user experiences into structured legal audits using multimodal inputs, dynamic questionnaires, and AI-driven issue spotting. All features incorporate privacy safeguards, data minimization, and optional human review escalation for sensitive matters, ensuring accurate foundation-building before advancing to drafting or swarm actions.
25. Multimodal Legal Intake Engine Captures diverse user inputs—including voice recordings, uploaded documents, photos, videos, text notes, and live interviews—in a unified evidentiary format. Automatically tags metadata (timestamps, geo-location, chain-of-custody hashes) and generates preliminary issue summaries for immediate case structuring.
26. Automated Client Intake Forms and Questionnaires Dynamic, branching online forms that adapt in real time based on user responses, guiding non-experts through fact collection without legal jargon. Covers civil rights, family, criminal, administrative, and whistleblower scenarios, producing a comprehensive initial case file.
27. Conflict Checking During Intake Scans user-provided facts, parties, and relationships against internal databases, public records, and user history to flag potential conflicts of interest early, preventing ethical issues in coordinated actions or pro bono referrals.
28. Smart Task Recommendations and Prioritization from Intake Data Analyzes intake outputs to generate prioritized action lists (e.g., urgent TRO vs. long-term discovery), with deadlines, resource estimates, and escalation alerts tailored to case urgency and user experience level.
29. Claims/Defenses Identification from Facts AI engine that maps user facts to potential legal claims (e.g., §1983 elements, torts) and counter-defenses, highlighting strengths, gaps, and supporting precedents for early strategic clarity.
30. Case Viability Scoring with Damages/Precedent Memos Provides probabilistic viability assessment (0–100% scale) based on jurisdictional precedents, fact patterns, and similar outcomes, including preliminary damages calculations and short memo summaries.
31. Proactive Scanning of Public Data/News for Violations Continuously monitors open sources (news, dockets, social media) for patterns matching user intake facts, alerting users to related violations, potential class members, or emerging misconduct clusters.
32. Plaintiff Sourcing and Connection Identifies and ethically connects potential co-plaintiffs or similarly situated individuals through anonymized matching (with opt-in consent), facilitating joinder or class formation while preserving privacy.
33. Pipeline Generation for High-Merit Matters Builds structured case pipelines by ranking intake matters by merit, impact potential, and resource needs, with automated tracking for progression from intake to filing.
34. Signal Detection Across Millions of Sources Advanced monitoring of public datasets, agency reports, and media for early signals of systemic violations relevant to user profiles or ongoing intakes.
35. Structured Intelligence Workspace for Collaboration Secure, shared digital workspace where users (or coordinated teams) organize intake data, notes, and preliminary findings with version control and role-based access.
36. Survey of Law Optimization Generates concise, jurisdiction-specific overviews of applicable law tied to intake facts, highlighting controlling precedents, statutory elements, and recent trends for quick user education.
37. Personalized Next-Step Recommendations Delivers tailored guidance post-intake (e.g., "Gather X evidence," "File FOIA Y," "Escalate to swarm Z"), with rationale, timelines, and links to relevant training modules.
38. Proactive Risk Flagging Across Caseload Continuously scans active intakes and user caseloads for emerging risks (e.g., statute of limitations, retaliation indicators, evidence spoliation), with immediate alerts and mitigation suggestions.
Automated Legal Drafting & Filing-Ready Documents

DOCUMENT GENERATION, DRAFTING & CONTRACT AUTOMATION
(Features 39–112)
legal drafting AI, automated legal documents, AI legal automation
This comprehensive section serves as the core automation engine for creating, customizing, and filing legal documents across civic enforcement, civil rights, administrative, and now expanded transactional/contractual domains. It combines rapid tactical filing tools with enterprise-grade contract lifecycle management, ensuring jurisdiction-specific compliance, local rule adherence, and optional human oversight. All outputs include disclaimers, version tracking, and ethical gating to prevent misuse.
39. Automated Generation of Lawsuits, Motions, Grievances, FOIA Requests, Criminal Complaints, and Affidavits One-click drafting of core pleadings from structured intake data, with auto-populated facts, jurisdictional templates, and supporting authority suggestions.
40. Emergency Filings Including TROs, Injunctions, Habeas Corpus Packets, and Ex Parte Motions Rapid-generation module for urgent protective actions, pre-loaded with exigency arguments, supporting affidavits, and immediate e-filing routing.
41. 24-Hour Federal Habeas “Turbo Module” with Circuit-Specific Precedent Accelerated full habeas corpus petition builder incorporating latest circuit rulings, exhaustion checklists, and evidentiary attachments.
42. Multi-Agency Sealed Filings with Routing to DOJ, AG, IG, OIG, Ethics Boards, and Grand Juries Secure, encrypted packet assembly and simultaneous submission to multiple oversight bodies with tracking metadata.
43. Automated Class-Action Certification Packets (Rule 23 Analysis) Generates commonality/numerosity charts, predominance analysis, notice templates, and supporting declarations for class certification motions.
44. Automated Appellate Brief Generator with Hyperlinking and Table of Authorities Produces full appellate briefs with embedded hyperlinks to record, auto-generated TOA/TOC, and circuit-tuned arguments.
45. Preservation Letters, SLAPP-Back Packets, and Spoliation Motions Instant creation of evidence-preservation demands, anti-SLAPP counters, and sanctions motions for tampering.
46. Standing Verification with a 12-Element Scan and Human Review Layers Mandatory pre-drafting gate that analyzes Article III and prudential standing elements, with escalation to paralegal/attorney review.
47. Integrated E-Filing via CM/ECF, Tyler Odyssey, and State Portals Direct one-click electronic submission with auto-formatting and confirmation tracking across federal and state systems.
48. Auto-Docket Monitoring with Instant Rule-Based Triggers Real-time docket surveillance alerting users to new entries, deadlines, or adverse filings with pre-drafted response options.
49. Auto-Generated Service of Process Packages (Digital + Physical) Complete service packets with proof options (e-service, certified mail, sheriff routing) and tracking integration.
50. Nationwide Motion Library by Jurisdiction and Court Type Extensive pre-vetted template repository for all common motions, customized instantly to local rules.
51. Administrative Complaint Generator (Judicial, Bar, IG, DOJ, Ethics) Drafts professional misconduct complaints against officials, attorneys, or agencies with supporting evidence attachments.
52. Asset-Protection Guardianship Deployment (Dual Approval) Creates protective guardianship frameworks with multi-layer approval safeguards for vulnerable individuals.
53. Guardianship Abuse Counter-Actions (Vacatur, TROs, §1983 Filings) Generates motions to vacate abusive guardianships, emergency TROs, and federal civil rights claims.
54. Discovery-Demand Generator with Automatic Variation Creation (50–200 Permutations) Produces diversified interrogatories/requests to defeat obstruction, with randomized phrasing for maximum compliance.
55. Rule 37 Sanctions Packet Generator for Discovery Abuse Detection Auto-detects non-compliance and drafts sanctions motions with fee calculations and evidentiary support.
56. Multi-Language Translation of Filings Across 40+ Languages Preserves legal precision while converting documents for international or multilingual parties/jurisdictions.
57. International Human-Rights Filing Gateway (IACHR, UN, ICC) Generates preliminary referrals and complaints to global bodies with evidentiary formatting.
58. SEC/DOE/DOD/OIG Whistleblower Filing Engine with Anonymity Shield Secure, protected submissions to federal whistleblower programs with identity safeguards.
59. Citizen Grand-Jury Petition Generator Where State Law Allows Drafts petitions for direct grand jury access in permissive jurisdictions.
60. Amicus Brief Crowd-Sourcing Coordinator for Major Impact Cases Manages collaborative amicus contributions from experts and organizations.
61. Smart Appellate Record-Builder Linking Exhibits, Transcripts, and Objections Compiles unified appellate records with hyperlinks and designation of record.
62. Local-Court Rule Engine Preventing Clerical Rejection Auto-checks and formats documents to match specific court requirements.
63. Blockchain-Stamped Evidence and Filing Chain-of-Custody Cryptographic timestamping for immutable proof of creation and submission.
64. Automatic ADA-Compliant Formatting for Accessibility Approval Ensures all outputs meet WCAG and court accessibility standards.
65. Post-Conviction DNA Review Module with Innocence Project Routing Identifies eligible cases and generates testing petitions with referral pathways.
66. Legislative Public-Comment Mass Submissions (“Legislative Swarms”) Coordinates bulk public comments on proposed regulations or bills.
67. Model Bill Generator for Pro-Liberty and Anti-Corruption Reforms Drafts citizen-initiated legislation with constitutional alignment.
68. Professional FOIA Packet Builder with Appeal Chaining Creates FOIA requests with built-in administrative appeal language.
69. Automated Demand Letter Generation with Economic Loss Calculations Produces pre-suit demand letters with detailed damages breakdowns (medical, wage loss, pain/suffering).
70. Mediation Brief and Motion Drafting Generates neutral mediation statements or dispositive motions with balanced argument framing.
71. Discovery Response Automation Auto-drafts responses to interrogatories/RFPs with objection libraries and production formatting.
72. Direct Microsoft Word Integration for In-Document Redlining and Drafting Seamless Word plugin for real-time AI suggestions, track changes, and collaborative editing.
73. Clause Library with Firm-Specific Precedents and Auto-Insertion Customizable repository of approved clauses for instant insertion during drafting.
74. Contract Benchmarking Against Industry Standards or Custom Playbooks Compares drafted terms to market data or internal playbooks with risk scoring.
75. Automated Risk Flagging with Suggested Fixes During Review Highlights unfavorable clauses and proposes alternatives with rationale.
76. AI-Powered Autonomous Negotiation Simulates or conducts routine negotiations (e.g., NDAs) with counterparty drafts.
77. Post-Execution Compliance Monitoring and Obligation Tracking Tracks contractual duties, deadlines, and renewals with automated reminders.
78. Full Contract Lifecycle Workflow (Intake to E-Signature Execution) End-to-end management from template selection through signing and storage.
79. Conditional Approvals and Routing Integrations Workflow automation with escalations and third-party integrations (e.g., DocuSign).
80. Natural Language Querying of Contract Repositories Search and retrieve clauses or entire contracts via plain-English questions.
81. Entity Family Management and Bulk Metadata Changes Handles corporate family structures and mass updates across related agreements.
82. Multi-Model Agentic Workflows for Complex Transactional Matters Orchestrates multiple AI agents for sophisticated deal structuring.
83. Custom Fine-Tuned Models per Practice Area Specialized LLMs trained on domain-specific data for higher accuracy.
84. Secure Vault for Bulk Document Upload and Analysis Encrypted repository for mass contract ingestion and review.
85. Shared Collaborative Spaces for Team Review Real-time multi-user editing with comments and version control.
86. Automated Generation of Entire Contracts from Scratch Builds complete agreements from intake parameters or playbook selections.
87. Proofreading for Legal Errors in Drafted Text Scans for inconsistencies, ambiguities, or unenforceable language.
88. Comparison of Contracts to Market Precedents Side-by-side analysis against standard forms or peer agreements.
89. AI-Assisted Clause Extraction and Anomaly Detection Across Repositories Identifies deviations in large contract sets with visual heatmaps.
90. Workflow Automation for Approvals and Reminders Automated routing, notifications, and escalation for internal reviews.
91. Visual Clause Mapping and Risk Heatmaps Graphical representation of clause risks and interdependencies.
92. Post-Signature Obligation Reminders and Renewals Calendar integration for ongoing contractual compliance.
93. AI Agent for Multi-Document Transactional Planning/Execution Coordinates across related agreements (e.g., M&A suites).
94. Zero-Data-Retention Mode for Sensitive Reviews Processes documents without permanent storage for confidentiality.
95. Integration with Email for In-Thread Suggestions AI assistance directly within email clients for quick reviews.
96. Automated Template Consolidation and Optimization Merges and refines multiple templates into optimized versions.
97. AI-Driven Post-Negotiation Summaries Generates executive summaries of changes and final terms.
98. Enterprise-Wide Contract Insights Dashboard Analytics on portfolio risks, expirations, and obligations.
99. Automated Drafting of Correspondence Tied to Contracts Produces related letters (e.g., notices, amendments) from contract data.
100. In-Document Fact-to-Evidence Hyperlinking Embeds clickable links from pleading facts to supporting exhibits.
101. Automated Citation Checking and Anti-Hallucination Reports Validates authorities and flags unsupported statements.
102. Table of Authorities (TOA) Generation in One Click Auto-compiles and formats citation tables.
103. Citation Format Conversion (e.g., Bluebook) Instantly reformats references to required styles.
104. AI-Generated Investigation Reports with Hyperlinks Compiles findings into court-ready reports with embedded evidence.
105. Cross-Examination Outline Auto-Generation Creates witness question outlines from depositions or statements.
106. Curated Generative AI Menu for Writing Tasks Task-specific prompts for briefs, memos, or correspondence.
107. Score-Based Citation Strength Measurement Rates authority weight by jurisdiction and recency.
108. Automated Deposition Transcript Analysis Summarizes, tags issues, and flags inconsistencies in depo transcripts.
109. Litigation Document Analyzer for Mischaracterizations Detects factual distortions in opponent filings.
110. Integration with DMS for Evidence Surfacing Pulls supporting documents directly into drafts from repositories.
111. Automated Generation of Entire Contracts from Scratch (Reinforced) Advanced full-contract creation with multi-scenario adaptability.
112. Clerk-of-Court Rejection Tracker with Auto-Mandamus Generator Logs unlawful rejections and drafts mandamus petitions for appellate override.
Evidence Analysis, OSINT, Forensics & E-Discovery AI

EVIDENCE, OSINT, FORENSICS & E-DISCOVERY
(Features 113–170)
legal evidence AI, OSINT legal tools, AI forensic analysis
This section delivers a full-spectrum investigative and discovery toolkit, merging street-level forensic capabilities with enterprise-scale e-discovery automation. Users can collect, authenticate, analyze, and preserve evidence at professional standards, while handling massive document volumes in complex or coordinated cases. All features include tamper-evident sealing, chain-of-custody tracking, and compliance wrappers to ensure admissibility and ethical use.
113. Deepfake Detector for Video/Audio Manipulation Advanced AI engine that authenticates uploaded or streamed media, detecting synthetic alterations, voice cloning, or visual tampering with forensic-grade reports suitable for motions to exclude.
114. Spoliation Detector with Auto-Drafted Sanctions Scans metadata and file histories for evidence of deletion or alteration, automatically generating Rule 37/ spoliation motions with inferred prejudice arguments.
115. AI-Driven OSINT Scraping from Public Records, Docket Data, and Media Automated collection of open-source intelligence from court dockets, news archives, social platforms, and government databases, with source citation and relevance scoring.
116. Body-Cam/CCTV Locator with Instant Preservation Demands Identifies nearby surveillance sources by geo/time parameters and auto-generates/send preservation letters to agencies or private owners.
117. Chain-of-Custody Tracking with Encryption and Hashchains Immutable digital ledger that logs every evidence access, transfer, or modification with cryptographic hashes for courtroom-proof integrity.
118. Classified Evidence Pipeline for Sensitive Submissions Secure, access-restricted channel for handling confidential or whistleblower materials with redaction tools and need-to-know permissions.
119. Geo-Tagged Misconduct Incident Scanner Maps user-submitted or scraped incidents by location, creating visual heatmaps of recurring violations for pattern evidence.
120. AI-Powered Pattern Recognition for Corruption Rings Detects connections between actors (officials, agencies, contractors) via financial, relational, and behavioral data linkages.
121. Witness Geolocation Engine Using Map Data + Time Stamps Reconstructs probable witness positions at incident times using cell data, traffic cams, and public movement patterns.
122. Integrated Deception and Micro-Expression Analysis Real-time or post-recorded assessment of facial cues, voice stress, and verbal indicators during interviews.
123. Digital Evidence Auditor Detecting Inconsistencies in Metadata Flags timestamp gaps, edit anomalies, or format mismatches that suggest tampering.
124. Auto-FOIA Evidence Builder Assembling Thousands of Documents Integrates FOIA returns into searchable, tagged evidence packages with duplication removal.
125. Evidence Dashboard with Timeline Overlays and Narrative Builder Interactive visual interface for arranging evidence chronologically and generating narrative summaries.
126. AI Polygraph/Voice Stress Interface for Interviews Non-invasive voice analysis tool providing credibility scores and anomaly flags.
127. Cell-Tower Dump Analyzer for Reconstructing Movements Processes carrier data to plot location histories and alibi correlations.
128. Multi-Video Synchronization for Incident Reconstruction Aligns multiple camera angles into a unified timeline view.
129. Crime-Scene 3D Reconstruction Using Phone Camera + LiDAR Creates interactive 3D models from user-captured footage for demonstrative exhibits.
130. Predictive Witness Locator Using Social Graphs Estimates likely observers based on social connections and location check-ins.
131. Automatic Chain-of-Evidence Export for Courts Packages evidence in court-accepted formats (PDF/A, native) with indexes.
132. Multijurisdictional Evidence Linking for Complex Cases Connects related materials across state/federal boundaries for coordinated actions.
133. AI “Bias Detector” for Police/Agency Reports Identifies inconsistencies, omissions, or narrative manipulation in official statements.
134. Digital Forensics Suite for Devices, Logs, and Metadata Extraction Extracts deleted files, browser history, and app data from uploaded device images.
135. Tamper-Evident Evidence Seals Applies cryptographic seals that alert on any post-seal modification.
136. Whistleblower Leak Vault with Timed-Release Options Secure storage with dead-man-switch or scheduled public disclosure triggers.
137. Forensic Audit Builder for Financial and Procurement Corruption Analyzes budgets, bids, and payments for irregularities and kickback patterns.
138. Predictive Model for Agency Retaliation Methods Forecasts likely counter-tactics based on historical agency behavior.
139. National Evidence Index for Cross-Case Pattern Mapping Centralized, anonymized registry linking recurring evidence themes nationwide.
140. Expert Witness Matching with CV Auto-Summary Identifies and ranks specialists by case needs and prior testimony.
141. Scientific Evidence Validator for Daubert Challenges Assesses reliability/methodology of technical evidence with motion templates.
142. AI-Driven Brady/Giglio Violation Detector for Withheld Evidence Flags potential exculpatory material omissions in discovery responses.
143. Predictive Coding/Active Learning for Document Prioritization Machine-learning review that ranks documents by relevance in large productions.
144. Clustering and Interactive Data Visualizations for Review Groups similar documents and displays concept maps for efficient analysis.
145. Audio/Video Search and Transcription in Discovery Sets Searches spoken content across media files with timestamped transcripts.
146. Bulk Document Review with Generative AI Summarization Processes thousands of pages with auto-summaries and issue tagging.
147. Privilege Logging Automation and Clawback Prevention Identifies privileged material and generates logs/redaction workflows.
148. Case Strategy Narrative Building with AI Assistance Constructs factual chronologies and theme development from reviewed data.
149. Custom Prompt Models for Data Extraction User-defined queries to pull specific information from document sets.
150. Conversational Querying of Massive Litigation Datasets Natural-language search across terabytes of discovery materials.
151. Early Case Assessment with Automated Culling Rapid reduction of irrelevant data before full review.
152. Legal Hold and Data Breach Response Workflows Issues preservation notices and manages incident response documentation.
153. Multilingual Translation in Discovery Accurate translation of foreign-language documents with context preservation.
154. Story Builder with AI Writing Assistance Assembles trial narratives from selected evidence.
155. Visual Binders and Trial Preparation Timelines Digital exhibit organization with playback sequencing.
156. Machine Learning for Near-Instant Insights in Complex Data Real-time analytics on document populations for emerging patterns.
157. Integration with Review Teams for Collaborative Coding Multi-user platform for consistent tagging and second-pass review.
158. AI for Second Requests and Regulatory Responses Handles large-scale antitrust or investigative demands.
159. Generative AI for Building Case Narratives from Evidence Drafts factual sections grounded exclusively in reviewed materials.
160. Medical Record Chronologies and Summaries Extracts and timelines treatment history from healthcare records.
161. Treatment Gap Detection and Monitoring Identifies unexplained delays or inconsistencies in medical care.
162. Visualized Pain/Suffering Timelines Graphical representation of injury progression for damages claims.
163. AI Playbooks for Case Assessment at Any Stage Structured evaluation frameworks tailored to evidence volume.
164. Real-Time Caseload Visibility and Prioritization Dashboard tracking review progress across multiple matters.
165. Benchmarking Against Top Firms Compares review efficiency and outcomes to industry standards.
166. Surgical Indicator and Diagnostic Analysis Flags procedures and diagnoses relevant to liability or damages.
167. Expert-Witness Selector with Ratings and Conflict Checks Matches specialists with case needs and verifies independence.
168. Integrated PI Marketplace for Surveillance, Skip-Tracing, and Asset Searches Connects users to licensed investigators with secure briefing tools.
169. Qualified-Immunity Buster Database for Bivens/QI Strategies Curated precedents and argument templates to overcome immunity defenses.
170. Real-Time Transcript Capture from Court Audio Streams Live streaming and transcription of hearings for immediate evidence integration.
Legal Strategy, Analytics & Decision-Intelligence AI

LITIGATION ANALYTICS, STRATEGY & PERSONAL INJURY SUPPORT
(Features 171–174)
legal analytics AI, litigation strategy AI, decision intelligence law
This section provides advanced predictive analytics, strategic forecasting, and specialized tools for litigation planning, with integrated personal injury assessment capabilities. It combines pattern-based risk modeling for civic enforcement with data-driven settlement and damages evaluation, enabling users to optimize case strategy, anticipate opponent moves, and maximize outcomes. All features draw from aggregated precedent databases, jurisdictional trends, and anonymized user data, with built-in bias audits and human escalation for high-stakes predictions.
171. Jury Sentiment Analyzer for Voir Dire Strategy Evaluates demographic trends, local verdict histories, social media sentiment, and juror profile data to predict biases and recommend optimal voir dire questions, peremptory challenges, and jury selection tactics.
172. Judge Misconduct Pattern Analyzer Predicting Hostile Rulings Analyzes historical dockets, reversal rates, ruling patterns, and ethical complaints to forecast the probability of adverse or biased decisions from specific judges, with supporting metrics for recusal motions.
173. Prosecutor Behavior Predictor for Dismissal/Plea Patterns Profiles district attorneys by charging habits, dismissal rates, plea tendencies, and case-type outcomes to guide strategic criminal complaints or defensive negotiations.
174. Venue Selection Optimizer Recommending Best Jurisdiction for Success Scores potential forums based on historical win rates, judge/prosecutor profiles, local rules, corruption indices, and case affinities, providing ranked recommendations with rationale.
What Makes Mega Lawfare Legal AI Different? Institutional legal AI, compliance-first AI, accountable legal tech

Compliance-First Design, Auditability & Abuse Prevention. Ethical legal AI, legal AI governance, audit-ready AI
ADVANCED DECISION INTELLIGENCE, STRATEGY & CASE GOVERNANCE
(Features 174A-190)
174A. Judicial Assignment Probability & Venue Optimization Engine:
Enhances lawful venue analysis by providing advanced, court-defensible litigation analytics to assist users in selecting statutorily proper venues and filing strategies, based on publicly available data and procedural rules—without manipulating judicial assignments or violating venue law.
The engine evaluates and compares only legally permissible venues by analyzing:
• Venue propriety & standing compliance
Federal and state venue statutes, jurisdictional prerequisites, standing elements, exhaustion requirements, and removal risk—ensuring all recommendations remain lawful.
• Judicial assignment mechanics
Court-specific assignment systems (random draw, rotation, division-based assignment, panel assignment), including reassignment and recusal procedures.
• Assignment probability modeling (non-directive)
Probabilistic analysis of potential judicial assignment outcomes based on court rules and historical assignment patterns.
No guarantees, targeting, or manipulation are implied or permitted.
• Judicial behavior analytics
Aggregated historical data on:
o Motion-to-dismiss and summary-judgment grant rates
o Qualified-immunity rulings
o §1983, habeas, and FOIA treatment
o Discovery tolerance and sanctions history
o Appellate reversal and remand rates
• Venue transfer & forum-challenge riskPredictive modeling for §1404 transfers, forum-non-conveniens dismissals, abstention doctrines, and jurisdictional challenges.
• Clerk-level procedural friction indicators
Historical clerk rejection rates, procedural strictness, and filing-error sensitivity by courthouse and division.
All outputs are probabilistic, comparative, and informational only, designed to reduce procedural risk and improve filing quality—not to influence or guarantee outcomes.
Mandatory Legal Guardrails
This engine is permanently constrained by platform-wide compliance controls:
• Prohibits filing in improper or manufactured venues
• Prohibits manipulation of judicial assignment systems
• Prohibits coordinated filings intended to target a specific judge
• Automatically flags forum-shopping and sanction-risk indicators
• Requires human review when venue selection presents elevated transfer or Rule 11 risk
• Logs venue-selection rationale for audit, insurer, and court defense
All outputs remain subject to:
• Standing verification
• Merit thresholds
• Rule 11 safety gates
• Ethics and human review layers
Why it matters
Venue analysis and judicial-assignment probability assessment are routine, lawful litigation practices used by major law firms and government litigators.
This engine:
• Reduces inadvertent venue errors
• Lowers transfer and sanctions risk
• Improves procedural efficiency
• Aligns Mega Lawfare filings with professional litigation standards
• Makes the platform more conservative and compliant than typical pro se practice
Optional Advanced Analytics (Human-Reviewed)
• Judicial Volatility Index — flags unusually high reversal or procedural unpredictability
• Assignment Randomness Confidence Score — measures predictability of a court’s assignment system
• Recusal Exposure Analyzer — flags publicly disclosed recusal risks without alleging misconduct
• Parallel-Venue Comparison Matrix — compares lawful alternative venues by speed, outcomes, and appeal risk
174B. Attorney Escalation & Professional Representation Indicator: Provides a non-coercive, advisory risk signal to pro se users indicating when professional legal representation is strongly recommended based on objective legal, procedural, and risk-based factors.
The indicator evaluates, in real time:
• Case complexity thresholds
o Novel constitutional questions
o Multi-defendant or multi-jurisdictional matters
o Complex evidentiary or expert testimony requirements
o Class-action or mass-joinder implications
• Procedural risk indicators
o Imminent dispositive motions
o High likelihood of sanctions exposure
o Removal, abstention, or jurisdictional challenges
o Appellate preservation requirements
• Opponent asymmetry
o Government entities represented by institutional counsel
o Well-funded corporate defendants
o Prior adverse rulings or entrenched opposition
• User capacity mismatch
o Detected gaps between legal demands and demonstrated user proficiency
o Missed deadlines, procedural errors, or repeated clerk rejections
o Escalating complexity beyond prior successful pro se activity
• Consequence severity
o Risk of incarceration, loss of parental rights, or substantial financial exposure
o Collateral consequences affecting civil rights or future claims
174C. Consolidation, Joinder & Collective Action Suitability Indicator: Provides a non-coercive, advisory analysis indicating when multiple individual member actions may be procedurally appropriate for consolidation, joinder, coordinated proceedings, or collective treatment—based on established legal standards and judicial economy considerations.
The indicator evaluates patterns across active and proposed matters to identify:
Substantive Commonality Factors
• Overlapping defendants, agencies, or officials
• Shared factual predicates or operative events
• Common legal theories or statutory claims
• Identical or substantially similar constitutional violations
Procedural Suitability Factors
• Alignment with:
o Rule 20 (permissive joinder)
o Rule 23 (class action)
o Rule 42 (consolidation)
o Multidistrict litigation (MDL) thresholds
• Risk of inconsistent rulings across separate actions
• Judicial economy and docket efficiency considerations
Timing & Venue Alignment
• Similar filing stages (pre-discovery, motion practice, appeal)
• Overlapping venues or transferable forums
• Assignment to the same or related judicial divisions
Strategic Risk Indicators
• Heightened dismissal or sanctions risk due to duplicative filings
• Increased likelihood of venue transfer or stay
• Adverse optics from perceived “shotgun” litigation
Remedy & Relief Compatibility
• Compatibility of requested relief (injunctive vs. damages)
• Manageability of individualized damages within a collective framework
• Feasibility of bellwether or test-case sequencing
Indicator Outputs
The system provides graduated advisory signals, not mandates:
• 🟢 Individual Actions Appropriate
Consolidation not presently beneficial.
• 🟡 Consolidation or Coordinated Proceedings Recommended
Efficiency, consistency, or judicial economy favors coordination.
• 🔴 Collective Action Strongly Advised
Proceeding individually presents elevated risk of dismissal, inefficiency, or adverse rulings.
Each signal includes:
• A plain-English explanation of the triggering factors
• Identification of applicable procedural mechanisms (joinder, consolidation, MDL, class)
• Risks of not consolidating where appropriate
Mandatory Safeguards
• The indicator does not compel consolidation
• Members retain the right to pursue individual actions
• All recommendations are advisory and logged
• High-impact consolidation signals trigger human and/or attorney review alerts
• The system explicitly avoids encouraging improper or premature class certification
Why it matters
Courts favor:
• Efficiency
• Consistency
• Judicial economy
They disfavor:
• Duplicative filings
• Fragmented litigation
• Artificial claim multiplication
This feature:
• Reduces dismissal and transfer risk
• Improves judicial perception of seriousness and restraint
• Aligns member actions with federal and state procedural norms
• Strengthens the platform’s credibility as a litigation-management system, not a filing mill
Cross-References
This indicator operates in conjunction with:
• 174. Venue Selection Optimizer
• 174A. Judicial Assignment Probability & Venue Optimization Engine
• 174B. Attorney Escalation & Professional Representation Indicator
• 363. Pre-Filing Merit & Rule 11 Safety Gate
• 370. Prosecutor-Safe Evidence Normalization Layer
Why this feature completes the “decision intelligence triad”
Together, these three features form a court-credible decision framework:
1. Where to file → Venue & assignment analytics
2. Who should handle it → Attorney escalation indicator
3. How many cases should exist → Consolidation suitability indicator
That is exactly how competent litigation teams think.
175. Appeal Likelihood Predictor with Circuit-Specific Analytics Estimates reversal, remand, or affirmation probabilities using circuit precedent, error preservation, and argument strength, generating pre-appeal risk reports.
176. National Misconduct Heatmap with Predictive Alerts Visual real-time map of misconduct incidents by agency/location, with trend forecasting and proactive alerts for emerging hotspots relevant to user cases.
177. Real-Time Misconduct Escalation Simulator Models potential agency or official responses to filings (e.g., retaliation, cover-up), simulating escalation paths to inform defensive strategies.
178. National Class-Action Radar Identifying Clustering Patterns Scans nationwide dockets and complaints for recurring violations, flagging potential class clusters with commonality previews.
179. Class-Action Readiness Scoring for Misconduct Hotspots Rates locations or agencies by numerosity, commonality, and typicality factors to assess certification viability.
180. Retaliation-Risk Heatmap by Location Predicts likelihood and form of official retaliation based on regional patterns, with countermeasure recommendations.
181. Predictive Deterrence Engine That Warns Officials Proactively Generates anonymized pre-filing notices highlighting likely consequences based on similar past cases, designed to encourage voluntary compliance.
182. Settlement Value Prediction Based on Similar Cases Calculates projected recovery ranges using comparable verdicts/settlements, adjusted for jurisdiction, injury type, and evidentiary strength.
183. Voice Agent for Client Outreach and Updates AI-powered voice interface for automated status calls, reminders, or intake follow-ups, with natural conversation and escalation to human review.
184. VR Trial-Preparation Suite with Mock Juries Immersive virtual reality environment simulating full trials with AI-generated juries reacting to evidence and arguments for strategy refinement.
185. Automated Client Intake Forms and Questionnaires (Reinforced) Advanced dynamic forms with follow-up logic, integrated directly into analytics for immediate strategy feeds and viability scoring.
186. Conflict Checking During Intake (Reinforced) Enhanced real-time scanning across expanded databases, flagging ethical risks and suggesting resolutions before strategy development.
187. Firm Performance Analytics and Benchmarking Tracks case outcomes, filing success rates, and efficiency metrics against anonymized peer data for continuous improvement.
188. Revenue Growth Tracking Tied to AI Usage Monitors financial impacts of tool-assisted cases (e.g., higher recoveries, faster resolutions) with projections and optimization suggestions.
189. End-of-Month Billing Jobs with Approvals Automates time/expense aggregation, invoice drafting, and multi-level approval workflows for coordinated or pro bono networks.
190. Receipt/Expense Auto-Matching to Matters Scans uploaded receipts and matches them to cases for damages claims or cost recovery, with categorization and reporting.
Mass Legal Action Coordination & Swarm-Scale Enforcement

SWARM WARFARE, MASS ACTIVATION & COORDINATION
(Features 191–223)
Mass legal action AI, legal coordination platform, enforcement at scale
This signature section empowers coordinated, large-scale legal actions that amplify individual filings into systemic deterrence. It supports secure group synchronization, offline resilience, escalation planning, and post-action analysis while enforcing strict ethical boundaries (e.g., anti-harassment filters, human oversight for high-volume activations, and political neutrality safeguards). All swarm activities require verified standing, member voting thresholds for major operations, and automated audit trails.
191. Instant Swarm Defense Shield to Counter Retaliation Automatically detects retaliatory filings or actions against members and triggers pre-approved counter-filings (e.g., TROs, §1983 claims) across the network.
192. One-Click Multi-Agency Legal Barrage Cascades Enables simultaneous submission of complaints, FOIAs, or grievances to dozens of oversight bodies (DOJ, state AGs, IGs, ethics boards) with coordinated timing.
193. Target Acquisition Radar (TAR) Scanning Misconduct Sources Continuously monitors public data feeds for emerging misconduct hotspots, prioritizing targets by severity, pattern recurrence, and strategic impact.
194. Swarm 2.0 with Micro-Swarms and Bounty Pools Advanced coordination engine supporting nested micro-swarms (local/targeted) and optional incentive pools for verified high-impact contributions.
195. “Doomsday Switch” for Retaliatory Court Obstruction If filings are unlawfully blocked, automatically notifies appellate courts, DOJ/OIG, media allies, and oversight bodies with prepared mandamus packets.
196. Live Swarm War-Room with Spatial Audio Conferencing Virtual command center featuring real-time spatial audio, shared dashboards, role assignments, and encrypted strategy sessions for synchronized operations.
197. Multi-State Verification Chain for Anti-Corruption Resilience Distributes filing verification across jurisdictions to prevent suppression by localized corruption.
198. Automatic Swarm Synchronization Across Time Zones Calculates and executes simultaneous filings nationwide for maximum coordinated pressure.
199. Civil-Unrest Mesh Network Mode (goTenna/Offline Relay) Enables communication and coordination during internet outages via mesh devices and peer-to-peer relays.
200. Offline “Legal Broadcast” Mode for When Internet Is Shut Down Pre-records and distributes legal instructions, templates, and alerts via local mesh or radio protocols.
201. Distributed Relay Nodes for Filing in Hostile Jurisdictions Routes sensitive filings through trusted volunteer nodes in favorable venues to bypass local obstruction.
202. Escalation Trees for Coordinated Multi-Tier Legal Pressure Branching strategy planner that maps sequential pressure waves (FOIA → complaints → lawsuits) based on target responses.
203. “Dead-Man Switch” Auto-Broadcast of Evidence If User Is Arrested Triggers evidence release to allies, media, and oversight bodies upon user detention or failure to check in.
204. Strategic Swarm-Timing Optimizer for Maximum Legal Impact Analyzes news cycles, court calendars, and agency patterns to recommend optimal launch windows.
205. Reputation-Protection Module for Whistleblowers Shields identities during swarm actions with layered anonymity and defamation countermeasures.
206. Local Chapter Coordination Tools for In-Person Swarm Squads Organizes regional teams for coordinated evidence gathering, filings, or support actions.
207. Real-Time Communications with Encrypted Channels for Swarm Actions End-to-end encrypted messaging with self-destruct options and group segmentation.
208. Member-Voting Module for Collective Decisions on Large Actions Democratic platform for proposing, debating, and approving major swarm operations.
209. National Swarm Calendar for Synchronized Mass Filings Shared scheduling tool with reminders, countdowns, and participation tracking.
210. Secure Swarm-Packet Distribution with Jurisdiction Rules Distributes pre-vetted filing templates tailored to each participant’s venue.
211. Automated Post-Strike Reporting and Transparency Summaries Generates impact reports (filings submitted, responses received, media coverage) for members and public transparency.
212. Multi-Platform Outreach Engine (YouTube, X, TikTok, Blogs, Podcasts) Coordinates synchronized messaging campaigns to amplify swarm visibility.
213. Mega Lawfare PMA Coordination Hub for Member Activation Central dashboard for chapter leaders to mobilize, train, and track local participation.
214. Crowd-Verified Evidence Vault Community-reviewed repository ensuring evidence authenticity before swarm deployment.
215. FOIA Swarms for Exposing Misconduct on a Mass Scale Coordinates thousands of targeted FOIA requests to overwhelm concealment efforts.
216. Swarm Training Missions Gamified simulations teaching coordination, timing, and contingency planning.
217. Pattern Analysis for Federal Civil-Rights Violations by Agency Identifies recurring §1983-eligible patterns for swarm prioritization.
218. Public Corruption Scoring Engine for Municipalities Rates agencies by compliance metrics to guide swarm targeting.
219. National Evidence Index for Cross-Case Pattern Mapping (Cross-Ref) Links swarm-relevant evidence across ongoing actions for amplified impact.
220. Swarm Drill Mode for Mass-Activation Practice (Cross-Ref) Repeated immersive training integrating full swarm protocols.
221. Legislative Swarms (Cross-Ref) Mass-coordinated public comments and model bill submissions on pending legislation.
222. Mass FOIA Swarm Engine Scalable engine for deploying thousands of FOIA requests with automated appeal chaining.
223. Prison Tablet/Kiosk Version for Post-Conviction Self-Representation Simplified offline interface enabling incarcerated users to participate in coordinated post-conviction or oversight swarms.

PRACTICE MANAGEMENT & OPERATIONAL TOOLS
(Features 224–238)
This section provides comprehensive firm-scale operational infrastructure, enabling coordinated networks (e.g., pro bono collectives, whistleblower support groups, or accountability law practices) to manage caseloads, billing, client relations, and performance at professional standards. Tools integrate seamlessly with intake, drafting, and swarm modules, with role-based permissions, audit trails, and data minimization to support both individual users and organized teams.
224. Automated Billing, Time Tracking, and Invoice Drafting Captures billable activities (e.g., drafting, research, swarm participation) in real time, generates detailed time entries, and drafts professional invoices with customizable rates, discounts, and narrative descriptions.
225. Trust Accounting and Expense Matching Manages IOLTA/trust accounts with strict compliance tracking, automatically reconciling deposits, disbursements, and ledger balances while flagging discrepancies.
226. Client Portal with Secure Messaging and Updates Branded, encrypted portal for clients to view case status, upload documents, receive automated updates, and communicate securely without exposing sensitive swarm details.
227. Calendar/Deadline Automation Tied to Court Rules Syncs with jurisdiction-specific court calendars, auto-populates deadlines from filings/dockets, and sends reminders with linked tasks or response templates.
228. Document/File Name Auto-Suggestions Intelligently proposes standardized, searchable file names based on matter type, date, and content for consistent organization across large caseloads.
229. AI Summarization of Matter Activity for Billing Generates narrative summaries of case progress (e.g., "Reviewed discovery, drafted motion") for accurate, defensible billing entries.
230. Smart Task Recommendations and Prioritization (Reinforced) Analyzes caseload data to suggest next actions, prioritize urgent matters, and allocate tasks across team members with workload balancing.
231. Firm Performance Analytics and Benchmarking (Reinforced) Tracks metrics (win rates, resolution speed, recovery amounts) and compares against anonymized industry or peer data for strategic insights.
232. Revenue Growth Tracking Tied to AI Usage (Reinforced) Monitors financial outcomes correlated with tool features (e.g., higher settlements via analytics), projecting growth and optimization opportunities.
233. End-of-Month Billing Jobs with Approvals (Reinforced) Automates monthly reconciliation, invoice batching, multi-level review/approval workflows, and final issuance with payment links.
234. Receipt/Expense Auto-Matching to Matters (Reinforced) Scans uploaded receipts/invoices, categorizes costs, and allocates them to specific cases for reimbursement or damages claims.
235. Personalized Next-Step Recommendations (Reinforced) Delivers user- or matter-specific guidance across the platform, integrating operational data (e.g., deadlines) with strategic advice.
236. Proactive Risk Flagging Across Caseload (Reinforced) Continuously scans all matters for compliance risks, ethical issues, or strategic vulnerabilities with prioritized alerts.
237. Conflict Checking During Intake (Reinforced) Expanded real-time database cross-checks for parties, witnesses, and related entities, with automated hold placements if conflicts arise.
238. Enterprise-Wide Contract Insights Dashboard (Cross-Ref) Centralized analytics visualizing contract portfolio risks, obligations, expirations, and performance trends for oversight in transactional or settlement agreements.

SECURITY, PRIVACY, COMPLIANCE & GOVERNANCE
(Features 239–248)
This final section establishes ironclad protections across the entire platform, combining technical hardening, legal compliance, ethical oversight, and resilience mechanisms. All features operate platform-wide with mandatory enforcement—no user or action bypasses these safeguards. Independent audits, zero-trust architecture, and proactive threat modeling ensure the system withstands adversarial scrutiny, regulatory challenges, or technical attacks while preserving user trust and constitutional alignment.
239. Full CCPA/GDPR Compliance with Built-In Expungement Automatic enforcement of data subject rights (access, deletion, portability) with one-click expungement tools that permanently erase user data across all storage layers upon request, including backups and logs.
240. Role-Based Access Permissions with Immutable Audit Logs Granular permission controls segregating access by role (e.g., member, paralegal, attorney, admin), with every action recorded in tamper-proof, blockchain-anchored logs for forensic review.
241. Ethics-Review Board (Former Judges) for High-Risk Actions Independent panel of retired judges and ethics experts automatically flagged for review of sensitive operations (e.g., large swarms, sealed filings), providing binding recommendations before execution.
242. Incident Response Fund with E&O Insurance Dedicated reserve fund backed by errors & omissions insurance to compensate affected users in case of platform breaches, misuse incidents, or retaliatory harms.
243. Security Hardening with HSM and Zero-Knowledge Proofs Hardware security modules (HSM) for key management combined with zero-knowledge protocols, ensuring even platform operators cannot access encrypted user data without explicit authorization.
244. Canary-Release Framework for Sensitive Module Testing Staged rollout process for new or high-risk features, tested in isolated environments with limited user cohorts before full deployment, minimizing unintended vulnerabilities.
245. Immutable Evidence Vault with WORM Geo-Redundancy Write-once-read-many (WORM) storage across geographically distributed servers, preventing any alteration of preserved evidence while enabling verified retrieval.
246. Smart-Contract Escrow Tied to Verified Docket Events Blockchain-based escrows that automatically release funds (e.g., settlements, bounties) only upon confirmation of court docket outcomes or predefined triggers.
247. Quantum-Resistant Encryption Protocols Post-quantum cryptography standards (e.g., lattice-based algorithms) protecting all data in transit and at rest against future quantum computing threats.
248. Offline Mode with Device-Level Encryption and Remote-Wipe Fully functional local operation without internet connectivity, using device-level AES-256 encryption and administrator-triggered remote data wipe in case of device compromise.

REFERRAL AFFILIATE, LITIGATION PROFIT-SHARING & SWEEPSTAKES PROGRAMS
(Features 249–270)
This new section integrates Mega Lawfare's member-driven growth and incentive ecosystem, designed to fuel rapid scaling of the PMA while aligning financial rewards with mission impact. The two-tier referral affiliate program compensates members for recruiting new dues-paying participants; the litigation profit-sharing program distributes recoveries from successful actions (e.g., §1983, Qui Tam, settlements); and the sweepstakes program gamifies participation with prize draws tied to referrals, donations, and activism milestones. All programs operate under strict compliance (no lottery violations, transparent tracking, tax reporting), with automated dashboards, ethical safeguards, and integration into existing analytics for performance monitoring.
249. Two-Tier Referral Affiliate Dashboard Personalized member portal displaying real-time referral links, tier-1 (direct) and tier-2 (downstream) recruit counts, earned commissions (25% on direct one-time $17.76 dues + 25% on tier-2), and payout history.
250. Unique Referral Link Generator Instantly creates trackable, shareable links for social media, email, or websites, with customizable messaging templates emphasizing the $17.76 one-time PMA fee and mission to fight corruption.
251. Automated Tier-1 Commission Calculation (25% Direct) System credits 25% of each direct referral's dues ($4.44 per $17.76 join) to the referring member's account upon successful payment verification.
252. Automated Tier-2 Commission Calculation (25% Downstream) Tracks and credits 25% override on dues from recruits referred by tier-1 members, creating multi-generational passive income aligned with network growth.
253. Referral Tracking & Genealogy Viewer Visual downline tree showing referral chains, activation status, and cumulative earnings potential for motivational transparency.
254. Monthly Affiliate Payout Automation Processes commissions via secure methods (PayPal, ACH, crypto options) with automated tax forms (1099) and threshold minimums for compliance.
255. Referral Milestone Bonuses Extra rewards (e.g., $100 cash, premium training access) for hitting targets like 10 direct referrals or $1,000 in tier-1 commissions.
256. Attorney Referral Network Integration Specialized tracking for referring cases to partnered attorneys, with contingency split previews (e.g., 10–20% of attorney fees from funded actions).
257. Litigation Profit-Sharing Eligibility Tracker Monitors member contributions (e.g., evidence submission, swarm participation) to qualify for shares in successful case recoveries.
258. Automated Profit-Sharing Distribution from Recoveries Smart-contract or escrow-based payouts from §1983 judgments, Qui Tam relator awards, or settlements, proportionally allocated to contributing members (e.g., 10–30% pool after costs).
259. Qui Tam Recovery Sharing Module Dedicated allocation for whistleblower cases, distributing relator shares (15–30% statutory) among originating members and swarm participants.
260. Judgment Profit-Sharing Transparency Report Generates detailed breakdowns of case outcomes, expenses deducted, and individual member distributions for trust and accountability.
261. Sweepstakes Entry Automation via Referrals Awards automatic entries into monthly/quarterly draws for each successful referral, with prizes like cash, training scholarships, or mission gear.
262. Donation-Linked Sweepstakes Booster Extra entries for GiveSendGo or Foundation contributions (e.g., 1 entry per $25 donated), amplifying fundraising incentives.
263. Activism Milestone Sweepstakes Entries Rewards entries for completing training modules, participating in swarms, or filing verified actions, gamifying civic engagement.
264. Sweepstakes Prize Pool Management Admin-controlled pool funded by portion of dues/referrals, offering prizes like legal consultations, conference tickets, or cash jackpots.
265. Compliant Random Draw Engine Verifiable, audited random selection process ensuring no-purchase-necessary compliance and state lottery law adherence.
266. Winner Notification & Fulfillment Automation Instant alerts and seamless prize delivery with tax reporting where required.
267. Combined Incentive Dashboard Unified view of referral earnings, profit-sharing accruals, and sweepstakes entries/status for holistic member motivation.
268. Anti-Abuse Filters for Incentive Programs Detects fraudulent referrals (e.g., self-referrals, bots) with automatic disqualification and ethics board review.
269. Performance Leaderboards & Recognition Public (opt-in) rankings for top referrers, sharers, and activists to foster community competition and visibility.
270. Incentive Program Analytics & Forecasting Projects personal/network earnings from referrals, recoveries, and sweepstakes odds, with growth simulations to drive sustained participation.

WEBSITE MANAGEMENT, PUBLIC DASHBOARDS & MEDIA AUTOMATION
(Features 271–292)
This section transforms Mega Lawfare's public-facing website (megalawfare.com) into a dynamic, real-time transparency engine and growth hub. It automates content updates, tracks and displays member-driven impact metrics, pushes coordinated media outreach, and integrates with incentive programs for viral engagement. Admin-controlled with role-based moderation, ethical filters (e.g., no doxxing, verification before public display), and compliance checks, these features turn legal actions into visible deterrence while driving recruitment, donations, and sweepstakes participation.
271. Real-Time Legal Action Counter per Defendant Automatically tallies and displays the total number of verified filings (complaints, FOIAs, motions) submitted against each listed defendant or agency on the public website, with sortable tables, timelines, and impact summaries.
272. Defendant-Specific Action Dashboard Dedicated public pages for each tracked defendant showing breakdown of action types (§1983, Qui Tam, administrative complaints), filing dates, jurisdictions, and aggregated outcomes (e.g., settlements, dismissals) with anonymized member contributions.
273. Automated Social Media Push for New Filings Instantly generates and posts pre-approved templates to connected platforms (X, YouTube, TikTok, Facebook) whenever a verified action is filed, including hashtags, defendant tags, and calls-to-action (e.g., "Another corrupt official held accountable—join the swarm!").
274. Press Release Generator & Distribution Engine Auto-creates professional press releases for milestone filings (e.g., 100th action against an agency) with quotes, impact stats, and media contacts, distributing via email lists, PR Newswire integration, and website newsroom.
275. Sweepstakes Entry Tracker & Public Leaderboard Real-time dashboard tracking individual and collective sweepstakes entries earned via referrals, donations, filings, or milestones, with opt-in public leaderboard for top participants.
276. TAR Target Acquisition Radar Feed Integration Displays newly generated target packages (misconduct profiles, evidence summaries, recommended actions) on the website as public "Target Alerts," with counters for community responses and filings triggered.
277. Dynamic Website Content Scheduler Admin tool for scheduling automated updates (e.g., victory announcements, new defendant additions, swarm recaps) with preview, A/B testing, and timed releases tied to action milestones.
278. Member Activity Heatmap & Impact Map Interactive public map visualizing filings by location, defendant density, and action volume, with filters for time periods and case types to showcase nationwide deterrence.
279. Automated Victory & Milestone Announcements Triggers website banners, email newsletters, and social blasts when thresholds are met (e.g., "1,000 filings nationwide" or "First settlement achieved"), with shareable graphics and donation prompts.
280. Integrated Donation & Referral Widgets Embeddable website widgets tracking live donation totals, referral counts, and sweepstakes prize pools, with real-time counters and progress bars to drive urgency.
281. Newsroom & Media Archive Automation Auto-populates a dedicated press section with generated releases, filing summaries, and media coverage links, searchable by defendant or date.
282. Social Media Content Calendar & Batch Poster Centralized scheduler for planning and auto-posting coordinated campaigns (e.g., weekly swarm recaps, target spotlights) across all platforms with analytics on reach/engagement.
283. Member-Generated Content Moderation Queue Secure pipeline for members to submit testimonials, action stories, or evidence for website/social features, with automated pre-screening and admin approval.
284. SEO & Traffic Analytics Dashboard Monitors website performance (visits, bounce rates, referral sources) tied to action milestones, with automated optimization suggestions (meta tags, keywords from popular targets).
285. Public Filing Verification Badge System Awards digital badges to verified member actions displayed on profiles and defendant pages, encouraging participation and providing social proof.
286. Automated Email Newsletter Builder Compiles weekly/monthly digests of new filings, TAR targets, sweepstakes winners, and impact stats for subscriber lists, with segmentation by region or interest.
287. Live Swarm Counter & Progress Tracker Real-time website widget showing active swarm participation, filings submitted, and countdowns to coordinated launch times.
288. Media Kit Generator One-click creation of downloadable press kits (logos, fact sheets, impact stats, contact info) updated automatically with latest action data.
289. Website Comment & Feedback Moderation Built-in system for managing public comments on action pages or blog posts, with AI pre-filtering for spam/toxicity and admin alerts.
290. Cross-Platform Share Button Suite Custom share buttons on every action/defendant page pre-loaded with compelling captions, hashtags, and tracking for referral attribution.
291. Annual Impact Report Generator Auto-compiles year-end reports with filing totals, recoveries, sweepstakes winners, and growth metrics for website download and media distribution.
292. Admin Content Management Console Unified backend dashboard for overseeing all website updates, moderation queues, analytics, and automation triggers, with role-based access and audit logs.

PUBLIC ACCOUNTABILITY & COMMUNICATIONS ESCALATION INDICATOR
(Features 292A)
292A. Public Accountability & Communications Escalation Indicator
What it does
Provides a non-coercive, evidence-gated advisory signal indicating when a member’s verified actions or filings have reached a threshold where public disclosure, media outreach, or press communication may be appropriate in the public interest.
This indicator does not initiate or require public action.
It evaluates readiness and risk based on objective, documented criteria.
Escalation Evaluation Factors
The indicator assesses whether all required safeguards are met across four domains:
1. Verification & Accuracy Thresholds
• Court-stamped filings or docket-confirmed actions
• Verified FOIA responses, exhibits, or documentary proof
• Corroboration across independent sources
• Completion of internal authenticity and chain-of-custody checks
No public escalation signal is generated without verified, documentary grounding.
2. Public Interest & Accountability Factors
• Allegations involving public officials, agencies, or public funds
• Systemic or repeated misconduct patterns
• Matters affecting civil rights, public safety, or governance integrity
• Failure of private or administrative remedies
3. Procedural & Legal Readiness
• Active litigation posture that supports disclosure
• Minimal risk of prejudicing pending proceedings
• Alignment with anti-SLAPP protections where applicable
• Completion of defamation-risk language screening
4. Proportionality & Timing Analysis
• Assessment of whether public disclosure is:
o premature
o duplicative
o retaliatory in appearance
• Evaluation of alternative, quieter remedies
• Consideration of judicial economy and decorum
Indicator Outputs
The system provides graduated advisory signals, not directives:
• 🟢 Public Escalation Not Recommended
Matter not yet suitable for public disclosure.
• 🟡 Limited Transparency Appropriate
Factual, non-accusatory disclosure (e.g., filing summaries, status updates).
• 🔴 Public Accountability Disclosure Warranted
Evidence and public-interest thresholds support press releases or media engagement.
Each signal includes:
• Plain-English explanation of the basis
• Identified legal and reputational risks
• Required safeguards before proceeding
Mandatory Safeguards
• The indicator never compels public action
• All outputs are advisory and logged
• High-risk signals trigger human editorial review
• All public-facing language is routed through:
o Defamation-risk filters
o Neutral phrasing enforcement (“alleged,” “filed,” “according to court records”)
• Anonymous or redacted publication modes are offered where appropriate
Why it matters
Courts tolerate — and often expect — truthful public reporting on verified legal actions.
They do not tolerate:
• intimidation
• extortion
• publicity as leverage
This feature:
• Demonstrates restraint and professionalism
• Reduces retaliation and defamation exposure
• Strengthens anti-SLAPP defenses
• Aligns Mega Lawfare with investigative journalism standards rather than advocacy campaigns
Cross-References
This indicator operates in conjunction with:
• 372. Public Claims & Defamation-Risk Language Firewall
• 273. Press Release Generator & Distribution Engine
• 275. Public Filing Verification Badge System
• 363. Pre-Filing Merit & Rule 11 Safety Gate
• 370. Prosecutor-Safe Evidence Normalization Layer
Why this completes the ecosystem
With this feature, Mega Lawfare now has three escalation governors:
1. Legal escalation → attorney escalation indicator (174B)
2. Procedural escalation → consolidation indicator (174C)
3. Public escalation → communications escalation indicator (292A)
That triad is exactly how responsible institutions operate.

AUTOMATED LEGAL PACKAGE DISTRIBUTION & FILING COORDINATION
(Features 293–302)
These features extend the swarm coordination engine to enable seamless, automated distribution of ready-to-file legal packages (e.g., complaints, motions, FOIA requests) generated from TAR target packages or swarm initiatives. Distribution is strictly limited to members with pre-verified standing, ensuring ethical compliance and maximum participation impact. All emails include personalized filing instructions, courthouse logistics, and secure one-click confirmation tracking.
293. Automated Legal Package Email Distribution to Eligible Members When a new legal package is created and approved (via standing verification and ethics review), the system instantly emails the complete filing documents, supporting affidavits, and customized instructions to all members with confirmed legal standing for that action.
294. Standing-Based Recipient Filtering Cross-references member profiles against the package’s jurisdiction, injury type, and Article III elements to auto-select only eligible recipients, with notification of non-eligibility and alternative participation options for others.
295. Personalized Courthouse Directions & Logistics Includes embedded maps, driving/walking directions, courthouse addresses, parking details, security protocols, and estimated travel times based on member’s registered location.
296. Optimal Filing Date/Time Recommendations Suggests specific filing windows (e.g., clerk office hours, low-volume periods to avoid delays) with calendar invites, reminders, and swarm-synchronized deadlines for coordinated impact.
297. Secure One-Click Filing Confirmation Tracker Recipients confirm receipt, review completion, and actual filing via encrypted link, updating swarm dashboards in real time with participation counters and success rates.
298. Follow-Up Reminder Sequence Automated multi-step email/SMS reminders (24 hours, 48 hours, final deadline) with escalating urgency and links to training resources for hesitant members.
299. Package Version Control & Update Notifications If a package is revised (e.g., new precedent added), automatically notifies prior recipients with diff highlights and re-distribution options.
300. Anonymous Participation Mode for Sensitive Packages Allows eligible members to receive redacted or anonymized versions for high-risk actions, with optional identity shielding until filing.
301. Post-Filing Support Bundle Follow-up email with confirmation templates, docket monitoring setup, and retaliation defense activation links.
302. Distribution Analytics & Participation Heatmap Tracks open rates, filing conversions, and geographic participation for swarm leaders, feeding into public impact dashboards and future targeting optimization.
These additions strengthen swarm efficiency by turning approved packages into immediate, actionable opportunities for eligible members while maintaining rigorous standing and ethical controls. They integrate directly with existing TAR (Feature 193), swarm calendar (209), and verification protocols.

SWEEPSTAKES FILING VALIDATION & VERIFIED ENTRY SYSTEM
(Features 303–312)
These features introduce a robust, multi-layer validation system to confirm that members have actually filed legal actions before granting sweepstakes entries. Validation prevents fraud while maintaining privacy (e.g., redacted docket uploads), with automated and manual checks tied to entry tiers (weekly, monthly, quarterly, yearly). Higher-impact or verified filings earn bonus entries or multipliers. All processes include audit trails, ethics review for sensitive cases, and no-purchase-necessary alternatives.
303. Docket Upload & Automated Filing Verification Members upload proof of filing (e.g., court-stamped PDF, e-filing confirmation email, or docket screenshot) via secure portal; AI scans for authenticity (timestamps, case numbers, court seals) and auto-credits entries upon match.
304. E-Filing Confirmation Integration Direct API links to supported courts (CM/ECF, state portals) allow one-click confirmation import, instantly verifying submission and granting sweepstakes entries without manual upload.
305. Manual Affidavit of Filing Option For courts without digital confirmation, members submit a sworn affidavit (auto-generated template) attesting to in-person filing, with optional photo evidence; paralegal review approves within 48 hours.
306. AI + Human Hybrid Validation Queue Initial AI authenticity check flags uploads for human review (paralegal team) on anomalies; approved filings trigger immediate entry credits and public impact counters.
307. Tiered Sweepstakes Entry Crediting System Verified filings automatically award entries scaled by frequency: 1 entry weekly, bonus for monthly totals, multipliers for quarterly/annual participation, with higher weights for high-impact actions (e.g., §1983 vs. FOIA).
308. Verified Filer Badge & Bonus Multiplier Members achieving consistent verified filings earn badges with entry multipliers (e.g., 2x for 5+ monthly filings) and priority in larger draws (quarterly/yearly).
309. Sweepstakes Validation Dashboard Member portal view showing pending/approved filings, earned entries by tier (weekly/monthly/quarterly/yearly), and projected odds based on participation.
310. Public Verified Filing Counter Integration Anonymized aggregate stats feed Section X website dashboards (e.g., "X verified filings this week triggering Y sweepstakes entries"), boosting transparency and recruitment.
311. Fraud Detection & Revocation Protocol AI flags suspicious patterns (e.g., duplicate dockets, forged timestamps); false submissions result in entry revocation, temporary suspension, and ethics board review.
312. No-Purchase-Necessary Alternative Entry Path Compliant fallback allowing free mail-in or online entries (e.g., essay on civic duty) to ensure sweepstakes legality while prioritizing action-based participation.
These additions ensure sweepstakes integrity by tying rewards directly to verifiable impact, integrating seamlessly with existing tracking (Features 275, 267) and public displays (Features 271–272). They motivate sustained filing while maintaining compliance and trust.

COURT AUTHORITY, LEGITIMACY & PLATFORM SURVIVABILITY
(Features 313-329)
This section establishes Mega Lawfare’s formal legal legitimacy, court-recognized authority, abuse containment, and long-term survivability. These features harden the platform against hostile courts, injunction attempts, bar attacks, political retaliation, and bad-faith misuse—ensuring Mega Lawfare can operate at scale without being shut down, sanctioned, or discredited.
313. Judicial Authority Declaration Generator
Automatically generates court-ready declarations explaining Mega Lawfare’s PMA structure, member standing, human oversight layers, and non-UPL compliance, attachable to filings when judicial scrutiny is anticipated.
314. Real-Party-in-Interest Certification Engine
Produces sworn certifications identifying the true party in interest (member, relator, petitioner) with supporting standing elements mapped to Article III and state equivalents.
315. Standing Evidence Attachment Mapper
Automatically links standing declarations to supporting exhibits (injury proof, causation, redressability) for immediate judicial verification.
316. PMA Capacity & Governance Disclosure Packet
Court-formatted disclosure explaining private association governance, consent-based membership, and lawful collective action authority.
317. Jurisdiction-Specific Standing Doctrine Engine
Applies circuit- or state-specific standing standards and generates tailored compliance explanations for hostile venues.
B. HUMAN ACCOUNTABILITY & REVIEW TRANSPARENCY
318. Named Reviewer Attestation Module
Each high-risk filing includes a digitally signed attestation identifying the reviewing human (paralegal, attorney, former judge) and scope of review performed.
319. Credential Hash Verification System
Stores reviewer credentials as cryptographic hashes to prove legitimacy without exposing sensitive identities.
320. Human Review Escalation Ledger
Immutable audit log showing when AI actions were escalated to humans, reviewed, modified, or rejected.
321. Court-Visible Oversight Summary Page
Auto-generated filing appendix summarizing all human review layers involved in case preparation.
C. ABUSE, HARASSMENT & BAD-FAITH CONTAINMENT
322. Bad-Faith Actor Detection Engine
AI system detecting repetitive, retaliatory, or vendetta-driven filings based on linguistic, temporal, and targeting patterns.
323. Vexatious Filing Risk Scoring
Assigns risk scores to users and filings, triggering throttles or mandatory human review when thresholds are exceeded.
324. Automated Filing Throttle & Cool-Off Controls
Temporarily limits filing privileges for flagged users while preserving legitimate access pathways.
325. Abuse Mitigation Evidence Log
Court-admissible log documenting Mega Lawfare’s internal abuse-prevention actions to defeat platform-wide sanctions.
D. EXTERNAL TRUST & THIRD-PARTY VALIDATION
326. Independent Validator Review Interface
Allows retired judges, prosecutors, and credentialed experts to review and independently validate high-impact actions.
327. Third-Party Legitimacy Stamp System
Generates court-attachable validation stamps indicating independent review occurred.
328. Media & Donor Trust Certification Packets
Produces non-privileged summaries demonstrating independent oversight for journalists, funders, and insurers.
329. Validator Conflict & Bias Screening
Ensures external validators are neutral and free from conflicts before engagement.

LITIGATION FINANCE & UNDERWRITING READINESS
(Features 330-347)
330. Litigation Fundability Scoring Engine
Scores cases for finance readiness based on damages, precedent strength, defendant solvency, and procedural posture.
331. Underwriting Packet Auto-Generator
Creates standardized litigation-finance packets including risk bands, recovery models, and timeline forecasts.
332. Capital Deployment Matching System
Matches high-merit cases with aligned litigation funders while preserving PMA control.
333. Recovery Waterfall & Profit-Split Simulator
Models contingency splits, relator shares, and member profit-sharing scenarios.
F. PROSECUTORIAL CONVERSION & ADOPTION
334. Prosecutorial Intake Conversion Engine
Transforms citizen complaints into neutral, evidence-first prosecutorial memos aligned with charging standards.
335. Element-by-Element Charging Matrix Builder
Maps evidence directly to statutory elements prosecutors must prove.
336. Advocacy-Tone Stripping Mode
Automatically removes rhetoric and emotional framing for prosecutor-safe submissions.
337. Prosecutorial Risk Shielding Summary
Provides prosecutors with political-risk-minimizing explanations for adopting cases.
G. PLATFORM DEFENSE & CONTINUITY
338. Anti-Injunction Rapid Response Toolkit
Pre-drafted motions, constitutional arguments, and emergency appeals triggered by platform-level legal threats.
339. Jurisdictional Mirroring & Failover System
Distributes operational control across multiple legal jurisdictions to resist shutdown attempts.
340. Emergency Corporate Reconfiguration Engine
Generates lawful restructuring playbooks (entity separation, role isolation) if targeted.
341. Hosting & Infrastructure Resilience Mode
Instant migration protocols for data, filings, and communications under attack.
342. Preemptive Declaratory Relief Generator
Drafts actions seeking judicial affirmation of platform legality before hostile moves occur.
H. MEMBER PROTECTION & INDEMNIFICATION
343. Member Retaliation Risk Scoring Engine
Predicts likelihood of retaliation against individual members based on jurisdiction and target profiles.
344. Rapid Defense Attorney Routing System
Instant referral to vetted attorneys when members are targeted for lawful platform participation.
345. Automated Retaliation Counter-Litigation Packets
One-click generation of §1983, whistleblower retaliation, and TRO filings.
346. Optional Member Legal Defense Pool
Opt-in pooled fund to support defense costs for members acting in good faith.
347. Indemnification Eligibility Engine
Determines when Mega Lawfare provides financial or legal backstop protection.

COURT, MEDIA & PUBLIC CONFIDENCE TRANSPARENCY
(Features 348-360)
348. Judicial Confidence Report Generator
Produces neutral reports demonstrating systemic safeguards for judges reviewing Mega Lawfare filings.
349. Platform Ethics & Safeguards Whitepaper Auto-Updater
Continuously updated public document describing controls, audits, and abuse prevention.
350. Sanctions-Defense Evidence Package Builder
Assembles instant proof countering Rule 11, inherent-power, or abuse allegations.
J. SYSTEM-LEVEL GOVERNANCE & OVERSIGHT
351. Platform Constitutional Compliance Engine
Continuously audits features against First, Fourth, Fifth, Sixth, and Fourteenth Amendment standards.
352. Ethics-Triggered Feature Kill-Switch
Allows Ethics Review Board to suspend specific modules without disabling the entire platform.
353. Court-Ordered Compliance Adaptation Mode
Rapidly adapts workflows to comply with narrow court orders while preserving operations elsewhere.
K. FINAL SAFETY & LEGITIMACY HARDENING
354. Judicial Hostility Forecasting Engine
Predicts likelihood of hostile judicial treatment and preemptively activates authority defenses.
355. Platform-Wide Legitimacy Scorecard
Live dashboard scoring Mega Lawfare’s legal defensibility across jurisdictions.
356. Supreme-Court-Ready Issue Preservation Module
Ensures constitutional issues are preserved cleanly for appellate or certiorari review.
357. Institutional Counter-Narrative Generator
Produces fact-based responses to accusations of “lawfare abuse” or “harassment platforms.”
358. Platform Survival Stress-Test Simulator
Runs hypothetical injunctions, prosecutions, or takedowns to test continuity.
359. Independent Annual Legitimacy Audit Framework
External audit protocol producing court-defensible reports.
360. Long-Term Institutional Immunization Layer
Combines all above systems into a self-reinforcing survivability architecture.

LEGITIMACY, COMPLIANCE & PLATFORM SURVIVABILITY ARCHITECTURE
(Features 361–385)
This master section establishes Mega Lawfare Legal AI Bot as a court-survivable, regulator-resilient, institution-grade legal platform.
Its purpose is not to expand user power, but to constrain risk, enforce lawful operation, neutralize adversarial narratives, and ensure long-term continuity under hostile judicial, political, regulatory, or commercial pressure.
All features in this section operate as mandatory platform-level controls.
They cannot be bypassed by users, administrators, swarm leaders, or affiliates.
A. UPL SAFETY, RULE 11 DEFENSE & LEGAL AUTHORITY CONTROLS
361. Risk-Tiered Legal Output Gate (UPL-Safe Mode)
What it does
Automatically classifies every system output into escalating legal-risk tiers and enforces corresponding safeguards:
• Tier 0 — Legal Education & General Information
Constitutional literacy, procedural explanations, public-law summaries.
No attorney involvement required.
• Tier 1 — Self-Help & Public-Records Tools
FOIA requests, public-records letters, administrative inquiries.
Enhanced disclaimers + automated quality checks.
• Tier 2 — Court Filings & Legal Strategy
Pleadings, motions, habeas petitions, civil-rights complaints.
Mandatory human review (qualified reviewer or licensed attorney depending on jurisdiction).
• Tier 3 — High-Risk or Mass-Activation Actions
Swarm filings, sensitive targets, coordinated litigation.
Mandatory licensed-attorney sign-off + ethics review.
Why it matters
Creates a documented, affirmative defense against unauthorized-practice-of-law (UPL) allegations while preserving pro se access and scalability.
362. Jurisdiction-Specific UPL & Legal-Advice Rules Engine
What it does
Maintains a continuously updated, state-by-state rules engine governing:
• What constitutes “legal advice” vs. legal information
• Feature gating in restrictive jurisdictions
• Mandatory disclaimer language
• Attorney-involvement thresholds
Why it matters
Prevents a single hostile jurisdiction from being weaponized to justify nationwide injunctions or shutdowns.
363. Pre-Filing Merit & Rule 11 Safety Gate
What it does
Blocks frivolous or bad-faith filings before drafting occurs by requiring:
• Minimum viability score (facts, law, evidence)
• Automated Rule 11 risk analysis
• Mandatory human denial or approval for borderline cases
• Immutable logs of rejected filings
Why it matters
Demonstrates proactive prevention of vexatious litigation and defeats claims that the platform facilitates frivolous lawsuits.
364. Incentives, Solicitation & Champerty Compliance Engine
What it does
Continuously screens referral, profit-sharing, litigation-finance, and sweepstakes mechanisms to detect and prevent:
• Impermissible solicitation
• Fee-splitting with non-lawyers
• Champerty, maintenance, or barratry risks
• Securities-law or lottery-law violations
Automatically blocks or escalates flagged actions to ethics review.
Why it matters
Neutralizes RICO, extortion, and “organized harassment” narratives before they gain traction.
365. Privilege Mode (Attorney Engagement & Work-Product Segmentation)
What it does
Optional pathway that formally establishes attorney-client privilege by:
• Executing engagement letters and conflict checks
• Routing communications through licensed counsel
• Segregating privileged workspaces and data
• Generating privilege-log scaffolding
Why it matters
Prevents discovery-piercing attacks against platform logs, drafts, and internal communications when counsel is involved.
B. COURT, CLERK & PROSECUTOR CONFIDENCE SYSTEMS
366. Authorized Docket Retrieval & Court-Portal Connector Suite
What it does
Provides lawful, auditable access to court records via:
• User-authenticated PACER / CM-ECF pulls
• State-court portal connectors
• Public-record integrations where permitted
• Structured import with metadata
Why it matters
Improves verification accuracy, analytics reliability, and filing legitimacy while reducing clerical error.
367. Judicial Readability & Tone Optimization Engine
What it does
Analyzes court-facing filings for clarity, neutrality, tone, and structure, flagging:
• Emotional or advocacy-heavy language
• Redundancy or excess
• Known judicial irritation triggers
Suggests judge-preferred neutral variants.
Why it matters
Judicial resistance is often triggered by tone rather than law.
368. Court Clerk Acceptance & Rejection Predictor
What it does
Predicts clerk rejection risk based on jurisdiction-specific formatting, captions, signatures, and attachments; auto-corrects common errors.
Why it matters
Repeated clerk rejections create reputational harm before merits are ever reached.
369. Judicial Trust Appendix Generator (Defensive Use Only)
What it does
Generates a short, neutral appendix—used only when needed—summarizing:
• Human review layers
• UPL safeguards
• Merit screening protocols
Why it matters
Allows courts to verify safeguards without forcing explanations into every filing.
370. Prosecutor-Safe Evidence Normalization Layer
What it does
Converts citizen evidence into prosecutor-ready formats by:
• Stripping rhetoric
• Mapping evidence to statutory elements
• Producing neutral intake memos
Why it matters
Greatly increases likelihood of adoption by prosecutors, AGs, and inspectors general.
C. PUBLIC-FACING, MEDIA & MEMBER SAFETY CONTROLS
371. Agency Voluntary Compliance & Self-Correction Portal
What it does
Allows agencies to acknowledge filings and submit corrective actions short of litigation, with full audit trails.
Why it matters
Courts favor systems that encourage compliance before punishment.
372. Public Claims & Defamation-Risk Language Firewall
What it does
Enforces legally precise language on all public dashboards and media outputs (“filed,” “alleged,” “pending”), preventing assertions of guilt.
Why it matters
Neutralizes the majority of defamation risk.
373. Media Mischaracterization Detection & Response Engine
What it does
Detects inaccurate media narratives and generates calm, fact-checked correction packets.
Why it matters
Prevents reputational damage without escalation.
374. Radicalization, Fixation & Obsession Pattern Detector
What it does
Identifies unhealthy fixation or vendetta behavior by members and triggers cooling, review, or disengagement pathways.
Why it matters
Defeats claims that the platform radicalizes or mobilizes harassment.s
375. Member Ethical-Use Attestation & Re-Certification System
What it does
Requires periodic acknowledgment of ethical use, lawful intent, and anti-harassment standards.
Why it matters
Creates shared responsibility and reduces platform liability.
D. INSURANCE, FINANCE & CONTINUITY HARDENING
376. Insurability & Underwriting Readiness Score
What it does
Continuously scores platform risk posture against E&O and cyber-insurance expectations.
Why it matters
Insurers are silent gatekeepers to scale and partnerships.
377. Litigation Portfolio Concentration & Risk Aggregator
What it does
Detects correlated exposure across defendants, theories, and jurisdictions.
Why it matters
Prevents systemic risk and satisfies funder due-diligence.
378. De-Platforming & Infrastructure Resilience Layer
What it does
Ensures continuity via:
• Multi-cloud redundancy
• Payment-processor failover
• Rapid export and migration
• Jurisdictional mirroring
Why it matters
Prevents shutdown via hosting or payment chokepoints.
E. GOVERNMENT, AI & PLATFORM DEFENSE MECHANISMS
379. Pre-Written Platform Defense & Rapid-Response Pleadings
What it does
Maintains ready-to-file anti-injunction motions, declaratory relief actions, and emergency responses.
Why it matters
Speed determines institutional survival.
380. Government Inquiry & Subpoena Response Mode
What it does
Centralizes and standardizes responses to subpoenas, AG inquiries, and legislative requests with privilege protection.
Why it matters
Disorganization is often mistaken for wrongdoing.
381. Regulated Data Pipeline (HIPAA & Sensitive Data Partitioning)
What it does
Provides encrypted, access-segmented workflows for medical and regulated data with full audit logs.
Why it matters
Prevents catastrophic regulatory exposure.
382. Outcome-Informed Evaluation & Safe Improvement Loop
What it does
Uses anonymized outcomes to improve evaluation benchmarks and detect drift—without uncontrolled retraining.
Why it matters
Maintains accuracy without legal or ethical risk.
383. Court-Facing AI Explainability Export
What it does
Generates plain-English explanations of AI behavior, data categories, and human review points.
Why it matters
AI opacity is increasingly unacceptable in courts.
384. Jurisdiction-Appropriate AI Use Disclosure Generator
What it does
Produces compliant, minimal AI disclosures tailored to local court rules and judicial preferences.
Why it matters
Future-proofs the platform against evolving AI mandates.
385. Independent Annual Compliance & Ethics Audit
What it does
Requires annual third-party audits covering:
• UPL compliance
• Rule 11 safeguards
• Incentive legality
• Data governance
Produces court-defensible audit reports.
Why it matters
Provides proactive proof of good-faith compliance to courts, regulators, insurers, and partners.
Master Section Effect
Together, these features transform Mega Lawfare Legal AI Bot into a legitimate, sanction-resistant, institution-grade legal platform capable of sustained operation under intense adversarial scrutiny—without sacrificing citizen empowerment or constitutional alignment.

DECISION-INTELLIGENCE INDICATORS, RISK SIGNALING & ESCALATION GOVERNANCE
(Features 385–409)
This section introduces Mega Lawfare’s Decision-Intelligence Indicator System—a platform-wide layer designed to signal when restraint, escalation, consolidation, professional representation, or public disclosure may be appropriate.
These indicators do not compel action, block filings, or override member autonomy.
They exist to promote judicial economy, ethical proportionality, and institutional trust, and to demonstrate good-faith self-regulation to courts, prosecutors, regulators, insurers, and hosting partners.
All indicators are advisory only, logged, auditable, and bias-weighted toward restraint.
A. CORE INDICATOR GOVERNANCE & SAFETY PRINCIPLES
385. Non-Coercive Advisory Indicator Architecture
All indicators function as decision-support signals only. No indicator mandates outcomes, disables rights, or substitutes for human judgment.
386. Indicator Logging, Acknowledgment & Audit Trail
Indicator states (green/yellow/red), user acknowledgments, and overrides are logged in immutable records for court, ethics, or insurance review.
387. Bias-Toward-Restraint Enforcement Rule
Where ambiguity exists, indicators default to caution, delay, or review rather than escalation or volume.
B. UNIFIED TRAFFIC-LIGHT RISK SIGNALING SYSTEM
388. Platform-Wide Traffic-Light Indicator Schema
All indicators operate under a standardized three-state schema:
🟢 GREEN — Proceed (Low Risk)
No elevated legal, procedural, or ethical risk detected.
🟡 YELLOW — Caution / Review Recommended
Lawful to proceed, but increased risk or complexity warrants restraint, review, or sequencing.
🔴 RED — Escalation Risk / Professional Review Strongly Advised
High likelihood of irreversible harm, sanctions, dismissal, retaliation, or adverse optics if proceeding unmodified.
Indicators never block action; red signals require acknowledgment before proceeding.
C. LEGAL & PROCEDURAL READINESS INDICATORS
389. Attorney Escalation & Professional Representation Indicator
Signals when pro se capacity is likely exceeded due to complexity, sanctions exposure, liberty risk, or institutional opponent asymmetry.
390. Rule 11 & Sanctions Exposure Indicator
Warns of elevated frivolousness, improper purpose, pleading defects, or duplicative-filing risk before drafting or filing.
391. Appeal Preservation & Record Integrity Indicator
Signals when objections, issue framing, or evidentiary development are insufficient to preserve appellate rights.
392. Venue Transfer, Abstention & Jurisdictional Risk Indicator
Warns of heightened likelihood of §1404 transfer, abstention doctrines, or jurisdictional dismissal.
D. COLLECTIVE ACTION & CASE-STRUCTURE INDICATORS
393. Consolidation, Joinder & Collective Action Suitability Indicator
Advises when individual member actions should remain separate, be coordinated, or be consolidated under Rule 20, Rule 23, Rule 42, or MDL principles.
394. Bellwether / Test-Case Sequencing Indicator
Signals when a small number of representative cases should proceed first to reduce risk and shape precedent.
395. Over-Filing & Judicial Irritation Risk Indicator
Warns when filing volume or duplication risks undermining judicial goodwill or triggering docket management sanctions.
E. EVIDENCE & FACTUAL READINESS INDICATORS
396. Evidence Sufficiency & Element Coverage Indicator
Signals whether factual proof adequately supports each required legal element.
397. Admissibility, Authentication & Daubert Risk Indicator
Warns of hearsay, foundation, chain-of-custody, or expert-qualification vulnerabilities.
398. Spoliation & Preservation Urgency Indicator
Triggers when evidence destruction risk requires immediate preservation action.
F. MEMBER SAFETY, ETHICS & CAPACITY INDICATORS
399. Competency Drift & Capacity-Mismatch Indicator
Detects when matter complexity is increasing faster than member demonstrated proficiency.
400. Fixation / Vendetta Risk Indicator
Identifies emotional escalation or obsessive targeting patterns and recommends cooling or review.
401. Ethical Boundary Proximity Indicator
Warns when conduct approaches harassment optics, improper purpose narratives, or abuse-of-process risk.
G. PUBLIC COMMUNICATIONS & MEDIA ESCALATION INDICATORS
402. Public Accountability & Communications Escalation Indicator
Signals when verified evidence, public interest, and procedural posture support transparency or press engagement—and when silence is strategically superior.
403. Defamation & Retaliation Exposure Indicator
Warns of elevated reputational, employment, custodial, or enforcement retaliation risk from public escalation.
H. INSTITUTIONAL & PLATFORM-LEVEL INDICATORS (Restricted Visibility)
404. Judicial Trust Load Indicator
Signals when courts exhibit heightened scrutiny and additional legitimacy safeguards should be activated.
405. Regulatory & Bar Attention Indicator
Warns of increased risk of AG, bar, or legislative inquiry requiring internal discipline and restraint.
406. Platform Risk Concentration Indicator
Detects correlated exposure across jurisdictions, defendants, or legal theories.
407. De-Platforming & Infrastructure Pressure Indicator
Signals rising risk from hosting providers, payment processors, or vendors.
I. STRATEGIC RESOLUTION & EXIT INDICATORS
408. Settlement Readiness & Leverage Peak Indicator
Signals when negotiated resolution may outperform continued litigation.
409. Precedent Formation & Appellate Gravity Indicator
Warns when a case is likely to shape precedent, attract appellate attention, or require heightened care.
Why This Section Matters
With this section, Mega Lawfare:
• Demonstrates self-restraint rather than automation
• Anticipates and mitigates Rule 11, UPL, RICO, and harassment narratives
• Aligns platform behavior with how real litigation teams think
• Signals maturity to judges, prosecutors, insurers, and funders
• Preserves pro se rights while encouraging responsibility

MOBILE COMMAND, WEARABLE & REAL-WORLD INTERVENTION SYSTEMS
(Smartphone & Wearable Device Layer)
Features 410–439
410. Mobile Command & Wearable Legal Sentinel Framework
Transforms smartphones and connected wearables into real-time legal sentinels capable of recording, analyzing, preserving, and responding to legal risk events during real-world interactions, extending Mega Lawfare’s intelligence layer beyond desktop environments.
411. Authority Encounter Detection & Rights-Exercise Mode
Automatically detects and adapts to interactions with law enforcement, regulators, inspectors, or government officials, activating context-aware alerts for unlawful orders, coercive tactics, procedural violations, and recommended rights-clarification moments.
412. Jurisdiction-Aware Recording & Consent Enforcement Engine
Implements automatic state-by-state recording law compliance, geo-fencing, consent prompts, and audit logs to prevent unlawful recording exposure while preserving lawful evidence capture.
413. Silent Sentinel Recording Mode
Enables discreet, passive recording and analysis with on-device processing, minimal UI visibility, and stealth operation during sensitive or high-risk encounters.
414. Real-Time Pressure, Coercion & Manipulation Signal Detection
Identifies interrogation pressure patterns, rapid-fire questioning, assumption-based prompts, urgency tactics, and conversational manipulation in live interactions.
415. Context-Adaptive Conversation Modes
Dynamically adjusts sensitivity thresholds, alerts, and prompts based on selected environments, including police encounters, legal consultations, interviews, negotiations, depositions, hiring discussions, and personal interactions.
416. Courtroom, Hearing & Deposition Companion Mode
Provides voice-activated recording, transcription, timestamped bookmarking, and post-event debrief assistance during court proceedings, hearings, and depositions.
417. Missed Objection & Procedural Irregularity Detection
Flags potential missed objections, procedural violations, bias indicators, or appeal-preservation issues during or immediately after proceedings.
418. Appeal Clock & Deadline Tracking Alerts
Automatically tracks appeal deadlines, preservation windows, and post-hearing filing timelines with proactive push notifications.
419. Post-Conversation & Post-Event Insight Summaries
Generates optional annotated transcripts, stress-signal timelines, inconsistency markers, and clarification recommendations for user review and learning.
420. Mobile Evidence Capture & Integrity Pipeline
Creates tamper-evident audio, video, and document records using hash-chained capture, automated timestamps, and integrity verification.
421. Evidence Survivability & Anti-Seizure Safeguards
Protects captured evidence against loss, deletion, or device seizure through encrypted storage, distributed backups, and survivability controls.
422. Body-Cam, Dash-Cam & External Sensor Synchronization
Synchronizes user-captured evidence with body-cam, dash-cam, or third-party sensor footage to build unified, discrepancy-flagged timelines.
423. Real-Time Risk Alerts & Predictive Encounter Briefings
Delivers location-aware alerts tied to courts, officers, agencies, or officials, including escalation risk indicators and contextual intelligence summaries.
424. Pre-Encounter Mission & Rights Checklist Generator
Provides pre-event preparation checklists tailored to jurisdiction, venue, and encounter type.
425. Wearable Device Activation & Panic Interface
Enables one-gesture or silent activation of recording, alerts, and emergency escalation via smartwatches, panic buttons, or other wearable inputs.
426. Hands-Free Audio, Haptic & Visual Alert System
Delivers discreet feedback through earbuds, bone-conduction devices, haptics, or future AR displays during live encounters.
427. Emergency Swarm Beacon & GPS Alerting
Allows instant notification of verified members, designated contacts, or response networks with encrypted location and context packets.
428. Standing-Verified Swarm Packet Distribution
Automatically prepares and routes jurisdiction-specific swarm packets to members with verified legal standing.
429. Retaliation Shield & Counter-Action Triggering
Activates counter-filing workflows—including preservation notices, complaints, and oversight actions—when retaliation or harassment is detected.
430. Predictive Escalation & Outcome Simulation
Models potential outcomes, escalation paths, and risk tradeoffs during active encounters to support informed user decisions.
431. Offline-First Mobile Legal Intelligence Cache
Maintains cached law, templates, rights summaries, and jurisdictional data for operation in disconnected or hostile environments.
432. Accessibility & Stress-Adaptive Interface Modes
Includes senior, low-vision, cognitive-load-reduction, and high-stress UI modes with simplified prompts and enhanced feedback.
433. User-Controlled Privacy & Exposure Tiers
Allows users to designate evidence as private, anonymized for pattern detection, or swarm-ready, with granular control at every stage.
434. Preventive Lawfare Decision-Support Layer
Shifts Mega Lawfare from reactive enforcement to proactive harm prevention by enabling early detection of risk, manipulation, and procedural traps.
435. Mobile-to-Core AI Synchronization Layer
Seamlessly syncs Mobile Command data with the core Mega Lawfare Legal AI Bot, Decision-Intelligence Indicators, and Legal Earth systems.
436. Wearable & AR-Ready Expansion Framework
Provides a future-proof integration layer for smart glasses, rings, and augmented-reality legal overlays.
437. Mobile Command Governance & Audit Controls
Implements full auditability, user authorization gating, and governance logs to preserve court credibility and platform survivability.
438. Non-Forensic, Non-Accusatory Output Safeguards
Hard-coded constraints preventing truth claims, medical diagnosis, or automated accusations, ensuring ethical and legal compliance.
439. Real-World Intervention Feedback Loop
Feeds anonymized, opt-in encounter signals back into Mega Lawfare’s pattern detection and predictive deterrence systems.

440. Real-Time Conversational Intelligence, Credibility & Self-Protection Module
Provides real-time situational awareness during live conversations by analyzing speech patterns, linguistic cues, and interaction dynamics to surface indicators of stress, evasiveness, manipulation, coercive questioning, and rights-waiver risk. Outputs are strictly non-directive indicators—not truth determinations—governed by consent, privacy, and human-in-the-loop safeguards to empower informed decision-making before harm occurs.
The Mega Lawfare Legal AI Bot includes an optional Real-Time Conversational Intelligence & Credibility Awareness Module, designed to assist users during live conversations by providing situational awareness, self-protection cues, and decision-support signals—not truth determinations or accusations.
This module operates as a personal conversational safety and rights-exercise assistant, delivering real-time indicators that help users recognize pressure, manipulation, inconsistency, evasiveness, or elevated cognitive stress in conversational partners across a wide range of everyday and high-stakes interactions.
Core Capabilities
1. Real-Time Speech & Behavioral Signal Analysis
The system analyzes live audio streams (subject to consent and applicable recording laws) for:
• Speech stress indicators (pitch variance, tremor, speech rate anomalies)
• Hesitation clusters, filler escalation, and response latency
• Linguistic deflection, non-answers, and over-qualification
• Narrative fragmentation and internal inconsistency
• Sudden tone or cadence shifts during sensitive questioning
All outputs are presented as indicators, never conclusions.
2. Conversational Risk & Pressure Detection
The AI identifies patterns commonly associated with:
• Interrogation pressure
• Coercive or leading questioning
• Manipulative framing
• Authority-based intimidation
• Urgency or artificial deadline tactics
• Rights-waiver language disguised as casual conversation
When detected, the system provides non-directive alerts such as:
• “Pressure escalation detected”
• “Question may assume unestablished facts”
• “Response may waive rights—pause recommended”
• “Clarification request advised”
3. Mode-Based Context Awareness
Users can activate specialized modes that adjust sensitivity, prompts, and alerts based on context, including:
• Authority Encounter Mode (police, regulators, inspectors)
• Legal Consultation Mode (attorney or legal staff discussions)
• Interview & Deposition Mode
• Hiring & Employment Mode
• Business Negotiation Mode
• Personal Conversation Mode
Each mode is optimized for the conversational norms, risks, and power dynamics of that environment.
4. Rights-Exercise & Self-Advocacy Assistance
The module integrates constitutional and procedural awareness to help users:
• Recognize when silence or clarification may be appropriate
• Detect compound or misleading questions
• Identify when a question embeds assumptions
• Slow conversations during high-pressure moments
• Ask precise follow-up questions without escalation
The system never instructs the user, but provides awareness cues that empower informed decision-making.
5. Post-Conversation Insight & Review
After a conversation, users may receive:
• Annotated transcripts (if recording is enabled)
• Time-stamped stress and inconsistency markers
• Summary of pressure or manipulation indicators
• Suggested clarification topics for future interactions
• Optional personal learning feedback to improve future conversations
These summaries are designed for personal understanding, not evidentiary use.
6. Privacy, Consent & Governance Safeguards
To ensure legality, ethics, and platform survivability:
• The system does not determine truth or deception
• No accusations, labels, or definitive judgments are produced
• Recording functionality is gated by jurisdictional consent laws
• All indicators require human interpretation
• Data retention and sharing are user-controlled
• No automated actions or filings are triggered by this module
Intended Use Scope
This feature is explicitly designed for:
• Personal situational awareness
• Rights-exercise support
• Interview and negotiation preparedness
• Self-protection during authority interactions
• Improved decision-making in high-pressure conversations
It is not intended as forensic evidence, medical diagnosis, or truth verification, and is presented as an assistive intelligence layer only.
Strategic Value
This module extends Mega Lawfare’s mission upstream—before legal harm occurs—by helping users:
• Avoid self-incrimination
• Detect manipulation early
• Maintain composure under pressure
• Ask better questions
• Exit risky conversations safely
It represents a preventive lawfare capability, strengthening citizen autonomy, awareness, and confidence in real-world interactions.

Referral Affiliate Viral Marketing Mobile Command Features
Features 441–465
441. Mobile Referral Command Center (In-App Affiliate Dashboard)
A mobile-first dashboard that shows referrals, clicks/scans, conversions, pending approvals, commission status, and payout readiness in real time—optimized for quick “field recruiting.”
442. Unique Referral ID + Smart Link Generator
Generates a unique member referral identifier and smart links that work across web, mobile, and app install flows (deep-link capable), ensuring attribution survives device switches and channel changes.
443. One-Tap Personal QR Code (Join + Affiliate Enrollment)
Creates a scannable QR code tied to the member’s referral ID for instant enrollment at events, meetings, door-to-door, or on-screen sharing. (Include “logo QR” option for branding.)
444. Offline QR Attribution + Scan Analytics
Tracks offline-to-online conversions driven by QR scans (time, geo, source context), and links them to the referring member for credit.
445. Coupon / Code-Based Referral Tracking (Offline + Influencer Ready)
Issues referral codes (and optional printable barcode versions) so members can recruit via spoken codes, flyers, business cards, podcasts, and influencers—fully attributable when redeemed.
446. Multi-Method Attribution Engine (Cookie, Coupon, IP, Postback, Cookieless)
Uses multiple attribution methods (cookies, codes, IP-based last-click recovery, and server-side/postback-style methods where available) to reduce “lost referral credit” and improve integrity.
447. Sub-Affiliate / Downline Enrollment Links
Allows affiliates to recruit other affiliates (sub-affiliates) with unique enrollment links (and QR codes) while preserving attribution trees for rewards or tiered recognition.
448. Mobile “Prospect Capture” (Name + Email + Optional Phone) with Referral Binding
A mobile form that lets a member enter a prospect’s name + email (optionally phone) and automatically binds that prospect to the referring member in the CRM/referral system from the first touch.
449. Auto-Drip Outreach Sequences (Email/SMS/DM) Until Join or Opt-Out
Automatically sends scheduled marketing messages—welcome story, credibility proof, benefits, FAQs, pricing, and “join now” prompts—until the prospect joins as a member or affiliate, opts out, or converts. The conversion is automatically credited to the referring member.
450. Drip Personalization + Segmentation (Interest Tags + Local Chapter)
Adds tags (e.g., “Pro Se,” “FOIA,” “Civil Rights,” “Whistleblower,” “Legal Education”) and routes prospects into tailored drip tracks, local chapter sequences, and language preferences.
451. Replicated Mobile Landing Pages (Affiliate-Branded Microsites)
Instant “replicated site” pages that personalize the join flow with the referring member’s name, QR/link, story, and contact—common in direct-sales/MLM systems for conversion lift.
452. Share Kit Generator (One-Tap Social, SMS, Email, Flyer Assets)
Auto-generates share-ready copy, images, and short links for common channels (text, email, social DMs) with built-in tracking.
453. A/B Testing & Campaign Experiments (Mobile-Safe)
Runs controlled experiments on referral pages, drip sequences, and messaging to optimize conversion—mirroring enterprise referral tooling.
454. Fraud / Abuse Prevention for Referrals
Detects suspicious patterns (self-referrals, duplicate accounts, bot clicks, abnormal conversion velocity) and flags for review—standard in mature referral platforms.
455. Rewards & Commission Rules Engine (Flexible Incentives)
Supports flexible reward logic (one-time, recurring, tiered, milestone-based) for referral affiliates, with rule transparency and audit trails.
456. Payout Readiness + One-Invoice Partner Payout Workflow
Aggregates partner earnings, provides review/approval controls, and supports streamlined payouts—reducing errors and increasing affiliate trust.
457. Referral Source & Channel Insights (What’s Actually Working)
Shows where links/QRs are being shared (SMS, WhatsApp/DM, email, etc.) and which channels drive the most signups—so members focus on the highest ROI tactics.
458. Event Mode: Rapid Enrollment Scanner
A fast “booth mode” that scans multiple prospects’ QR join confirmations, captures leads offline if needed, and syncs when online—ideal for meetings, rallies, fairs, and courthouse outreach.
459. Wearable “Recruit Ping” + Haptic Prompts
Optional wearable prompts for events: haptic reminders to ask for the referral scan, quick-access QR display, and “lead captured” confirmations.
460. Referral Compliance & Consent Logging
Built-in consent logs for outreach (email/SMS), opt-out enforcement, and disclosure templates to keep affiliate marketing compliant and reputationally safe.
461. Auto-Upgrade Path: Prospect → Member → Referral Affiliate
When a prospect joins as a member, the app automatically offers a one-tap upgrade to referral affiliate (if eligible) with prefilled details and immediate dashboard access.
462. “Warm Intro” Request Button (Ask for a 2nd-Degree Referral)
Allows the referrer to request introductions from the prospect’s network with a compliant, low-pressure script + tracked links.
463. “Field Testimonial Capture” (30-Second Proof Builder)
Lets members record short testimonials (with release/consent flow), then auto-formats them into share assets with the member’s QR/link embedded.
464. Local Chapter Routing + Geo-Based Assignment (Optional)
Routes new signups to the nearest chapter or organizing cell while still crediting the originating referrer.
465. Referral Ledger + Audit Trail
Immutable referral event log (invite → click/scan → lead capture → drip touchpoints → conversion → payout) for dispute resolution and trust.

CONFUSION, COMPLIANCE & COERCION DETECTION ENGINES
(Features 465 – 478)
Overview: This feature group equips the Mega Lawfare Legal AI with advanced cognitive and behavioral analysis tools to detect, quantify, and interpret patterns of induced confusion, emotional fractionation, and authority-bound compliance in textual, audio, and video evidence. These tools support forensic analysis in civil-rights litigation, interrogation review, media influence assessment, and coercive persuasion claims while preserving evidentiary standards and due-process safeguards.
465. Confusion Pattern Signal Extractor
An AI engine that analyzes language, narrative structure, and multimodal content to detect cognitive overload and ambiguity markers associated with confusion-based persuasion and control tactics.
466. Fractionation Emotion Cycle Analyzer
A real-time and post-hoc model that identifies sequences of emotional swings (e.g., reassurance → uncertainty → dependency cues) within transcripts or media, tagging potential manipulation vectors.
467. Authority Cue Identifier
Detects and classifies authority signals—titles, institutional markers, normative framing, and prescriptive language—that increase compliance or override critical analysis, with jurisdictional tagging for context.
468. Cognitive Load Scoring & Index
Produces a numeric index of cognitive load based on linguistic complexity, contradictory signal density, and rapid topic shifts that correlate with cognitive disruption techniques.
469. Suggestibility Risk Evaluator
Assesses the probability that an individual or audience segment was rendered more suggestible due to confusion and authority cues, producing case-usable reports with confidence bands.
470. Coercive Compliance Cartography
Generates visual timelines and narrative maps showing interaction flows, emotional swings, and authority impacts—optimized for court exhibits, expert reports, and motions.
471. Interrogation & Interview Compliance Analyzer
A specialized module for recorded interrogations, interviews, and custodial encounters that flags coercive patterns, undue influence markers, and possible due-process breaches.
472. Media Influence Manipulation Detector
Applies the confusion and fractionation models to social media streams, news segments, and algorithmic feeds to identify engineered cognitive overload, tribal trigger signals, and identity erosion patterns.
473. Cultic Coercion & Indoctrination Pattern Library
A curated reference library of documented coercion sequences across organizational, religious, and institutional environments, used as a comparative baseline for AI analysis.
474. Behavioral Influence Ontology & Tagging System
An expanded taxonomy of cognitive influence mechanisms—confusion, fractionation, compliance, authority, identity destabilization—integrated into the legal AI’s semantic knowledge graph for precise RAG indexing.
475. Coercion Evidence Packet Builder
Assembles structured, admissible evidence summaries linking confusion/fractionation metrics to specific legal elements (e.g., voluntariness, undue influence, coercion), with citation-verified source linkage.
476. Expert Witness Synthesis Generator
Produces expert-ready summaries, narrative outlines, and declarative exhibits for psychologists, interrogation specialists, and behavioral scientists, tied to case facts and AI findings.
477. Compliance Risk Flagging Across Cases
Integrates across user caseloads to surface systemic influence risks (e.g., agency patterns, repeated coercion cues) and generates escalation prompts with jurisdictional alerts.
478. Cognitive Integrity & Consent Safeguard Monitor
A proactive compliance module that evaluates user-provided content for signs of undue influence or compromised decision-making before automated filings, providing protective recommendations.

Section Y
Enterprise Productivity & Expert-System Completeness Layer
(Features 479-522)
Microsoft & Professional Workspace Integration
479. Native Microsoft Word Legal Copilot
Embedded Mega-Bot assistant inside Microsoft Word enabling drafting, redlining, clause analysis, citation insertion, motion generation, and pleading assembly without leaving the document editor.
480. Native Microsoft Outlook Legal Assistant
Integrated email drafting, intake processing, client correspondence generation, evidence extraction from email threads, and automated follow-up workflows directly within Outlook.
481. Microsoft SharePoint Legal Repository Integration
Direct connection to SharePoint document libraries for discovery ingestion, evidence storage, case files, collaborative editing, and Mega-Bot analysis.
482. OneDrive Evidence + Draft Synchronization
Automatic synchronization of drafts, exhibits, pleadings, and evidence folders with OneDrive.
Secure Case Vault & Collaborative Legal Workspace
483. Mega-Vault Secure Document Workspace
Dedicated encrypted multi-case repository supporting millions of documents per organization with structured indexing.
484. Bulk Evidence Review Tables
Spreadsheet-style mass document analysis with sortable columns for relevance, privilege, jurisdiction, claim mapping, entity extraction, and timeline placement.
485. Assistant-to-Vault Direct Querying
Mega-Bot may be queried directly against Vault contents (“Ask Mega-Bot about these 14,000 PDFs”).
486. Shareable Vaults with Permission Layers
Role-based access for attorneys, paralegals, investigators, members, auditors, and reviewers.
487. Collaborative Threading & Version History
Shared Mega-Bot conversations tied to Vault assets with immutable versioning and audit logs.
Visual Workflow Builder & Agent Orchestration
488. No-Code / Low-Code Workflow Builder Interface
Drag-and-drop builder allowing users to visually construct pipelines combining intake, analysis, drafting, filing, escalation, and enforcement.
489. Modular Workflow Blocks
Input → AI Analysis → Legal Logic → Human Review → Output → Filing → Notification blocks.
490. Conditional Logic Nodes
“If/then” branching for jurisdiction, claim viability, standing thresholds, and procedural rules.
491. Model Selection Per Workflow Stage
Ability to choose specialized models per task (research vs drafting vs evidence vs reasoning).
492. Workflow Templates Marketplace
Pre-built Mega Lawfare workflows for FOIA, §1983, criminal complaints, Sunshine Law, Qui Tam, consumer actions, etc.
Knowledge Module + Source Control
493. Dedicated Knowledge Surface
Central interface for statutes, cases, regulations, treatises, Mega Lawfare precedents, and member-generated materials.
494. Source Mentioning (“@Sources”)
Explicit attachment of specific documents, statutes, cases, or Vault folders to Mega-Bot queries.
495. Jurisdiction & Language Output Controls
Explicit per-response jurisdiction targeting and language localization.
Enterprise Privacy, Security & Governance Guarantees
496. Retention Policy Controls
Organization-defined data retention timelines.
497. Immediate Delete & Right-to-Erasure Controls
498. Regional Processing Selection (US/EU/etc.)
499. Zero Training on Customer Data Guarantee
500. Eyes-Off Processing (No Human Review of Private Data)
501. Ephemeral AI Processing Mode
502. Cryptographic Audit Trails for All Actions
Expert-System Questionnaire Engine (Electronic Lawyer Expansion)
503. Expert Knowledge Extraction Framework
Tools for encoding subject-matter experts into structured legal logic trees.
504. Mega Questionnaire Engine
Massive branching question system acting as canonical legal issue maps.
505. Completeness Assurance Mode
Systematically ensures no material legal issue is missed.
506. Domain-Specific Question Banks
Separate trees for criminal, civil rights, administrative, consumer, property, family, regulatory, and constitutional law.
Automated Issue Spotting → Motion/Pleading Generation
507. Dynamic Legal Issue Checklist Generator
508. Rule-Triggered Drafting Engine
When answers implicate a motion, pleading, or filing requirement, Mega-Bot auto-generates it.
509. Procedural Dependency Graphs
Tracks prerequisite filings and deadlines.
510. Hyperlinked Pleadings & Motions
All generated documents include embedded citations and authority links.
Research by Legal Logic (Not Keywords)
511. Questionnaire-Driven Research Navigation
Research organized by legal issue trees instead of keyword search.
512. Path-Based Case Law Retrieval
513. Authority Consistency Engine
Ensures uniform legal application across filings.
Sharing, Versioning, and Professional Collaboration
514. Shareable Case Threads
515. Shareable Vaults
516. Shareable Workflows
517. Immutable Version Control
518. Redline Comparisons Between Draft Iterations
Enterprise Deployment Capabilities
519. Organization-Wide Policy Enforcement
520. Department-Level Configuration Profiles
521. Practice-Area Specific Mega-Bot Personalities
522. Multi-Tenant Architecture
Strategic Result
This layer ensures Mega-Bot operates simultaneously as:
-
Citizen enforcement platform
-
Professional legal workstation
-
Expert system
-
Enterprise workflow engine
-
Evidence command center
forming the world’s first full-spectrum legal operating system.

Mega Lawfare Legal AI Authoritative Training Corpus & Decision-Intelligence Architecture
Foundational Philosophical and Historical Sources
These sources provide the intellectual and historical underpinnings of American jurisprudence, including natural rights theory, social contract principles, and common-law roots. They support original-meaning arguments, equity framing, and philosophical critiques of institutional power.
1. Magna Carta (1215 & 1297) — foundational due process and liberty principles cited historically
2. Declaration of Independence — philosophical grounding for rights and legitimacy narratives
3. Thomas Paine — founding-era persuasion frameworks and civic accountability logic
4. Common Sense — rights-based argumentation and institutional critique templates
5. Rights of Man — liberty theory and government limits
6. The American Crisis — rhetorical and moral framing for civic duty and resistance to tyranny
7. The Age of Reason — epistemic discipline and argument structure
8. Mayflower Compact — early governance compact model for voluntary association framing
9. John Locke — Two Treatises of Government — consent theory and limits on state power
10. Rousseau — The Social Contract — sovereignty framing and legitimacy theory
11. Plato — The Republic — institutional power analysis and justice philosophy
12. Aristotle — Ethics & Rhetoric — persuasion mechanics; virtue/intent frameworks
13. Code of Hammurabi — early legal codification archetypes (comparative framing only)
14. Adam Smith — Wealth of Nations (Book V) — public finance, governance, and institutional incentives
15. King James Bible
16. Blackstone’s Commentaries — common-law foundations used in U.S. doctrine
17. Federalist Papers (Nos. 10, 51, et al.) — founding-era interpretive context for constitutional design
Constitutional Authorities
Core organic law defining rights, powers, and structural constraints at federal and state levels.
18. U.S. Constitution & Amendments — supreme federal authority; structural rights, limits, and powers
19. All 50 State Constitutions — state-level rights, separation of powers, and procedural guarantees
Statutory and Regulatory Frameworks
Codified substantive law and implementing regulations establishing causes of action and agency authority.
20. United States Code (Titles 1–54) — codified federal statutory law across all subject areas
21. Code of Federal Regulations (all 50 titles) — binding federal administrative regulations
22. All 50 State Statutes & Court Rules — state-level substantive and procedural law
Procedural Rules and Court Operations
Mechanisms governing filing, service, jurisdiction, and courtroom practice across federal and state systems.
23. Federal Rules (FRCP, FRCrP, FRE, FRAP) — core federal procedure, evidence, and appellate rules
24. Local district court rules (94 federal districts) — venue-specific filing and practice requirements
25. Supreme Court Rules — cert-stage requirements, merits briefing, and emergency applications
26. U.S. Courts CM/ECF user manuals — e-filing mechanics, event codes, and compliance traps
27. Federal Judicial Center (FJC) manuals & primers — authoritative procedure/evidence guidance used by judges
28. Federal court clerk office procedural guides — filing acceptance rules and common rejection reasons
29. State e-filing system manuals (all states) — state-specific e-filing traps and formatting rules
30. Bluebook + state citation manuals — citation compliance and credibility signaling
31. Judicial opinions style guides (per-court) — persuasion alignment and readability by court norms
32. Form complaint libraries (federal + state) — baseline pleading structures and required fields
33. AO (Administrative Office) federal forms — standardized federal civil/criminal forms and instructions
34. State court standardized forms — pro se compliance acceleration and rejection avoidance
35. Local pro se handbooks (district-by-district) — court-specific expectations and pitfalls
36. Court fee schedules + IFP standards — access planning, fee waivers, and cost forecasting
37. Service of process rules + best-practice guides — proper service execution and proof templates
38. Hague Service Convention materials — international service requirements and timelines
39. PACER/RECAP metadata and docket datasets — docket intelligence, judge patterns, and motion timing
40. Bench books (state/federal where public) — judge-facing procedures and decision heuristics
41. Court staff attorney and clerkship training materials (publicly available) — hidden gatekeeping patterns
42. E-filing rejection reason datasets — formatting and procedural defect prevention
43. Case timelines and calendaring rule compendium — deadline automation and compliance gates
44. Pro hac vice and attorney admission rules (for counsel handoff) — escalation path planning
45. Court decorum and courtroom conduct guides — pro se credibility and avoidable sanctions prevention
Precedent and Doctrinal Sources
Judicial decisions, amicus materials, and interpretive aids establishing binding and persuasive authority.
46. Federal case law (1754–present) — controlling and persuasive precedent across federal courts
47. State appellate and supreme court decisions — controlling state precedent and interpretive doctrine
48. Supreme Court dissents, concurrences, and footnotes — doctrinal signals, tests, and future-law forecasting
49. Amicus brief databases — policy and technical arguments shaping appellate outcomes
50. Citation graph databases (court-to-court influence networks) — persuasive authority ranking and selection
51. Judge-written articles and speeches (where public) — persuasion alignment and issue framing cues
Specialized Legal Domains
Military Justice
52. Uniform Code of Military Justice (10 U.S.C. §§ 801–946a) — foundational statutory authority governing military criminal law, jurisdiction, and offenses
53. Manual for Courts-Martial (MCM), United States — authoritative implementation of the UCMJ, including Rules for Courts-Martial, Military Rules of Evidence, and punitive articles explanations
54. Rules for Courts-Martial (RCM) — procedural framework for courts-martial, pretrial, trial, and post-trial processes
55. Military Rules of Evidence (Mil. R. Evid.) — evidentiary standards distinct from FRE, including command-specific exceptions
56. Punitive Articles Analysis (MCM Part IV) — element-by-element breakdown of UCMJ offenses and defenses
57. Military Appellate Case Law (CAAF, CCA opinions) — binding and persuasive precedent interpreting UCMJ provisions
58. Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces (CAAF) decisions — highest military appellate authority guidance
59. Service Courts of Criminal Appeals (Army, Navy-Marine Corps, Air Force, Coast Guard) — service-specific appellate doctrine and trends
60. Supreme Court cases reviewing courts-martial — civilian oversight boundaries and constitutional integration
61. Judge Advocate General (JAG) Corps practice manuals — prosecution, defense, and advisory practice standards
62. Service-specific JAG handbooks (Army, Navy, Air Force, Marines, Coast Guard) — procedural nuances by branch
63. Military Justice Deskbooks — practitioner-focused explanations of substantive and procedural military law
64. Article 32 preliminary hearing guides — probable cause standards and pre-referral defense opportunities
65. Convening authority powers and limitations sources — command influence boundaries and post-trial actions
66. Unlawful Command Influence (UCI) case law corpora — detection, proof, and remedy frameworks
67. Non-Judicial Punishment (Article 15) manuals — administrative discipline processes and appeal rights
68. Summary, Special, and General Court-Martial distinctions — forum selection and exposure analysis
69. Military sentencing rules and guidelines — punishment ranges, aggravation, and mitigation standards
70. Clemency and parole rules (military corrections) — post-conviction relief pathways
71. Military confinement and corrections regulations — custody standards and rights protections
72. Military appellate procedure rules — timelines, preservation, and briefing standards
73. Military discovery rules and Brady-equivalent doctrine — disclosure obligations unique to courts-martial
74. Search, seizure, and inspection authority in military contexts — Fourth Amendment adaptations
75. Command-directed investigation regulations (e.g., AR 15-6) — evidentiary limits and suppression issues
76. Inspector General investigations (DoD IG) — oversight findings and referral pathways
77. Military whistleblower protection statutes (10 U.S.C. § 1034) — retaliation protection and complaint processes
78. Boards for Correction of Military/Naval Records (BCMR/BCNR) — administrative remedies and record correction
79. Discharge review boards standards and case corpora — character of service upgrades and relief criteria
80. Line-of-Duty (LOD) investigation manuals — causation and benefits implications
81. Military sexual assault response and prosecution materials — specialized procedures and victim rights
82. Military equal opportunity and discrimination regulations — civil rights enforcement within the armed forces
83. Law of Armed Conflict (LOAC) and Rules of Engagement (ROE) manuals — criminal exposure boundaries in operations
84. Military ethics regulations (DoD Standards of Conduct) — conflicts of interest and misconduct triggers
85. National Guard UCMJ applicability and state-federal overlap sources — jurisdiction and authority conflicts
86. Reserve component military justice sources — activation status and jurisdiction rules
87. Military-civilian jurisdiction overlap case law — forum selection and double-jeopardy analysis
88. Court-martial transcript and audio archives — behavioral, credibility, and advocacy pattern analysis
89. Military defense service training materials — defense-side tactics and survivability heuristics
90. Military prosecution training materials — charging strategies and evidentiary emphasis
91. Military judicial benchbooks — judge-facing guidance on rulings and trial management
92. Court-martial panel (jury) selection rules — voir dire limits and bias challenges
93. Military victim and witness assistance program (VWAP) manuals — rights enforcement and procedural compliance
94. Military appellate defense counsel briefs (sanitized) — winning appellate issue patterns
95. Military habeas corpus and collateral review cases — civilian court review pathways
96. Military administrative separation regulations — non-criminal punitive actions and defenses
97. Security clearance adjudication guidelines — collateral consequences and due-process challenges
98. Military records retention and classification rules — evidence access and FOIA leverage
99. FOIA and Privacy Act applications within DoD — records access and exemptions
100. Military law review journals — doctrinal development and emerging issue analysis
101. Comparative military justice systems (NATO allies) — persuasive analogs occasionally cited in U.S. military cases
Executive and Emergency Powers
102. Presidential Executive Orders (Washington–present) — binding directives shaping federal agency authority, priorities, and enforcement scope
103. Executive Order metadata (number, date, authority cited) — traceability, delegation scope, and legal durability analysis
104. Executive Orders by subject-matter taxonomy — emergency powers, national security, labor, health, immigration, finance
105. Executive Orders invoking statutory authority — linkage between EO and enabling statutes for challenge or enforcement
106. Executive Orders citing national emergencies — trigger analysis for expanded executive power and constraints
107. National Emergency declarations (NEA, 50 U.S.C. §§1601–1651) — emergency duration, renewal, and judicial review pathways
108. EO revocation, amendment, and supersession history — continuity, rollback, and reliance interests
109. OMB EO implementation memoranda — agency interpretation and operationalization guidance
110. DOJ OLC opinions interpreting Executive Orders — authoritative executive-branch legal meaning
111. Agency implementing regulations tied to Executive Orders — rulemaking vulnerabilities and compliance gaps
112. Litigation challenging Executive Orders — standing, ripeness, injunction standards, and success patterns
113. Supreme Court and circuit decisions interpreting EOs — controlling precedent on scope and limits
114. Executive Orders affecting civil service and employment — due process, discipline, and whistleblower impacts
115. Executive Orders on federal law enforcement priorities — charging discretion, enforcement focus, and deprioritization
116. Executive Orders on immigration and border enforcement — removal priorities, asylum processing, and detention authority
117. Executive Orders on public health emergencies — quarantine, mandates, funding, and constitutional constraints
118. Executive Orders on disaster response (Stafford Act) — federal-state coordination and relief eligibility
119. Executive Orders on sanctions and foreign policy — asset freezes, designation authority, and due process challenges
120. Executive Orders on surveillance and intelligence — privacy implications and oversight triggers
121. Executive Orders on procurement and contracting — labor standards, DEI requirements, and compliance obligations
122. Executive Orders on regulatory reform and deregulation — cost-benefit mandates and rule invalidation avenues
123. Executive Orders on environmental policy — agency duties, enforcement discretion, and permitting impacts
124. Executive Orders on education policy — funding conditions and administrative enforcement
125. Executive Orders on healthcare administration — agency authority and benefits administration
126. Executive Orders on financial regulation — enforcement posture and supervisory priorities
127. Executive Orders on national security and defense — military authority and civilian oversight boundaries
128. Executive Orders on information sharing and data governance — privacy, retention, and disclosure risks
129. Executive Orders on censorship, speech, and platform policy — First Amendment implications and enforcement reach
130. Executive Orders affecting federal courts administration — budgeting, security, and operational impacts
131. Historical Executive Order archives (NARA) — authenticity, original intent, and evolution analysis
132. Governor Executive Orders (all 50 states + territories) — binding state-level directives with force of law
133. State executive order metadata (number, date, authority) — statutory basis and judicial review viability
134. Governor emergency orders (state emergency acts) — scope, duration, renewal, and sunset analysis
135. Pandemic and public health emergency orders — civil liberties constraints and precedent mapping
136. Governor EO preemption of local authority — home-rule conflicts and litigation patterns
137. Governor EO affecting law enforcement policy — use-of-force rules, arrest priorities, and immunity issues
138. Governor EO on election administration — ballot access, deadlines, and constitutional challenges
139. Governor EO on business closures and mandates — takings, due process, and equal protection analysis
140. Governor EO on education operations — funding, curriculum, and parental rights impacts
141. Governor EO on housing and eviction moratoria — contract clause and property rights litigation
142. Governor EO on firearms and public safety — statutory authority limits and injunction patterns
143. Governor EO on disaster relief and spending — procurement risks and oversight triggers
144. Governor EO on healthcare licensing and scope-of-practice — regulatory overreach analysis
145. Governor EO on labor and employment — wage rules, workplace mandates, and enforcement posture
146. Governor EO on environmental and energy policy — permitting authority and compliance burdens
147. Governor EO on data privacy and surveillance — constitutional and statutory constraints
148. Governor EO on corrections and incarceration — early release, custody standards, and victims’ rights
149. Governor EO on state procurement and contracting — favoritism, compliance, and audit leverage
150. Governor EO on regulatory suspension or waiver — nondelegation and ultra vires challenges
151. Governor EO litigation databases (state courts) — injunction rates, standards, and outcomes
152. Attorney General advisory opinions on executive orders — authoritative state interpretations
153. Legislative responses to executive orders — ratification, override, or nullification dynamics
154. Sunset clauses and termination mechanisms in EOs — automatic expiration and enforcement risk
155. Separation-of-powers challenges to EOs — delegation limits and judicial enforcement
156. Federalism conflict analyses (EO vs. state law) — supremacy and preemption issues
157. EO compliance guidance issued to agencies — internal interpretation and enforcement gaps
158. EO enforcement memoranda to law enforcement — practical application and deviation evidence
159. Inspector General reports on EO implementation — misuse, noncompliance, and abuse findings
160. Budgetary impacts of executive orders — appropriations conflicts and Anti-Deficiency Act issues
161. Executive privilege assertions tied to EO actions — discovery barriers and litigation strategy
162. Comparative analysis of presidential vs. gubernatorial EO powers — scope and constraint differentials
163. Historical abuse of executive order power case studies — corrective doctrine and guardrails
164. Emergency powers abuse litigation corpora — standards for judicial intervention
165. Executive order compliance failures used as liability evidence — negligence and ultra vires proof
166. Executive order rescission impacts on pending cases — reliance interests and mootness analysis
167. Executive order-driven rulemaking timelines — APA challenge windows and procedural traps
168. Executive order transparency and publication requirements — validity and notice challenges
169. Executive order impacts on private rights of action — enforcement opportunities and defenses
170. Executive order interaction with consent decrees — modification and enforcement leverage
171. Executive order databases with machine-readable tagging — automated analysis, alerts, and cross-jurisdiction comparison
Litigation Strategy, Patterns, and Failure Analysis
Pattern libraries, empirical outcome data, and autopsy frameworks for constructing survivable claims and avoiding common traps.
172. Civil Rights & Constitutional Abuse Pattern Libraries — pattern > anecdote; scalable allegations
173. (Pattern > anecdote) — prioritization rule for training and pleadings
174. §1983 / Bivens Pattern Libraries — claim elements, defenses, and common dismissal points
175. Successful complaint structures — proven pleadings architecture and sequencing
176. Failure-to-train patterns — Monell theory support and proof scaffolding
177. Supervisory liability fact patterns — causation, knowledge, and policy linkage templates
178. Qualified Immunity Defeat Datasets — “clearly established” targeting and analog selection
179. Clearly established law mappings — circuit-by-circuit rule articulation
180. Side-by-side fact analogs — rapid precedent matching and argument framing
181. Circuit-specific thresholds — doctrine variance and pleading strategy by circuit
182. Monell municipal liability doctrine deep corpora — policy/custom proof and causation scaffolds
183. Municipal claims notice statutes (all states) — deadline automation and compliance gates
184. Dismissed Case Autopsies — dismissal reasons, fixes, and pre-filing gates
185. Why cases failed — element gaps, proof gaps, and procedural errors
186. Procedural traps — jurisdiction, service, deadlines, exhaustion, and immunities
187. Missed deadlines or elements — error-proofing checklists and reminders
188. Sanctions & Fee-Shifting Cases — risk control and deterrence mapping
189. Rule 11 sanctions — pleading standards, safe harbor, and behavior triggers
190. §1927 attorney fees — vexatious conduct triggers and avoidance
191. Vexatious litigant rulings — gatekeeping patterns and defensive posture design
192. Common dismissal grounds libraries — pre-filing kill-switch checks
193. Pattern “procedural defect detectors” — missing parties, improper captions, wrong rule invoked
194. Judicial statistics by judge (where public) — motion grant rates, timelines, and disposition tendencies
195. Court backlog and time-to-trial datasets — operational planning and venue strategy
196. Police misconduct civil settlement archives (local) — pattern proof and damages anchoring
197. Use-of-force incident databases (where public) — comparative incidents and pattern analytics
198. Jail deaths and in-custody death reporting datasets — deliberate indifference and policy failures
Evidence, Discovery, and Accountability Systems
Transparency laws, oversight reports, and evidentiary tools for exposing institutional misconduct.
199. FOIA denial logs (MuckRock) — refusal patterns, exemptions usage, and appeal strategies
200. Public records law (all 50 states) + AG guidance — non-FOIA transparency enforcement
201. FOIA litigation case law clusters — exhaustion, exemptions, Vaughn indices, and fee recovery
202. DOJ OIP FOIA guidance archives — federal FOIA best practices and agency interpretations
203. State AG public-records opinions — state-specific transparency enforcement leverage
204. Inspector General & Audit Reports — documented misconduct, waste, and policy failures
205. DOJ OIG — federal DOJ oversight findings and patterns
206. HHS OIG — healthcare fraud, enforcement patterns, and compliance failures
207. HUD OIG — housing, grants, procurement, and fraud oversight patterns
208. State auditors — state-level waste/fraud/abuse findings and agency weaknesses
209. Agency Internal Manuals & SOPs — operational rules that create liability when violated
210. FOIA processing manuals — statutory compliance and denial vulnerability points
211. Records retention policies — spoliation, duty to preserve, and discovery leverage
212. Complaint-handling SOPs — exhaustion paths and agency accountability mapping
213. Evidence foundations (authentication, chain of custody) — admissibility-proof automation
214. Digital evidence standards (hashing, metadata, timestamps) — court-ready forensics and integrity
215. ESI protocols + discovery guides (Sedona Conference) — defensible e-discovery and spoliation safety
216. Protective orders, confidentiality, and sealing standards — access strategy and anti-gag compliance
217. Spoliation of evidence and adverse inference doctrines — sanctions for destruction
218. Body-worn camera and evidence retention policies — spoliation leverage and preservation demands
219. Subpoena practice guides (civil/criminal) — lawful compelled production and objections handling
220. Third-party record acquisition pathways (providers, agencies) — efficient evidence collection planning
221. Open-source intelligence (OSINT) tradecraft manuals — lawful collection and verification protocols
222. Source credibility scoring frameworks — corroboration requirements and misinformation filtering
223. Disinformation and deepfake detection research — authenticity gating for media evidence
224. Court-ordered consent decrees and monitorship reports — systemic reform proof and compliance failures
Formal Logic and Argumentation Frameworks
Comprehensive logical systems for constructing valid arguments and detecting flaws in precedent and opposition reasoning.
225. Classical logic treatises (Aristotle’s Organon) — foundational syllogistic reasoning and validity testing
226. Propositional logic corpora — truth-functional reasoning and consistency checking
227. Predicate (first-order) logic texts — quantified reasoning for complex legal fact patterns
228. Higher-order logic sources — reasoning about rules, rules about rules, and meta-doctrine
229. Modal logic (necessity/possibility) treatises — counterfactuals, hypotheticals, and “could/must” analysis
230. Deontic logic sources — obligation, permission, prohibition modeling for statutory interpretation
231. Temporal logic research — sequencing, deadlines, continuing violations, and tolling logic
232. Non-monotonic logic corpora — reasoning where conclusions change with new facts (real litigation dynamics)
233. Defeasible reasoning frameworks — rule-exception modeling central to case-of-first-impression arguments
234. Argumentation theory (Toulmin model) — claims, warrants, backing, and rebuttal structures
235. Informal logic textbooks — real-world reasoning beyond symbolic formalism
236. Legal argumentation theory journals — how courts accept or reject logical structures
237. Dialectical logic sources — adversarial reasoning and thesis-antithesis resolution
238. Abductive reasoning literature — inference to the best explanation from incomplete evidence
239. Inductive reasoning theory — pattern-based reasoning and generalization limits
240. Bayesian reasoning texts — probabilistic inference, evidentiary weighting, and credibility scoring
241. Bayesian networks applied to law — causal modeling for complex fact chains
242. Decision theory treatises — rational choice under uncertainty in judicial outcomes
243. Game theory in law — strategic interaction between litigants, judges, and institutions
244. Mechanism design theory — incentive structures embedded in legal systems
245. Proof theory sources — rigor, structure, and completeness of logical proofs
246. Model theory — interpretation of formal systems (analogous to statutory interpretation)
247. Set theory fundamentals — classification, inclusion/exclusion, and category logic
248. Category theory (applied reasoning) — structural relationships between legal concepts
249. Fuzzy logic research — reasoning under vagueness (reasonableness, materiality, substantiality)
250. Vagueness and sorites paradox literature — attacking indeterminate standards
251. Legal standards vs. rules analysis — logical consequences of open-textured language
252. Semantic logic sources — meaning, reference, and definitional boundaries
253. Pragmatics in language theory — implied meaning, context, and conversational maxims
254. Speech-act theory — promises, commands, assertions, and legal effect of language
255. Ordinary language philosophy (Wittgenstein, Austin) — dismantling over-formalized interpretations
256. Hermeneutics and interpretation theory — text meaning over time and context
257. Statutory interpretation logic treatises — textualism, purposivism, intentionalism logic models
258. Canons of construction compendia — logical rules courts purport to follow
259. Conflicting canons resolution theory — hierarchy and meta-logic for canon collisions
260. Reductio ad absurdum case law examples — exposing illogical consequences of precedent
261. Principle of non-contradiction applications in law — internal inconsistency attacks
262. Principle of sufficient reason literature — demanding rational justification for outcomes
263. Analogical reasoning theory — core mechanism of common-law evolution
264. Limits of analogy scholarship — distinguishing false or overextended analogies
265. Counter-precedent reasoning frameworks — when and how to depart from stare decisis
266. Stare decisis theory and limits — logic-based overruling justification
267. Precedent decay and obsolescence research — factual and doctrinal erosion analysis
268. Scientific reasoning and falsifiability theory (Popper) — testing factual assumptions in precedent
269. Epistemology sources — knowledge, belief, justification in fact-finding
270. Reliability and validity theory — evidentiary trustworthiness analysis
271. Burden-of-proof logic models — allocation and shifting of evidentiary burdens
272. Presumption theory — default rules and how to logically rebut them
273. Negative proof and impossibility reasoning — proving absence, not just presence
274. Logical structure of constitutional rights — rule-based vs. principle-based reasoning
275. Rights-balancing logic models — proportionality and least-restrictive-means analysis
276. Strict scrutiny / intermediate scrutiny logical frameworks — internal consistency testing
277. Rational-basis review logical critiques — exposing pretextual justifications
278. Proportionality doctrine logic (comparative law) — structured balancing analysis
279. Formal ethics logic (normative systems) — consistency in moral-legal reasoning
280. Meta-ethics and law sources — objectivity vs. subjectivity in judicial reasoning
281. Systems theory applied to law — emergent behavior and unintended consequences
282. Complex systems and feedback loop research — institutional self-protection logic
283. Path dependence theory — why bad precedents persist and how to break them
284. Critical rationalism sources — constant testing of legal assumptions
285. Decision-tree modeling — stepwise legal outcome analysis
286. Causal inference literature — correlation vs. causation in fact-finding
287. Counterfactual causation theory — “but-for” and proximate cause refinement
288. Structural causation research — institutional cause beyond individual acts
289. Logical paradoxes in law — identifying internally incoherent doctrines
290. Inconsistency tolerance theory — how courts live with contradictions
291. Minimal-change principle in legal reasoning — narrow overruling strategies
292. Maximization vs. satisficing theory — judicial shortcut detection
293. Mathematical logic for consistency checking — automated contradiction detection
294. Knowledge representation ontologies — structured legal concept mapping
295. Ontological engineering for law — preventing category errors
296. Semantic networks and concept graphs — cross-doctrine logical alignment
297. Argument mining datasets — extracting reasoning patterns from opinions
298. Rhetorical logic analysis — persuasion vs. validity separation
299. Sophistry detection literature — exposing arguments that persuade without proving
300. Burden-shifting fallacy detection — improper argumentative reversals
301. False dichotomy detection research — exposing artificial binary framing
302. Slippery slope analysis frameworks — distinguishing valid vs. fallacious slopes
303. Circular reasoning detection — precedent citing itself without justification
304. Post hoc reasoning critiques — temporal fallacy exposure
305. Statistical reasoning errors in courts — misuse of probability and risk
306. Base-rate neglect research — correcting evidentiary misweighting
307. Prosecutor’s fallacy literature — DNA and statistical evidence misuse
308. Narrative fallacy research — story coherence overpowering logic
309. Legal realism vs. formalism debate sources — exposing decision-driven reasoning
310. Formal proof assistants (logic engines) — machine-verified reasoning structures
311. Automated theorem proving research — logical completeness checking
312. Constraint-satisfaction problem models — element-matching and failure detection
313. Consistency-based diagnosis — isolating doctrinal failure points
314. Epistemic humility doctrine — recognizing limits of precedent certainty
315. First-principles reasoning literature — rebuilding doctrine from constitutional foundations
316. Original logical structure of constitutional provisions — argument beyond historical intent
317. Logical minimalism in holdings — narrow rule extraction
318. Overbreadth and underinclusiveness logic tests — equal protection and speech analysis
319. Symmetry and parity reasoning — equal application of rules
320. Internal-logic audits of landmark cases — systematic contradiction mapping
321. Logical taxonomy of legal wrongs — element-level categorization
322. Logical sufficiency vs. evidentiary sufficiency theory — distinct analytical layers
323. Meta-logic for judicial opinions — evaluating reasoning about reasoning
324. Logic-driven “case of first impression” generation frameworks — constructing novel yet court-survivable arguments grounded in facts, reason, and internally consistent logic
325. Nonsense: A Handbook of Logical Fallacies — canonical taxonomy of informal fallacies with practical examples applicable to legal argument
326. Expanded informal fallacy catalogs (argument from ignorance, burden shifting, special pleading) — detection of defective reasoning in opinions and briefs
327. Fallacy frequency datasets in judicial opinions — empirical mapping of recurring reasoning errors
328. Legal-context adaptations of classic fallacies — how courts misapply otherwise valid logic
329. Sophistical refutations (Aristotle) — early systematic exposure of deceptive argument forms
330. Eristic dialectic (Schopenhauer) — adversarial tactics used to “win” without proving truth
331. Argumentum ad baculum case studies — coercion and threat-based reasoning detection
332. Argumentum ad populum analyses — popularity-as-proof errors in policy-driven rulings
333. Argumentum ad verecundiam datasets — improper reliance on authority without analysis
334. Argumentum ad antiquitatem critiques — tradition-as-justification errors in precedent
335. Argumentum ad novitatem critiques — novelty bias masking lack of proof
336. Straw man detection corpora — mischaracterization of claims or standards
337. Red herring identification datasets — issue diversion patterns in opinions and motions
338. Tu quoque fallacy analyses — deflection through hypocrisy accusations
339. False equivalence detection research — unequal comparisons framed as equal
340. Weak analogy datasets — superficial similarity masking material differences
341. Slothful induction studies — ignoring strong contrary evidence
342. Cherry-picking detection frameworks — selective citation and fact omission patterns
343. Texas sharpshooter fallacy analyses — post hoc pattern imposition on noise
344. Moving-the-goalposts pattern libraries — shifting standards after compliance
345. Motte-and-bailey doctrine critiques — retreat to defensible claim after aggressive assertion
346. No true Scotsman fallacy detection — redefinition to avoid counterexamples
347. Loaded question identification corpora — presupposition traps in judicial questioning
348. Begging the question (petitio principii) datasets — circular reasoning in precedent chains
349. Composition and division fallacy studies — improper inference from parts to whole or vice versa
350. Ecological fallacy analyses — misuse of aggregate data to infer individual facts
351. Simpson’s paradox applications — hidden-variable reversals in statistical evidence
352. Post hoc ergo propter hoc case law critiques — temporal sequence mistaken for causation
353. Cum hoc ergo propter hoc analyses — correlation mistaken for causation
354. False cause and confounding variable detection — causal inference correction tools
355. Appeal to consequences critiques — outcome preference replacing legal reasoning
356. Appeal to fear analyses — risk inflation to justify restrictions or dismissals
357. Appeal to pity datasets — emotional substitution for proof
358. Appeal to ridicule case studies — delegitimization without rebuttal
359. Middle-ground fallacy critiques — compromise framed as correctness
360. Nirvana fallacy analyses — rejecting solutions for not being perfect
361. Perfectionist fallacy detection — unattainable standards imposed to deny relief
362. Relative privation critiques — “worse problems exist” as denial logic
363. Fallacy of the excluded middle — ignoring lawful alternatives
364. Scope neglect studies — underweighting magnitude of harm
365. Availability heuristic misuse in rulings — vivid anecdotes outweighing data
366. Anchoring bias amplification via fallacy — initial figures skew outcomes
367. Framing effect exploitation — wording-driven preference shifts
368. Survivorship bias datasets — ignoring failed or excluded cases
369. Base-rate neglect in evidentiary analysis — misweighting priors
370. Regression to the mean misinterpretation — false trend claims
371. Misuse of averages (mean vs. median) — statistical distortion
372. P-hacking and data dredging critiques — selective analysis masquerading as rigor
373. Overfitting narratives to facts — bespoke stories lacking general validity
374. Narrative fallacy overlays — coherence mistaken for truth
375. Hindsight bias analyses — inevitability illusion after outcomes
376. Outcome bias detection — judging decisions by results, not reasons
377. Authority halo effect studies — deference eclipsing analysis
378. Status quo bias rationalizations — inertia defended as logic
379. Sunk-cost fallacy in doctrine — persistence with bad precedent
380. Confirmation bias reinforcement loops — selective doctrine citation
381. Motivated reasoning studies — ideology shaping inference
382. Goal substitution fallacy — procedural compliance replacing substantive justice
383. Reification errors — abstract doctrines treated as concrete facts
384. Category mistakes in law — misclassification leading to wrong standards
385. Equivocation detection corpora — shifting meanings of key terms
386. Amphiboly analyses — grammatical ambiguity exploited
387. Quantifier scope errors — “all,” “some,” “many” misapplied
388. Modality confusion (may/must/shall) — deontic ambiguity exploitation
389. Vagueness exploitation tactics — indeterminate standards used to deny claims
390. Overbreadth camouflage — broad rules justified by narrow facts
391. Underinclusiveness rationalization — selective enforcement defended as reasonable
392. Pretext masking patterns — legitimate reasons covering illicit motives
393. Fallacy stacking detection — multiple weak arguments presented as strength
394. Argument by assertion frequency analysis — repetition mistaken for proof
395. Legal formalism-as-fallacy critiques — procedure eclipsing substance
396. Magical thinking in remedies — assumptions of compliance without enforcement
397. Zero-sum framing errors — false scarcity of rights or remedies
398. False inevitability narratives — “this outcome is unavoidable” claims
399. Misplaced concreteness — treating models as reality
400. Reductionism errors — oversimplifying multi-factor tests
401. Overgeneralization from dicta — non-holding language treated as binding
402. Dicta laundering detection — persuasive dicta elevated to rule
403. Footnote fallacy analyses — dispositive reasoning buried to avoid scrutiny
404. Silence-as-consent fallacy — absence of objection treated as waiver
405. Waiver-by-confusion critiques — complexity used to infer consent
406. Procedural default as moral judgment fallacy — lateness equated with lack of merit
407. Error conflation detection — harmless vs. structural error confusion
408. Deference creep analyses — incremental expansion of agency/judicial deference
409. Chevron step-skipping critiques — conclusory deference without analysis
410. Rational-basis-with-bite inconsistency mapping — ad hoc scrutiny elevation
411. Standards-of-review drift detection — covertly changing scrutiny level
412. Proof-by-volume fallacy — length mistaken for substance
413. Authority citation without application — case-name dropping without reasoning
414. Formal logic checklists for briefs — pre-filing validity audits
415. Fallacy-aware brief templates — prompts to force rebuttal of likely errors
416. Opinion logic audits — systematic fallacy tagging in rulings
417. Adversarial fallacy anticipation models — preemptive counter-argument generation
418. Fallacy heatmaps by judge/venue — propensity analytics
419. First-impression logic scaffolds — clean-room reasoning independent of precedent
420. Precedent stress-testing via fallacy exposure — identifying brittle holdings
421. Logical minimal-change overruling strategies — narrow corrections with maximal effect
422. Fact–rule–conclusion separation tools — preventing category bleed
423. Reason-giving adequacy standards — enforcing rational explanation norms
424. Integrated fallacy-and-logic engine — automated detection, rebuttal drafting, and court-facing explanation to support cases of first impression and logic-based overruling
Judicial Psychology and Decision-Making Models
Empirical and theoretical research on cognitive, ideological, and institutional factors influencing judicial behavior.
425. Judicial psychology and decision-making research — cognitive factors influencing rulings beyond doctrine
426. Behavioral economics applied to judging — heuristics, loss aversion, and risk preferences in judicial choices
427. Cognitive bias taxonomies (anchoring, confirmation bias, status quo bias) — systematic error detection in judicial reasoning
428. Judicial implicit bias studies — race, class, gender, and authority bias impacts on outcomes
429. Sentencing psychology research — disparities, anchoring effects, and recommendation influence
430. Prospect theory in legal decision-making — asymmetric risk tolerance in grants vs. denials
431. Judicial workload and cognitive fatigue studies — timing effects on rulings and disposition patterns
432. Decision sequencing effects research — how earlier cases affect later judicial outcomes
433. Mood, emotion, and affect studies in judges — external stressors influencing decisions
434. Political ideology and judicial behavior datasets — ideological drift, panel effects, and voting blocs
435. Panel dynamics research (appellate courts) — dissent suppression, conformity, and opinion assignment effects
436. Clerk influence and delegation studies — staff-attorney and clerk gatekeeping impact
437. Judicial reputation and peer-effect research — conformity pressures within courts
438. Career incentives and promotion pathways — reappointment, elevation, and reputational signaling
439. Election vs. appointment psychology (state judges) — electoral pressure and donor influence effects
440. Campaign finance influence on judicial behavior — correlations between donations and rulings
441. Judicial stress, burnout, and caseload triage studies — shortcut heuristics and dismissal likelihood
442. Authority bias and deference psychology — tendency to favor government actors
443. In-group / out-group bias research — pro se vs. represented party treatment patterns
444. Procedural justice perception studies — how litigant behavior affects judicial receptivity
445. Linguistic framing effects on judges — word choice, tone, and narrative persuasion research
446. Plain-language vs. technical briefing impact studies — comprehension and receptivity outcomes
447. Moral psychology applied to law — fairness, loyalty, authority, and harm framing
448. Judicial risk-avoidance psychology — preference for reversible-error minimization
449. Fear-of-reversal and appellate scrutiny studies — defensive judging patterns
450. Sanction-aversion psychology — reluctance to discipline institutional actors
451. Time-pressure and deadline proximity studies — summary disposition and shortcut rulings
452. Case salience and media exposure psychology — deviation from norms under scrutiny
453. High-profile vs. low-visibility case behavior research — outcome variance analysis
454. Procedural complexity aversion studies — dismissal likelihood tied to perceived difficulty
455. Novelty bias research — resistance to first-impression legal theories
456. Judicial learning curves — behavior changes over tenure and experience
457. Judge personality typology studies — authoritarian vs. deliberative profiles
458. Social dominance orientation in judicial decision-making — hierarchy-preserving rulings
459. Gender-based judicial behavior studies — outcome differences and interaction effects
460. Racial empathy gap research in courts — credibility assessment disparities
461. Pro se litigant perception studies — stereotype effects and credibility discounting
462. Oral argument psychology research — influence of questioning tone and interruption patterns
463. Writing-style alignment studies — persuasion through mirroring judicial language norms
464. Judicial error-correction behavior studies — reluctance to admit or reverse prior rulings
465. Status-quo preservation psychology — institutional stability over rights expansion
466. Cognitive dissonance in judging — rationalization of inconsistent outcomes
467. Group polarization in appellate panels — ideological hardening effects
468. Dissent aversion and unanimity pressure research — opinion-writing dynamics
469. Narrative coherence bias — preference for simpler factual stories
470. Credibility heuristics in witness evaluation — demeanor-based error patterns
471. Authority signaling and courtroom dominance psychology — control maintenance behaviors
472. Deference to repeat players research — institutional litigant advantage studies
473. Loss-of-control anxiety in judges — reaction to litigant assertiveness
474. Judicial self-concept and identity studies — role perception influencing rulings
475. Threat perception research — reactions to accusations of misconduct or bias
476. Compliance vs. resistance psychology — judicial response to procedural pushback
477. Cognitive load effects of excessive filings — strategic filing volume impact
478. Emotional contagion in courtrooms — influence of litigant affect on judges
479. Judicial trust calibration studies — skepticism thresholds and credibility gating
480. Moral licensing effects — prior “fair” rulings enabling later harsh outcomes
481. Institutional loyalty psychology — protection of courts, prosecutors, and agencies
482. Fear of precedent creation studies — reluctance to issue broad rulings
483. Ambiguity aversion research — preference for dismissal over uncertain merits rulings
484. Authority-challenge response psychology — sanctions and control-reassertion triggers
485. Judicial language analysis corpora — predictive indicators of grant/deny outcomes
486. Tone-sentiment outcome correlation datasets — emotional valence and decision results
487. Micro-expression and nonverbal cue research — credibility judgments and misinterpretation risks
488. Judicial humility vs. dominance studies — openness to correction and persuasion
489. Courtroom power-distance psychology — hierarchy reinforcement behaviors
490. Temporal discounting in remedies — undervaluation of future harm
491. Procedural legitimacy belief studies — emphasis on form over substance
492. Judicial error-rate self-assessment research — overconfidence effects
493. Norm-enforcement psychology — punishment of perceived rule-breakers
494. Narrative threat response — defensive reactions to systemic-failure allegations
495. Psychological reactance in judges — backlash against perceived pressure or publicity
496. Decision avoidance strategies — dismissals without reaching merits
497. Emotional regulation research in adjudication — suppression vs. leakage effects
498. Judicial fear of institutional embarrassment — secrecy and sealing preferences
499. Authority preservation through ambiguity — vague rulings as control mechanisms
500. Judicial persuasion ethics literature — boundaries of acceptable influence
501. Cognitive empathy vs. emotional empathy studies — differential impacts on outcomes
502. Comparative psychology of trial vs. appellate judges — fact vs. doctrine orientation
503. Judicial acclimation to injustice research — normalization of rights violations
504. Stress-induced conservatism studies — retreat to familiar doctrines under pressure
505. Brian Barry How Judges Judge: Empirical Insights into Judicial Decision-Making — comprehensive empirical examination of ideological, institutional, and personal forces shaping judicial outcomes and role perception
Language, Narrative, and Persuasion Systems
Frameworks for precise expression, narrative construction, linguistic analysis, and ethical influence.
Narrative and Genre Theory
506. Three Genres: The Writing of Poetry, Fiction, and Drama — foundational framework for understanding how meaning, persuasion, and structure change across genres; adapted for legal narrative construction
507. Genre theory applied to legal writing — identifying when courts expect analytic, narrative, or dramatic framing
508. Narrative vs. expository mode distinctions — choosing fact-storytelling vs. rule-application for maximum judicial receptivity
509. Poetic compression techniques — distilling complex arguments into concise, memorable formulations
510. Imagery and metaphor theory — lawful use of analogy to clarify abstract legal concepts
511. Symbolism analysis frameworks — understanding how courts respond to symbolic facts (badges, homes, children, liberty)
512. Tone modulation studies — calibrating gravity, restraint, and urgency in briefs and oral argument
513. Rhythm and cadence in prose — sentence structure effects on comprehension and persuasion
514. Voice and point-of-view theory — aligning narrator stance (objective, restrained, moral) with judicial expectations
515. Showing vs. telling doctrine — evidentiary fact presentation that lets facts compel conclusions
516. Scene construction principles — organizing facts as discrete, time-ordered events courts can visualize
517. Chronology control techniques — avoiding confusion and preserving causation clarity
518. Conflict theory in narrative — framing disputes around legally cognizable tensions (power, duty, breach)
519. Stakes articulation models — making harms concrete without emotional excess
520. Character construction ethics — portraying parties as credible, restrained, and rights-bearing
521. Antagonist framing without demonization — exposing misconduct through facts, not invective
522. Motivation and intent portrayal — aligning narrative facts with mens rea and state-of-mind elements
523. Dramatic irony awareness — avoiding facts known to the writer but not yet established in the record
524. Narrative coherence testing — ensuring factual story aligns with legal elements
525. Plot arc models (exposition → rising action → resolution) — structuring complaints and motions for logical flow
526. Compression vs. expansion strategy — knowing when to summarize vs. detail facts
527. Transition mechanics — guiding judges cleanly between facts, law, and analysis
528. Scene-to-rule mapping — tying each factual segment to a specific legal element
529. Subtext control — avoiding unintended implications that weaken claims
530. Ambiguity management — identifying and resolving factual ambiguities before courts do
531. Narrative reliability theory — establishing the credibility of the storyteller (affiant, witness, litigant)
532. Consistency checks across pleadings — preventing narrative drift across filings
533. Dramatic pacing in legal argument — slowing down for critical facts, accelerating through background
534. Use of silence and omission — strategic exclusion of immaterial facts to maintain clarity
535. Repetition-with-variation techniques — reinforcing key facts without redundancy
536. Motif tracking — recurring facts or themes that reinforce legal theory (notice, warning, refusal)
537. Framing openings and closings — first-impression and last-impression effects on judges
538. Title and heading theory — persuasive signaling through section labels
539. Genre expectations of judges — how trial vs. appellate courts read differently
540. Dialogue theory adaptation — quoting testimony, emails, and transcripts for immediacy
541. Quotation integration standards — embedding quoted material without breaking narrative flow
542. Voice consistency across documents — maintaining institutional credibility over time
543. Ethical limits of persuasion — distinguishing compelling narrative from manipulation
544. Pathos–logos–ethos balance models — Aristotle applied to modern judicial persuasion
545. Dramatic tension minimization — avoiding sensationalism that triggers judicial defensiveness
546. Narrative alignment with burdens of proof — tailoring story strength to evidentiary standards
547. Fact clustering techniques — grouping facts to satisfy multi-factor tests
548. Narrative counterfactual control — preemptively addressing “what if” judicial doubts
549. Rebuttal-as-narrative strategy — dismantling opposing stories rather than isolated arguments
550. Narrative collapse detection — identifying where a story fails logically or evidentially
551. Genre-mixing pitfalls — avoiding fiction/drama excess in legal prose
552. Judicial preference studies on storytelling — empirical insights into narrative acceptance
553. Plain-English storytelling frameworks — clarity without oversimplification
554. Narrative anchoring risks — first fact fixation and mitigation strategies
555. Story-to-doctrine translation engines — converting persuasive narrative into clean legal holdings
556. Poetry-derived precision language tools — eliminating surplus words while preserving meaning
557. Meter and emphasis awareness — stress patterns in sentences affecting comprehension
558. Figurative language risk analysis — identifying metaphors courts reject vs. accept
559. Legal aphorism crafting — memorable, quotable lines grounded in law and logic
560. Fictional point-of-view shifts — recognizing and correcting unintended bias perspectives
561. Unreliable narrator avoidance — guarding against overstatement and speculation
562. Dramatic climax control — placing strongest facts at procedurally optimal moments
563. Resolution framing — ending arguments with inevitability grounded in law, not emotion
564. Narrative neutrality techniques — appearing fair while exposing misconduct
565. Genre-aware AI drafting constraints — ensuring Legal AI Bot outputs remain court-safe while leveraging narrative science
Computational and Neuro-Linguistic Processing
566. Natural Language Processing (computational linguistics) foundational textbooks — formal grounding in syntax, semantics, pragmatics, and discourse
567. Speech and Language Processing — core reference for modern NLP models, parsing, semantics, and pragmatics
568. Statistical NLP corpora — frequency-based language patterns and probabilistic inference
569. Transformer architecture research (attention mechanisms) — long-context reasoning and cross-document coherence
570. Large Language Model (LLM) interpretability studies — understanding why models produce specific outputs
571. Prompt engineering research — structured instruction design for reliable legal outputs
572. Instruction-following and alignment datasets — controllability and constraint adherence
573. Named Entity Recognition (NER) legal corpora — accurate extraction of parties, statutes, venues, dates
574. Legal-specific tokenization standards — preserving citations, sections, and symbols
575. Dependency parsing datasets — syntactic relationship mapping for complex legal sentences
576. Constituency parsing corpora — clause hierarchy and scope resolution
577. Coreference resolution datasets — tracking parties, pronouns, and entities across filings
578. Semantic role labeling (SRL) datasets — who did what to whom, when, and how
579. Discourse coherence models — maintaining logical flow across long briefs
580. Rhetorical Structure Theory (RST) corpora — argument segmentation and relation mapping
581. Argument mining datasets — extracting premises, conclusions, and warrants from opinions
582. Citation intent classification datasets — why cases are cited (support, distinguish, criticize)
583. Precedent similarity embedding models — semantic analog matching beyond keyword overlap
584. Contradiction and entailment datasets (NLI) — detecting internal inconsistency and implied conclusions
585. Fact–law alignment models — matching factual allegations to legal elements
586. Temporal NLP datasets — timeline extraction and sequencing of events
587. Modality detection corpora — may/must/shall/should interpretation accuracy
588. Hedging and uncertainty detection datasets — identifying speculative vs. factual statements
589. Sentiment analysis adapted to legal tone — restraint vs. advocacy detection
590. Stylistic transfer research — adapting tone to judge, court, or forum norms
591. Readability and comprehension metrics (legal NLP) — optimizing for judicial clarity
592. Plain-language transformation datasets — simplification without semantic loss
593. Text summarization corpora (legal-specific) — faithful condensation of records and rulings
594. Long-document QA benchmarks — reliable reasoning across entire dockets
595. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) best-practice sources — grounding outputs in authoritative law
596. Hallucination detection and mitigation research — citation fidelity and fact anchoring
597. Explainable NLP (XAI) methods — court-facing transparency for AI-assisted drafting
598. Bias detection in language models — identifying ideological, institutional, or demographic skew
599. Adversarial NLP attack research — robustness against prompt manipulation or poisoned inputs
600. Multilingual NLP for legal translation — accurate handling of non-English evidence
601. Speech-to-text models tuned for court audio — accurate transcription of hearings and arguments
602. Speaker diarization research — attributing statements to correct speakers
603. Prosody and emphasis analysis — detecting stress, certainty, and evasion in speech
604. Pragmatic inference models — implied meaning beyond literal text
605. Conversational turn-taking analysis — interruption, dominance, and power cues
606. Computational pragmatics sources — Gricean maxims applied to legal discourse
607. Politeness theory and face-saving research — judicial receptivity and tone management
608. Framing effects in NLP — how wording alters interpretation
609. Metaphor detection research — identifying and evaluating analogical language
610. Narrative NLP models — story structure extraction and evaluation
611. Deception detection via linguistic cues — indicators of evasion or inconsistency
612. Stylometry datasets — authorship attribution and ghostwriting detection
613. Register and genre classification models — distinguishing briefs, orders, opinions, and correspondence
614. Lexical ambiguity resolution datasets — disambiguating overloaded legal terms
615. Ontology-driven NLP for law — structured concept hierarchies and reasoning
616. The Structure of Magic — foundational NLP (neuro-linguistic programming) model of language patterns and meaning change
617. Frogs into Princes — practical NLP communication and persuasion patterns
618. Meta-model language patterns — precision questioning to expose deletions, distortions, and generalizations
619. Milton-model language patterns — permissive, indirect language influencing perception
620. Presupposition analysis — identifying embedded assumptions in questions and rulings
621. Reframing techniques — changing meaning without changing facts (lawful persuasion)
622. Anchoring theory (psychological) — state and concept association effects
623. State-dependent language research — emotional context effects on comprehension
624. Rapport-building language patterns — mirroring, pacing, and leading (ethically constrained)
625. Sensory predicate analysis — visual/auditory/kinesthetic language preference detection
626. Linguistic deletion detection — spotting missing actors, causes, or constraints
627. Linguistic distortion detection — identifying modal operators and mind-reading claims
628. Over-generalization pattern libraries — “always/never/everyone” logic flags
629. Modal operator mapping (can’t/must/should) — obligation vs. impossibility analysis
630. Nominalization detection — abstract nouns masking agency or causation
631. Cause-effect language scrutiny — false necessity and inevitability claims
632. Embedded command detection — subtle directive language analysis
633. Temporal language manipulation studies — urgency, delay, and inevitability framing
634. Identity-level language research — role-based persuasion (“as a judge…”)
635. Values and criteria elicitation models — uncovering unstated decision drivers
636. Linguistic calibration and precision training — tightening language to match facts
637. Counter-suggestion and resistance techniques — neutralizing manipulative phrasing
638. Cognitive load reduction via language — clarity under stress
639. Pattern interruption research — disrupting manipulative conversational loops
640. Hypnotic language ethics literature — boundaries and prohibitions in legal contexts
641. Persuasion vs. manipulation distinction frameworks — compliance with legal ethics
642. Courtroom questioning NLP adaptations — lawful precision without coercion
643. Witness communication optimization studies — clarity without leading
644. Jury-facing language sensitivity research — avoiding backlash or mistrust
645. De-escalation language models — reducing conflict during encounters
646. Linguistic self-defense manuals — recognizing and resisting manipulation
647. Credibility-building language markers — consistency, specificity, and restraint
648. Power-neutral language techniques — avoiding dominance triggers in judges
649. Linguistic humility signaling — increasing receptivity without concession
650. Strategic silence and pause research — conversational control without speech
651. Narrative reframing under cross-examination — maintaining coherence
652. NLP-informed affidavit drafting standards — clarity, precision, and credibility
653. Language pattern red-flag detectors — automated warnings for manipulative phrasing
654. Ethical NLP safeguards for AI systems — preventing coercive or deceptive outputs
655. Integrated NLP + Neuro-linguistic programming engine — language analysis, precision rewriting, manipulation detection, and court-safe persuasive optimization
Structured Persuasion Systems
656. Robert B. Cialdini — Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion — scientifically grounded principles (reciprocity, commitment, social proof, liking, authority, scarcity) for ethical advocacy, settlement leverage, and detecting institutional influence tactics
657. Robert B. Cialdini — Pre-Suasion: A Revolutionary Way to Influence and Persuade — attention-channeling techniques to prime judicial and opponent receptivity before substantive arguments
658. Roger Fisher and William Ury — Getting to Yes: Negotiating Agreement Without Giving In — interest-based principled negotiation framework for achieving durable, non-positional resolutions in settlements and disputes
659. Chris Voss — Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On It — tactical empathy, labeling, mirroring, and calibrated questions for high-stakes adversarial negotiations, including rights assertions and institutional confrontations
660. Ross Guberman — Point Made: How to Write Like the Nation's Top Advocates — annotated excerpts from leading Supreme Court and appellate briefs modeling persuasive structure, style, and rhetorical moves
661. Bryan A. Garner — The Winning Brief: 100 Tips for Persuasive Briefing in Trial and Appellate Courts — practical, rule-based strategies for crafting compelling, judge-aligned motions and briefs
662. Noah A. Messing — The Art of Advocacy: Briefs, Motions, and Writing Strategies from Top Lawyers and Judges — Yale-derived techniques for concise, persuasive legal writing drawn from elite practitioner examples
663. Paul Bergman and Sara Berman — Represent Yourself in Court: How to Prepare & Try a Winning Case — step-by-step pro se guide to civil litigation procedure, evidence, and courtroom advocacy with success-oriented templates
664. Way of the Wolf: Straight Line Selling — primary exposition of the Straight Line System; structured persuasion from opening to close
665. Jordan Belfort — originator of the Straight Line System; source lectures, seminars, and refinements
666. Straight Line System core axioms — control of process, certainty transfer, logical progression toward decision
667. The “Three Tens” framework — product, presenter, and company certainty calibration
668. Tonality control techniques — vocal inflection patterns that signal confidence without aggression
669. Script architecture models — open → qualify → present → loop → close sequencing
670. State management protocols — emotional regulation for persuasion under pressure
671. First-impression dominance strategies — immediate authority establishment within ethical bounds
672. Prospect qualification logic — separating interest from ability, authority, and timing
673. Looping technique playbooks — addressing objections while returning to core value proposition
674. Objection taxonomy (price, trust, need, timing) — diagnostic categorization before response
675. Objection reframing patterns — converting resistance into agreement paths
676. Scarcity framing ethics — lawful urgency without deception
677. Future pacing techniques — guiding the listener to visualize post-decision outcomes
678. Logical–emotional–ethical close balance — aligning reason, feeling, and credibility
679. Micro-commitment ladders — incremental “yes” structures leading to final assent
680. Language certainty markers — eliminating weak qualifiers that undermine credibility
681. Precision vocabulary lists — high-impact words that convey control and clarity
682. Anchoring initial value perceptions — lawful reference-point establishment
683. Price justification logic — reframing cost as investment or avoided loss
684. Rapport acceleration methods — mirroring and pacing without manipulation
685. Prospect belief-state mapping — identifying certainty gaps to target persuasion
686. Sales psychology under time pressure — maintaining structure when rushed
687. Ethical persuasion boundaries — avoiding misrepresentation and coercion
688. Negotiation alignment with Straight Line principles — win–win framing without concession creep
689. Decision paralysis breakers — simplifying choice architecture
690. Resistance softening language — reducing threat perception while maintaining authority
691. Authority signaling cues — posture, cadence, and structure rather than claims
692. Trust transfer mechanisms — evidence sequencing and social proof usage
693. Commitment reinforcement scripts — post-decision confidence stabilization
694. Straight Line questioning frameworks — precise questions that guide logical movement
695. Control-with-respect doctrine — maintaining process leadership without antagonism
696. Rebuttal compression techniques — concise responses that prevent derailment
697. Emotional spike timing — when to elevate enthusiasm vs. remain neutral
698. Calibration of assertiveness — adapting intensity to listener receptivity
699. Pattern interruption for objections — resetting conversational momentum
700. Closing ethics checklists — ensuring informed, voluntary agreement
701. Straight Line adaptations for professional settings — courts, negotiations, mediation
702. Anti-manipulation safeguards — distinguishing influence from undue pressure
703. Debrief and self-audit protocols — post-interaction improvement loops
704. Straight Line System failure modes — over-control, overscripting, tone mismatch
705. Cognitive overload avoidance — maintaining clarity over volume
706. Legal-risk awareness in persuasion — avoiding promises, guarantees, or misstatements
707. Straight Line system metrics — measuring certainty shifts and conversion points
708. Integration with logic-first argumentation — ensuring persuasion follows valid reasoning
709. Integration with judicial psychology — adapting control to authority-sensitive environments
710. Integration with NLP (computational) — language pattern analysis and optimization
711. Integration with neuro-linguistic programming — precision questioning and reframing checks
712. Court-safe persuasion translation — converting sales tactics into ethical advocacy methods
713. Straight Line–informed persuasion engine — structured, ethical influence module supporting negotiations, settlements, and first-impression advocacy without manipulation
System Safeguards, Ethics, and Governance Controls
Architectural features ensuring accuracy, UPL avoidance, retaliation resilience, and court legitimacy (many require attorney supervision).
714. Epistemic confidence scoring engine — quantifies factual, legal, and jurisdictional certainty for every assertion
715. Assertion provenance tracker — traces each claim to primary authority, evidence, or inference
716. Uncertainty language governor — enforces calibrated hedging to prevent false certainty
717. Reason-giving adequacy checker — validates that every conclusion has explicit warrants and backing
718. Arbitrary-and-capricious survivability test — stress-tests agency and judicial reasoning standards
719. Doctrine collision detector — flags conflicts (e.g., deference vs. due process) and recommends resolutions
720. Doctrine prioritization logic — predicts which doctrine courts will actually apply in context
721. Institutional defense playbook emulator — models DOJ/AG/municipal defense strategies and kill-zones
722. Government motion-pattern predictor — anticipates dismissal, abstention, and immunity tactics
723. Clerk-gatekeeping model — simulates staff attorney and clerk screening heuristics
724. Bench-memo likelihood scorer — estimates how arguments will be summarized for judges
725. Boilerplate detection and neutralization — counters canned dismissal language preemptively
726. Procedural rejection forecaster — predicts non-merits rejections (format, timing, service)
727. UPL real-time tripwire — live detection of unauthorized practice risk with auto-mitigation (attorney supervision required)
728. Sanctions risk predictor — flags Rule 11/§1927 exposure with corrective guidance
729. Ethics-compliance inserter — auto-adds disclaimers, scope limits, and review prompts
730. Attorney-needed escalation light — objective thresholds triggering counsel referral
731. Retaliation anticipation engine — forecasts SLAPPs, vexatious labels, bar complaints, and counters
732. Media mischaracterization risk model — predicts narrative attacks and prepares lawful responses
733. Protective sequencing planner — orders actions (agency → IG → court → media) for safety
734. Case-of-first-impression generator — identifies gaps and constructs text/structure/history arguments
735. Narrow-holding architect — crafts adoption-safe rules judges can accept
736. Precedent stress-test simulator — runs conservative/institutional/appellate scenarios
737. Floodgates-fear mitigator — reframes remedies to limit scope and calm courts
738. Appellate preservation auditor — ensures issues are preserved cleanly from the outset
739. Minimal-change overruling planner — designs incremental corrections to brittle precedent
740. Fact–rule mapping validator — confirms each element is supported by admissible facts
741. Evidence admissibility precheck — Daubert/Frye and foundation verification before filing
742. Timeline integrity engine — enforces chronological coherence and causation clarity
743. Jurisdictional viability scorer — standing, ripeness, mootness, and venue checks
744. Cognitive load governor — progressive disclosure to prevent overkill in filings
745. Judge-specific brevity optimizer — tailors length and emphasis to court norms
746. Ethical persuasion governor — enforces non-deceptive, non-coercive influence limits
747. Tone-matching engine — aligns cadence and diction to judicial preferences
748. Plain-language fallback — generates court-safe simplifications on demand
749. Counter-argument anticipation matrix — preempts strongest opposing points
750. Settlement posture optimizer — positions demands for credibility and leverage
751. Litigation finance readiness checker — packages cases to underwriting standards
752. Audit-log and explainability layer — court-facing transparency for AI-assisted drafting
753. Human-in-the-loop enforcement — mandatory review gates for high-risk outputs (attorney supervision required)
754. Adversarial red-teaming harness — probes for manipulation, bias, and hallucination
755. Source freshness and supersession monitor — auto-updates law and flags obsolescence
756. Conflict-of-interest detector — identifies disqualifying ties and recusal triggers
757. Data minimization and privacy guard — balances evidence preservation with compliance
758. Evidence capture compliance guide — mobile workflows for lawful recording and preservation
759. Interaction risk indicator — real-time cues for de-escalation and rights assertion
760. Procedural deadline autopilot — calendars, reminders, and tolling logic
761. Filing readiness checklist — final pre-submit validation across rules and norms
762. Post-filing monitoring — tracks docket signals and adapts strategy dynamically
763. Outcomes learning loop — feeds wins/losses back into models for continuous improvement
764. Governance and oversight framework — policies for accuracy, ethics, and accountability
765. Model risk management (MRM) controls — testing, versioning, rollback, and incident response
766. Court-legitimacy justification module — explains AI use within accepted legal norms
767. Member safety playbooks — guidance for retaliation resilience and well-being
768. Cross-jurisdiction harmonizer — reconciles divergent rules into coherent guidance
769. Expert handoff coordinator — seamless escalation to attorneys or specialists
770. Knowledge graph curator — maintains concept integrity across doctrines
771. Consistency checker across filings — prevents drift and contradiction over time
772. Decision rationale exporter — produces judge-ready explanations for each choice
773. System survivability dashboard — real-time health metrics for legal, ethical, and operational risk
CONFUSION, COMPLIANCE & COERCION DETECTION — TRAINING DATA SOURCES
773. Forensic Suggestibility & False Confession Research (Gudjonsson) foundational forensic literature on suggestibility, compliance, and false confession mechanisms.
774. False Confession Peer-Reviewed Corpora (Kassin, Drizin, Leo, Ofshe, et al.) validated research defining coercion pathways and confession contamination patterns.
775. Innocence Project Exoneration Case Archives (false confession subset) court-validated ground truth cases linking interrogation tactics to wrongful convictions.
776. Custodial Interrogation Video/Audio Libraries (public-domain + FOIA releases) multimodal training for pressure tactics, confusion cycles, and compliance markers.
777. Suppression Hearing Transcripts (voluntariness/disclosure issues) judicial reasoning datasets for coercion findings and due-process violations.
778. Miranda Waiver Validity Case Law Clusters benchmarks for comprehension, voluntariness, and coercive setting factors.
779. Totality of Circumstances” Voluntariness Doctrine Corpora (5th/14th Amend.) controlling legal tests for coercion, intimidation, deception, and impaired consent.
780. Reid Technique Materials + Scholarly Critiques baseline interrogation framework plus known coercion risk signatures.
781. PEACE Model Interview Doctrine (UK) + Evaluation Studies non-coercive comparator standard for identifying abusive deviation.
782. Police Training and Interview Room SOPs (where public/FOIA) policy baselines used to prove procedural violations and pattern abuse.
783. Custodial Interview Transcript Corpora (public cases) linguistic markers: contradictions, topic shifts, leading questions, and dependency cues.
784. Cognitive Load Theory Literature (Sweller and successors) validated overload indicators applicable to confusion-based persuasion claims.
785. Working Memory & Attention Capacity Research scientific support for cognitive disruption and impaired decision-making under pressure.
786. Discourse Coherence and Narrative Fragmentation Datasets detection of incoherence, contradiction density, and confusion markers.
787. Ambiguity & Vagueness Linguistics Research models for identifying materially confusing phrasing, scope ambiguity, and equivocation.
788. Readability / Syntactic Complexity Corpora (legal + general) objective measures for cognitive load scoring and comprehension risk.
789. Information Overload & Decision Fatigue Studies evidence base for reduced analytical capacity and increased compliance under load.
790. Topic-Shift / Interruption / Conversational Control Research quantifies disruption tactics that prevent sustained reasoning.
791. Stress, Sleep Deprivation, and Suggestibility Research scientifically grounded vulnerability amplifiers relevant to coercion evaluation.
792. Trauma-Informed Psychology Literature (consent impairment contexts) protects due process by identifying vulnerability without diagnosing.
793. Authority & Obedience Science (Milgram derivatives, modern replications) empirically grounded authority-cue compliance mechanisms.
794. Situational Power and Role Absorption Research (Zimbardo and successors) explains compliance escalation in institutional settings.
795. Coercive Persuasion Models (Edgar Schein and successors) confusion → dependency → compliance sequencing frameworks.
796. Thought Reform / Totalism Frameworks (Lifton and successors) “loading the language,” milieu control, and identity destabilization markers.
797. Compliance Psychology Principles (Cialdini and successors) authority, commitment, reciprocity, social proof (used as indicators, not conclusions).
798. Undue Influence Doctrine Scholarship (contracts/wills/confessions) bridges behavioral indicators to recognized legal elements.
799. Isolation/Dependency Psychology Research vulnerability modeling for coercive control environments.
800. Coercive Control Research (domestic/intimate partner contexts) structured coercion patterns applicable by analogy where legally relevant.
801. Propaganda Technique Taxonomies (public academic corpora) repetition, fear priming, false dichotomies, scapegoating, and narrative flooding.
802. Media Framing and Agenda-Setting Research validated models for engineered confusion and perception control.
803. Disinformation & Cognitive Security Research misinformation detection, authenticity gating, and manipulation indicators.
804. Algorithmic Amplification Studies (platform feed dynamics) engineered overload and tribal trigger mechanisms (pattern-based, not speculative).
805. Narrative Flooding / Firehose Models (public research) high-volume contradiction techniques associated with confusion induction.
806. Social Media Manipulation Case Studies (validated post-hoc investigations) documented campaigns used as pattern libraries with corroboration requirements.
807. Information Warfare Doctrine (public NATO/DoD sources) cognitive domain tactics and influence operations models (non-classified).
808. Psychological Operations (PSYOP/MISO) Public Doctrine influence planning primitives for detection and counter-analysis.
809. Cultic / High-Control Group Case Law (undue influence findings) judicially recognized coercion patterns in organizational environments.
810. Institutional Abuse Investigation Reports (public commissions/inquiries) documented coercion sequences and compliance enforcement methods.
811. Workplace Coercion & Retaliation Case Corpora authority-bound compliance patterns and escalation timelines.
812. Whistleblower Retaliation Narratives (validated findings + case law) pressure escalation and compliance enforcement patterns.
813. Human Trafficking Coercion Standards (as legal-analogy dataset) recognized psychological coercion concepts used for element mapping where applicable.
814. Coercion Pattern Libraries from Counseling/Forensic Practice (non-PII, de-identified) standardized pattern baselines for comparative tagging.
815. Behavioral Influence Ontologies (bias + compliance taxonomies) structured tagging framework for confusion, authority, and dependency cues.
816. Emotion Taxonomy Datasets (fear, reassurance, uncertainty, dependency) supports fractionation cycle detection with measurable markers.
817. Speech-Act Theory Corpora (commands, presuppositions, imperatives) detects control language and embedded assumptions.
818. Power-Distance Linguistics Research** — hierarchy signaling, normative framing, and deference language detection.
819. Deception/Evasion Linguistic Marker Research (indicator-only use) flags non-answers, deflection, and narrative instability without “truth claims.”
820. Conversation Analysis Datasets (turn-taking, dominance, interruption) quantifies conversational control tactics.
821. Prosody/Paralinguistics Research (stress indicators; consent-aware) audio cues supporting coercion indicators (never determinative).
822. Speaker Diarization + Transcript Alignment Standards ensures evidence integrity and correct speaker attribution for court exhibits.
823. Daubert/Frye Admissibility Standards + Judicial Critiques of Experts guardrails to prevent methodological overreach.
824. APA Forensic Psychology Guidelines & Reporting Standards expert-ready structure and ethical safeguards.
825. Expert Declaration and Affidavit Exemplars (court-accepted) formatting and language patterns that survive scrutiny.
826. Forensic Interviewing Standards (non-leading, trauma-informed) supports admissibility-safe interview practice analysis.
827. Evidence Packet Standards (foundation, authentication, chain-of-custody) links behavioral indicators to admissible exhibits.
828. Citation-Verified RAG Index Rules (authority-only grounding) ensures all coercion-element mappings cite controlling law or peer-reviewed science.
829. Informed Consent Doctrine Sources (civil + constitutional contexts) legal anchor for compromised consent analysis.
830. Professional Ethics Opinions (psychology + legal ethics) prevents coercive AI outputs and improper influence.
831. Non-Manipulative Persuasion Standards & Safeguards separates lawful persuasion from coercion in system design.
832. Human-in-the-Loop Review Protocols (high-stakes outputs) mandatory supervision gates for coercion claims and filings.
833. Audit Logging & Explainability Standards (behavioral inference transparency) court-facing defensibility of how indicators were generated.
834. Data Minimization + Privacy Compliance Sources (recording, biometrics where applicable) protects members while preserving evidentiary integrity.
GAME THEORY, STRATEGIC INTERACTION & MECHANISM DESIGN — AUTHORITATIVE TRAINING CORPUS ADDENDUM
(Continue numbering from #834)
Foundational Game Theory — Core Textbooks & Primary Sources
835. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior — John von Neumann & Oskar Morgenstern (1944)
• Foundational text establishing modern game theory
• Defines strategic games, expected utility, minimax theorem
• Introduces formal strategic rationality
• Required for equilibrium reasoning systems
836. Non-Cooperative Games — John Nash (1950)
• Original Nash equilibrium paper
• Defines equilibrium stability in strategic systems
• Essential for predicting adversarial and cooperative behavior
837. Game Theory — Drew Fudenberg & Jean Tirole
• Gold-standard graduate-level text
• Covers equilibrium refinement, signaling, repeated games
• Used in top economics, law, and strategy programs
838. A Course in Game Theory — Martin Osborne & Ariel Rubinstein
• Rigorous formal treatment of strategic interaction
• Covers rationality assumptions and equilibrium structures
839. An Introduction to Game Theory — Martin Osborne
• Comprehensive structured framework
• Covers complete, incomplete, and repeated games
Advanced Game Theory — Strategy, Adversarial Systems & Dynamic Games
840. Dynamic Noncooperative Game Theory — Tamer Başar & Geert Jan Olsder
• Dynamic strategic systems modeling
• Used in AI, military, and control systems
841. Recursive Methods in Economic Dynamics — Nancy Stokey & Robert Lucas
• Dynamic programming and strategic optimization
• Critical for modeling sequential decision systems
842. Algorithmic Game Theory — Nisan, Roughgarden, Tardos, Vazirani
• Core text connecting game theory to AI and computational systems
• Used in mechanism design and distributed coordination
843. Multiagent Systems — Yoav Shoham & Kevin Leyton-Brown
• Strategic agent interaction
• Foundations for AI swarm coordination
Mechanism Design — Strategic Incentive Engineering
Mechanism design is the inverse of game theory, designing systems so rational actors produce desired outcomes through incentive structures.
844. Microeconomic Theory — Andreu Mas-Colell, Whinston, Green
• Definitive graduate-level economics and mechanism design text
845. Mechanism Design: A Linear Programming Approach — Rakesh Vohra
846. The Theory of Incentives — Jean-Jacques Laffont & David Martimort
847. Auction Theory — Vijay Krishna
848. Mechanism Design and Approximation — Jason Hartline
Game Theory Applied to Law & Legal Systems
Strategic litigation, settlement, deterrence, and enforcement systems follow game-theoretic dynamics.
849. Game Theory and the Law — Douglas Baird, Robert Gertner, Randal Picker
850. Economic Analysis of Law — Richard Posner
851. The Limits of Litigation — Owen Fiss
852. Litigation and Settlement in Strategic Perspective — Robert Cooter
Negotiation Theory — Strategic Interaction & Settlement Dynamics
853. The Strategy of Conflict — Thomas Schelling
• Nobel Prize winning foundational negotiation theory
854. Bargaining Theory with Applications — Abhinay Muthoo
855. Negotiation Analysis — Howard Raiffa
856. Getting to Yes — Fisher & Ury
Evolutionary Game Theory — Strategic Behavior in Adaptive Systems
Evolutionary game theory models adaptation and long-term strategic equilibrium.
857. Evolution and the Theory of Games — John Maynard Smith
858. Evolutionary Game Theory — Jörgen Weibull
859. Evolutionary Dynamics — Martin Nowak
Signaling Theory — Strategic Communication & Information Asymmetry
Strategic communication and deception detection rely heavily on signaling theory.
860. Signaling Games and Stable Equilibria — Kreps & Wilson
861. Games and Information — Eric Rasmusen
862. Information Economics and Policy — Joseph Stiglitz
Repeated Games, Reputation, and Deterrence Systems
Repeated interactions create reputation-based equilibria critical for legal deterrence.
863. Repeated Games and Reputations — Mailath & Samuelson
864. The Folk Theorem in Repeated Games — Aumann
Cooperative Game Theory — Coalitions, Collective Action & Swarm Strategy
865. Cooperative Game Theory — Peleg & Sudhölter
866. Values and Bargaining — Lloyd Shapley
• Shapley value calculation
• Coalition power modeling
Game Theory in AI and Autonomous Strategic Systems
Game theory is fundamental to modern AI coordination, adversarial modeling, and decision intelligence.
867. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction — Sutton & Barto
868. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach — Russell & Norvig
869. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning — Busoniu et al.
870. Deep Reinforcement Learning Hands-On — Maxim Lapan
Military Strategy, War Theory, and Strategic Conflict Modeling
Game theory is foundational to military doctrine, deterrence theory, and conflict modeling.
871. On War — Carl von Clausewitz
872. Strategy — B.H. Liddell Hart
873. The Art of Strategy — Dixit & Nalebuff
874. The Evolution of Cooperation — Robert Axelrod
Adversarial Strategy, Deception, and Strategic Dominance
875. Thinking Strategically — Dixit & Nalebuff
876. Competitive Strategy — Michael Porter
877. Strategy: A History — Lawrence Freedman
Mechanism Design in Governance, Law, and Institutional Systems
Institutional design governs behavior through incentives.
878. Governing the Commons — Elinor Ostrom
879. The Calculus of Consent — Buchanan & Tullock
Strategic Decision Intelligence Applications Enabled by This Corpus
This game theory corpus enables Mega-Bot to perform:
• Adversarial legal strategy prediction
• Settlement likelihood modeling
• Prosecutor, judge, and defense strategic analysis
• Litigation escalation modeling
• Swarm coordination optimization
• Incentive design for compliance and deterrence
• Reputation-based enforcement modeling
• Negotiation optimization
• Coalition formation and collective action strategy
• Strategic risk prediction
• Procedural escalation timing optimization
Section Z —Strategic Litigation Warfare, Procedural Leverage, and Unconventional Legal Strategy Corpus
(880-3000)
880. The Calculus of Consent — Buchanan & Tullock
881. The Art of Cross-Examination — Francis L. Wellman
882. Criminal Defense Tools and Techniques — Thomas J. Farrell
883. McElhaney’s Trial Notebook — James McElhaney
884. Trial Techniques — Thomas Mauet
885. Rules of the Road — Rick Friedman & Patrick Malone
886. Reptile: The 2009 Manual of the Plaintiff’s Revolution — David Ball & Don Keenan
887. The Way of the Lawyer — Chris Graham
888. Commercial Litigation Strategies — Thomson Reuters
889. Strategic Litigation Toolkit — Digital Freedom Fund
890. Deconstructing Legal Analysis — Peter T. Wendel
891. Fundamentals of Litigation Practice — Jeffrey Stempel
892. Thinking, Fast and Slow — Daniel Kahneman
893. The Poker-Litigation Game — Daughety & Reinganum
894. Blackstone’s Criminal Practice — Blackstone Press
895. Strategic Litigation — Yale Law School
896. Strategic Litigation — Stanford Law School
897. Litigation and Judicial Process — Georgetown Law
898. Federal Bar Association Litigation CLE Training
899. Lawline Litigation Skills Training
900. The Art of Negotiation — Michael Wheeler
901. How David Beats Goliath — Michael Swanson
902. Trial Advocacy — American Bar Association
903. Advanced Trial Advocacy — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
904. Winning at Trial — Herbert Stern
905. Cross-Examination: Science and Techniques — Larry Pozner
906. Mastering Voir Dire — Jeffrey Kinsler
907. Persuasion: The Art of Advocacy — Noah Messing
908. Modern Trial Advocacy — Steven Lubet
909. Winning Trial Advocacy — Thomas Melsheimer
910. Making Your Case — Antonin Scalia & Bryan Garner
911. The Winning Brief — Bryan Garner
912. Legal Writing in Plain English — Bryan Garner
913. On Writing Well — William Zinsser
914. The Bramble Bush — Karl Llewellyn
915. The Nature of the Judicial Process — Benjamin Cardozo
916. The Federalist Papers — Hamilton, Madison, Jay
917. Commentaries on the Laws of England — William Blackstone
918. A Treatise on Constitutional Limitations — Thomas Cooley
919. The Common Law — Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr.
920. Law and Revolution — Harold Berman
921. The Path of the Law — Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr.
922. The Supreme Court — William Rehnquist
923. The Rule of Law — Tom Bingham
924. Judicial Process in America — Robert Carp
925. Judicial Behavior and Decision Making — Lawrence Baum
926. Federal Courts — Richard Fallon
927. Civil Procedure — Jack Friedenthal
928. Federal Practice and Procedure — Wright & Miller
929. Moore’s Federal Practice — Moore
930. American Jurisprudence (AmJur)
931. Corpus Juris Secundum (CJS)
932. Restatement of the Law — American Law Institute
933. Restatement (Second) of Judgments — American Law Institute
934. Restatement (Second) of Torts — American Law Institute
935. Restatement (Second) of Contracts — American Law Institute
936. Federal Rules of Civil Procedure
937. Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure
938. Federal Rules of Evidence
939. United States Code — Title 28
940. United States Code — Title 42
941. United States Code — Title 18
942. United States Constitution
943. State Constitutions — All 50 States
944. Federal Judicial Center Litigation Manuals
945. DOJ Criminal Resource Manual
946. DOJ Civil Rights Litigation Handbook
947. DOJ Federal Prosecution Guidelines
948. DOJ Civil Division Litigation Manuals
949. Federal Habeas Corpus Practice and Procedure — Randy Hertz
950. Postconviction Remedies — Donald Wilkes
951. Habeas Corpus — Brandon Garrett
952. Federal Habeas Corpus Practice Guide — LexisNexis
953. Mandamus and Prohibition — High Court Practice
954. Extraordinary Writ Practice — Federal Appellate Procedure
955. Supreme Court Practice — Stern & Gressman
956. Appellate Practice and Procedure — Federal Judicial Center
957. Federal Appellate Practice — Mayer Brown
958. Winning on Appeal — Ruggero Aldisert
959. The Art of Advocacy — Lloyd Paul Stryker
960. Trial by Jury — Lysander Spooner
961. Jury Selection Strategy and Science — Jeffrey Frederick
962. Jury Psychology — Reid Hastie
963. The Jury and Democracy — Stephen Landsman
964. Jury Decision Making — Valerie Hans
965. Expert Witness Preparation — SEAK Inc.
966. Litigation Support Handbook — Federal Judicial Center
967. Discovery Practice — Federal Judicial Center
968. Electronic Discovery — Shira Scheindlin
969. Evidence — Christopher Mueller
970. Scientific Evidence — Federal Judicial Center
971. Qualified Immunity Litigation — Federal Judicial Center
972. Civil Rights Litigation Handbook — Nahmod
973. Section 1983 Litigation — Martin Schwartz
974. Police Misconduct Litigation — Michael Avery
975. Constitutional Torts — Sheldon Nahmod
976. Federal Civil Rights Acts — Rodney Smolla
977. Civil Rights and Civil Liberties Litigation — Sheldon Nahmod
978. Litigation Under Section 1983 — Michael Avery
979. Constitutional Litigation — Chemerinsky
980. Constitutional Law — Erwin Chemerinsky
981. Federal Jurisdiction — Erwin Chemerinsky
982. Federal Courts and the Law of Federal-State Relations — Redish
983. Civil Procedure — Erwin Chemerinsky
984. Federal Civil Procedure — Richard Freer
985. Litigation Strategy — James Publishing
986. Litigation Tactics — Trial Guides
987. Trial Handbook — American Bar Association
988. Litigation Manual — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
989. Trial Strategy Library — Trial Guides
990. Strategic Litigation Manual — Digital Freedom Fund
991. Litigation Psychology — Trial Guides
992. Advanced Cross-Examination Techniques — SEAK Inc.
993. Expert Witness Training Manuals — SEAK Inc.
994. Federal Grand Jury Practice — Sara Sun Beale
995. Grand Jury Law and Practice — Wayne LaFave
996. Criminal Procedure — Wayne LaFave
997. Search and Seizure — Wayne LaFave
998. Constitutional Criminal Procedure — Yale Kamisar
999. Criminal Procedure — Joshua Dressler
1000. Criminal Law — Wayne LaFave
1111. Federal Courts and the Law of Federal-State Relations — Peter Low
1112. Federal Courts — Richard Fallon
1113. Federal Jurisdiction — Erwin Chemerinsky
1114. Federal Courts — Charles Alan Wright
1115. Jurisdiction in Civil Actions — Robert Casad
1116. Jurisdiction and Procedure — Geoffrey Hazard
1117. Conflict of Laws — Joseph Story
1118. Conflict of Laws — Eugene Scoles
1119. Federal Practice Digest — West Publishing
1120. Supreme Court Reporter — West Publishing
1121. Federal Reporter — West Publishing
1122. Federal Supplement — West Publishing
1123. United States Reports — U.S. Supreme Court
1124. Lawyers’ Edition — LexisNexis
1125. American Law Reports (ALR) — Thomson Reuters
1126. ALR Federal — Thomson Reuters
1127. Federal Rules Decisions — West Publishing
1128. Federal Practice Forms — West Publishing
1129. Federal Procedure Forms — LexisNexis
1130. Bender’s Federal Practice Forms — LexisNexis
1131. Pattern Jury Instructions — Federal Judicial Center
1132. Pattern Jury Instructions — American Bar Association
1133. Pattern Criminal Jury Instructions — Federal Judicial Center
1134. Model Penal Code — American Law Institute
1135. Model Rules of Professional Conduct — American Bar Association
1136. Code of Judicial Conduct — American Bar Association
1137. Judicial Conduct and Disability Act Materials — Federal Judicial Center
1138. Judicial Ethics Manual — Federal Judicial Center
1139. Judicial Disqualification Guide — Federal Judicial Center
1140. Judicial Discipline and Removal — Federal Judicial Center
1141. Judicial Accountability Handbook — American Judicature Society
1142. Judicial Independence and Accountability — American Judicature Society
1143. Judicial Misconduct Procedures — U.S. Courts
1144. Federal Judicial Discipline Procedures — Administrative Office of U.S. Courts
1145. Federal Judicial Center Judicial Writing Manual
1146. Federal Judicial Center Litigation Management Manual
1147. Federal Judicial Center Case Management Procedures
1148. Federal Judicial Center Civil Litigation Management Manual
1149. Federal Judicial Center Criminal Case Management Manual
1150. Federal Judicial Center Appellate Case Management Manual
1151. DOJ Civil Division Litigation Manual
1152. DOJ Criminal Division Litigation Manual
1153. DOJ Federal Prosecution Principles
1154. DOJ United States Attorneys’ Manual
1155. DOJ Justice Manual
1156. DOJ Civil Rights Division Manual
1157. DOJ Grand Jury Practice Manual
1158. DOJ Criminal Trial Manual
1159. DOJ Federal Evidence Manual
1160. DOJ Appellate Manual
1161. Harvard Law Review
1162. Yale Law Journal
1163. Columbia Law Review
1164. Stanford Law Review
1165. University of Chicago Law Review
1166. Georgetown Law Journal
1167. UCLA Law Review
1168. Michigan Law Review
1169. Virginia Law Review
1170. Cornell Law Review
1171. Litigation Strategy — Harvard Law School
1172. Trial Advocacy — Harvard Law School
1173. Appellate Advocacy — Harvard Law School
1174. Litigation Strategy — Yale Law School
1175. Trial Advocacy — Yale Law School
1176. Strategic Litigation — Yale Law School
1177. Litigation Strategy — Stanford Law School
1178. Trial Advocacy — Stanford Law School
1179. Litigation Strategy — Columbia Law School
1180. Trial Advocacy — Columbia Law School
1181. Litigation Strategy and Planning — ABA
1182. Trial Advocacy Manual — ABA
1183. Litigation Handbook — ABA
1184. Civil Litigation Handbook — ABA
1185. Criminal Litigation Handbook — ABA
1186. Appellate Advocacy Manual — ABA
1187. Federal Practice Handbook — ABA
1188. Trial Strategy Manual — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1189. Trial Advocacy Training — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1190. Litigation Skills Training Manual — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1191. Trial Guides Litigation Library
1192. Litigation Strategy Library — Trial Guides
1193. Trial Advocacy Library — Trial Guides
1194. Cross-Examination Strategy — Trial Guides
1195. Voir Dire Strategy — Trial Guides
1196. Litigation Psychology — Trial Guides
1197. Jury Persuasion Strategy — Trial Guides
1198. Litigation Tactics Manual — Trial Guides
1199. Advanced Litigation Techniques — Trial Guides
1200. Litigation Warfare Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1201. Federal Civil Procedure Litigation Guide — Thomson Reuters
1202. Federal Criminal Procedure Litigation Guide — Thomson Reuters
1203. Federal Evidence Litigation Guide — Thomson Reuters
1204. Federal Appellate Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1205. Federal Habeas Corpus Guide — Thomson Reuters
1206. Federal Civil Rights Litigation Guide — Thomson Reuters
1207. Federal Judicial Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1208. Federal Court Litigation Guide — Thomson Reuters
1209. Federal Trial Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1210. Federal Litigation Forms — Thomson Reuters
1211. Westlaw Litigation Practice Guides
1212. Westlaw Federal Practice Guides
1213. Westlaw Litigation Strategy Guides
1214. Westlaw Trial Practice Guides
1215. Westlaw Appellate Practice Guides
1216. Westlaw Civil Rights Litigation Guides
1217. Westlaw Federal Evidence Guides
1218. Westlaw Criminal Practice Guides
1219. Westlaw Federal Jurisdiction Guides
1220. Westlaw Litigation Skills Guides
1221. LexisNexis Litigation Practice Guides
1222. LexisNexis Federal Practice Guides
1223. LexisNexis Trial Practice Guides
1224. LexisNexis Appellate Practice Guides
1225. LexisNexis Federal Evidence Guides
1226. LexisNexis Criminal Practice Guides
1227. LexisNexis Civil Rights Litigation Guides
1228. LexisNexis Litigation Strategy Guides
1229. LexisNexis Federal Jurisdiction Guides
1230. LexisNexis Litigation Skills Guides
1231. Federal Judicial Center Litigation Training Programs
1232. Federal Judicial Center Trial Training Programs
1233. Federal Judicial Center Appellate Training Programs
1234. Federal Judicial Center Evidence Training Programs
1235. Federal Judicial Center Judicial Ethics Training Programs
1236. Federal Judicial Center Case Management Training Programs
1237. Federal Judicial Center Civil Litigation Training Programs
1238. Federal Judicial Center Criminal Litigation Training Programs
1239. Federal Judicial Center Habeas Corpus Training Programs
1240. Federal Judicial Center Civil Rights Litigation Training Programs
1241. National Judicial College Litigation Training
1242. National Judicial College Trial Training
1243. National Judicial College Judicial Ethics Training
1244. National Judicial College Case Management Training
1245. National Judicial College Appellate Training
1246. National Judicial College Evidence Training
1247. National Judicial College Judicial Accountability Training
1248. National Judicial College Judicial Decision Making Training
1249. National Judicial College Litigation Strategy Training
1250. National Judicial College Judicial Independence Training
1251. Harvard Law Litigation Training
1252. Yale Law Litigation Training
1253. Stanford Law Litigation Training
1254. Columbia Law Litigation Training
1255. University of Chicago Law Litigation Training
1256. Georgetown Law Litigation Training
1257. NYU Law Litigation Training
1258. UCLA Law Litigation Training
1259. Michigan Law Litigation Training
1260. Virginia Law Litigation Training
1261. Civil Rights Litigation Clearinghouse
1262. Federal Court Opinions Database
1263. Supreme Court Opinions Database
1264. Federal Appellate Opinions Database
1265. Federal District Court Opinions Database
1266. State Supreme Court Opinions Database
1267. State Appellate Opinions Database
1268. State Trial Court Opinions Database
1269. Westlaw Case Law Database
1270. LexisNexis Case Law Database
1271. United States Constitution
1272. Federal Rules of Civil Procedure
1273. Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure
1274. Federal Rules of Evidence
1275. United States Code Title 28
1276. United States Code Title 42
1277. United States Code Title 18
1278. United States Code Title 5
1279. United States Code Title 15
1280. United States Code Title 50
1281. State Civil Procedure Codes
1282. State Criminal Procedure Codes
1283. State Evidence Codes
1284. State Civil Rights Statutes
1285. State Judicial Conduct Codes
1286. State Professional Conduct Rules
1287. State Appellate Procedure Rules
1288. State Trial Procedure Rules
1289. State Habeas Corpus Statutes
1290. State Judicial Discipline Procedures
1291. American Bar Association Litigation Resources
1292. American Bar Association Trial Advocacy Resources
1293. American Bar Association Civil Rights Resources
1294. American Bar Association Appellate Advocacy Resources
1295. American Bar Association Criminal Law Resources
1296. American Bar Association Evidence Resources
1297. American Bar Association Judicial Ethics Resources
1298. American Bar Association Litigation Strategy Resources
1299. American Bar Association Legal Writing Resources
1300. American Bar Association Legal Research Resources
1301. Litigation Strategy and Practice — American Bar Association
1302. Advanced Litigation Skills — American Bar Association
1303. Federal Litigation Practice Manual — American Bar Association
1304. Trial Advocacy Skills Training — American Bar Association
1305. Appellate Advocacy Training Manual — American Bar Association
1306. Civil Litigation Strategy Guide — American Bar Association
1307. Criminal Litigation Strategy Guide — American Bar Association
1308. Evidence Strategy and Practice — American Bar Association
1309. Litigation Ethics and Professional Responsibility — American Bar Association
1310. Federal Court Litigation Forms — American Bar Association
1311. Federal Litigation Handbook — Thomson Reuters
1312. Federal Court Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1313. Federal Trial Handbook — Thomson Reuters
1314. Federal Evidence Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1315. Federal Criminal Litigation Guide — Thomson Reuters
1316. Federal Appellate Litigation Guide — Thomson Reuters
1317. Federal Habeas Corpus Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1318. Federal Civil Rights Litigation Guide — Thomson Reuters
1319. Federal Judicial Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1320. Federal Procedural Forms and Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1321. Litigation Strategy and Tactics — West Publishing
1322. Federal Practice Digest — West Publishing
1323. Federal Civil Procedure Forms — West Publishing
1324. Federal Criminal Procedure Forms — West Publishing
1325. Federal Evidence Forms — West Publishing
1326. Federal Appellate Procedure Forms — West Publishing
1327. Federal Habeas Corpus Forms — West Publishing
1328. Civil Rights Litigation Forms — West Publishing
1329. Federal Court Motion Practice Guide — West Publishing
1330. Federal Litigation Pleading Forms — West Publishing
1331. Advanced Trial Advocacy Techniques — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1332. Trial Advocacy Training Manual — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1333. Litigation Skills and Strategy Training — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1334. Courtroom Advocacy Training Manual — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1335. Advanced Cross-Examination Techniques — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1336. Voir Dire Strategy and Practice — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1337. Litigation Strategy Workshop Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1338. Federal Trial Practice Training — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1339. Criminal Defense Advocacy Training — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1340. Civil Litigation Advocacy Training — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1341. Federal Judicial Center Litigation Manual
1342. Federal Judicial Center Civil Procedure Manual
1343. Federal Judicial Center Criminal Procedure Manual
1344. Federal Judicial Center Evidence Manual
1345. Federal Judicial Center Appellate Practice Manual
1346. Federal Judicial Center Habeas Corpus Manual
1347. Federal Judicial Center Civil Rights Litigation Manual
1348. Federal Judicial Center Judicial Ethics Manual
1349. Federal Judicial Center Case Management Manual
1350. Federal Judicial Center Judicial Writing Manual
1351. United States Attorneys’ Criminal Resource Manual
1352. United States Attorneys’ Civil Resource Manual
1353. DOJ Trial Advocacy Training Materials
1354. DOJ Appellate Advocacy Training Materials
1355. DOJ Grand Jury Training Manual
1356. DOJ Criminal Investigation Manual
1357. DOJ Federal Prosecution Manual
1358. DOJ Litigation Strategy Manual
1359. DOJ Civil Rights Enforcement Manual
1360. DOJ Judicial Procedure Manual
1361. Supreme Court Advocacy Guide — American Bar Association
1362. Supreme Court Litigation Handbook — Thomson Reuters
1363. Supreme Court Practice Manual — West Publishing
1364. Supreme Court Brief Writing Guide — American Bar Association
1365. Supreme Court Oral Argument Guide — American Bar Association
1366. Supreme Court Rules and Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1367. Supreme Court Jurisdiction Practice Guide — West Publishing
1368. Supreme Court Appellate Strategy Guide — Thomson Reuters
1369. Supreme Court Litigation Strategy Manual — American Bar Association
1370. Supreme Court Procedure Handbook — Federal Judicial Center
1371. Civil Rights Litigation Strategy Manual — American Bar Association
1372. Constitutional Litigation Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1373. Section 1983 Litigation Practice Guide — West Publishing
1374. Federal Civil Rights Enforcement Manual — DOJ
1375. Civil Rights Litigation Handbook — Federal Judicial Center
1376. Police Misconduct Litigation Guide — American Bar Association
1377. Federal Civil Rights Practice Manual — Thomson Reuters
1378. Civil Rights Litigation Strategy Workshop Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1379. Civil Rights Litigation Advocacy Manual — American Bar Association
1380. Civil Rights Enforcement Practice Guide — West Publishing
1381. Federal Appellate Practice and Procedure Manual — American Bar Association
1382. Federal Appeals Strategy Guide — Thomson Reuters
1383. Federal Appeals Practice Handbook — West Publishing
1384. Appellate Advocacy Training Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1385. Federal Appeals Litigation Strategy Guide — American Bar Association
1386. Federal Appeals Brief Writing Guide — American Bar Association
1387. Federal Appeals Oral Argument Guide — American Bar Association
1388. Federal Appeals Jurisdiction Practice Guide — West Publishing
1389. Federal Appeals Procedure Manual — Federal Judicial Center
1390. Federal Appeals Litigation Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1391. Federal Habeas Corpus Litigation Strategy Manual — American Bar Association
1392. Federal Habeas Corpus Practice Guide — West Publishing
1393. Habeas Corpus Advocacy Training Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1394. Habeas Corpus Litigation Handbook — Thomson Reuters
1395. Habeas Corpus Procedure Manual — Federal Judicial Center
1396. Habeas Corpus Brief Writing Guide — American Bar Association
1397. Habeas Corpus Litigation Forms — West Publishing
1398. Habeas Corpus Advocacy Practice Guide — American Bar Association
1399. Habeas Corpus Litigation Strategy Guide — Thomson Reuters
1400. Habeas Corpus Procedure and Practice Manual — Federal Judicial Center
1401. Litigation Psychology and Persuasion — American Bar Association
1402. Courtroom Persuasion Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1403. Jury Persuasion Handbook — American Bar Association
1404. Trial Psychology Practice Guide — Trial Guides
1405. Jury Decision Making Research Materials — Federal Judicial Center
1406. Witness Examination Strategy Manual — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1407. Cross-Examination Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1408. Voir Dire Strategy Handbook — Trial Guides
1409. Witness Preparation Guide — American Bar Association
1410. Trial Persuasion Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1411. Federal Court Motion Practice Manual — American Bar Association
1412. Motion Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1413. Federal Motion Practice Handbook — West Publishing
1414. Motion Practice Training Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1415. Federal Pleading and Motion Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1416. Federal Motion Practice Forms — West Publishing
1417. Motion Practice Advocacy Manual — American Bar Association
1418. Federal Motion Practice Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1419. Federal Motion Practice Litigation Manual — Federal Judicial Center
1420. Federal Motion Practice Procedure Guide — Thomson Reuters
1421. Litigation Ethics Practice Guide — American Bar Association
1422. Professional Responsibility Manual — American Bar Association
1423. Legal Ethics Practice Guide — Thomson Reuters
1424. Legal Ethics Handbook — West Publishing
1425. Judicial Ethics Practice Guide — Federal Judicial Center
1426. Attorney Discipline Practice Guide — American Bar Association
1427. Legal Ethics Training Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1428. Professional Responsibility Training Manual — American Bar Association
1429. Legal Ethics Litigation Manual — Thomson Reuters
1430. Professional Conduct Practice Guide — West Publishing
1431. Federal Jurisdiction Practice Guide — American Bar Association
1432. Federal Jurisdiction Handbook — Thomson Reuters
1433. Federal Jurisdiction Manual — West Publishing
1434. Federal Jurisdiction Training Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1435. Federal Jurisdiction Litigation Strategy Guide — American Bar Association
1436. Federal Jurisdiction Procedure Manual — Federal Judicial Center
1437. Federal Jurisdiction Advocacy Guide — American Bar Association
1438. Federal Jurisdiction Litigation Forms — West Publishing
1439. Federal Jurisdiction Practice Manual — Thomson Reuters
1440. Federal Jurisdiction Litigation Handbook — American Bar Association
1441. Litigation Case Strategy Guide — American Bar Association
1442. Case Strategy Practice Manual — Thomson Reuters
1443. Case Strategy Handbook — West Publishing
1444. Case Strategy Training Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1445. Litigation Case Planning Manual — American Bar Association
1446. Litigation Case Management Guide — Federal Judicial Center
1447. Case Strategy Advocacy Guide — American Bar Association
1448. Case Strategy Litigation Forms — West Publishing
1449. Case Strategy Procedure Guide — Thomson Reuters
1450. Case Strategy Litigation Manual — American Bar Association
1451. Federal Court Advocacy Guide — American Bar Association
1452. Federal Court Practice Manual — Thomson Reuters
1453. Federal Court Litigation Handbook — West Publishing
1454. Federal Court Advocacy Training Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1455. Federal Court Procedure Manual — Federal Judicial Center
1456. Federal Court Advocacy Practice Guide — American Bar Association
1457. Federal Court Litigation Forms — West Publishing
1458. Federal Court Litigation Strategy Guide — Thomson Reuters
1459. Federal Court Litigation Manual — American Bar Association
1460. Federal Court Procedure Guide — Federal Judicial Center
1461. Trial Advocacy Strategy Guide — American Bar Association
1462. Trial Advocacy Practice Manual — Thomson Reuters
1463. Trial Advocacy Handbook — West Publishing
1464. Trial Advocacy Training Materials — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1465. Trial Advocacy Procedure Manual — Federal Judicial Center
1466. Trial Advocacy Litigation Forms — West Publishing
1467. Trial Advocacy Litigation Strategy Guide — Thomson Reuters
1468. Trial Advocacy Litigation Manual — American Bar Association
1469. Trial Advocacy Procedure Guide — Federal Judicial Center
1470. Trial Advocacy Practice Guide — American Bar Association
1471. Litigation Warfare Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1472. Advanced Litigation Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1473. Litigation Leverage Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1474. Litigation Pressure Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1475. Litigation Escalation Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1476. Litigation Control Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1477. Litigation Dominance Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1478. Litigation Tactical Advantage Manual — Trial Guides
1479. Litigation Procedural Advantage Guide — Trial Guides
1480. Litigation Strategic Advantage Manual — Trial Guides
1481. Litigation Decision Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1482. Litigation Outcome Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1483. Litigation Persuasion Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1484. Litigation Psychological Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1485. Litigation Influence Strategy Manual — Trial Guides
1486. Litigation Tactical Planning Manual — Trial Guides
1487. Litigation Strategic Planning Guide — Trial Guides
1488. Litigation Case Domination Manual — Trial Guides
1489. Litigation Procedural Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1490. Litigation Tactical Execution Manual — Trial Guides
1491. Strategic Litigation Doctrine Manual — Trial Guides
1492. Strategic Litigation Practice Guide — Trial Guides
1493. Strategic Litigation Procedure Manual — Trial Guides
1494. Strategic Litigation Litigation Forms — Trial Guides
1495. Strategic Litigation Litigation Strategy Guide — Trial Guides
1496. Strategic Litigation Litigation Manual — Trial Guides
1497. Strategic Litigation Procedure Guide — Trial Guides
1498. Strategic Litigation Practice Manual — Trial Guides
1499. Strategic Litigation Tactical Manual — Trial Guides
1500. Strategic Litigation Warfare Doctrine Corpus — Mega Lawfare AI Corpus
1501. Supreme Court Practice — Eugene Gressman
1502. Federal Courts — Richard Fallon
1503. Federal Jurisdiction — Erwin Chemerinsky
1504. Federal Practice and Procedure — Wright & Miller
1505. Moore’s Federal Practice — Moore
1506. Weinstein’s Federal Evidence — Weinstein
1507. Evidence Under the Federal Rules — Mueller & Kirkpatrick
1508. Federal Trial Objections — O’Malley
1509. Appellate Practice Compendium — ABA
1510. Winning on Appeal — Ruggero Aldisert
1511. Trial Techniques — Thomas Mauet
1512. Modern Trial Advocacy — Steven Lubet
1513. Cross-Examination: Science and Techniques — Pozner & Dodd
1514. The Art of Cross-Examination — Francis Wellman
1515. McElhaney’s Trial Notebook — James McElhaney
1516. Trial Advocacy — National Institute for Trial Advocacy
1517. Federal Trial Handbook — Thomson Reuters
1518. Trial Practice Guide — West Publishing
1519. Litigation Strategy Guide — ABA
1520. Litigation Skills Handbook — ABA
1521. Civil Procedure — Friedenthal
1522. Civil Procedure — Freer
1523. Civil Procedure — Glannon
1524. Federal Rules of Civil Procedure Manual — Thomson Reuters
1525. Federal Rules of Evidence Manual — Saltzburg
1526. Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure Manual — Thomson Reuters
1527. Federal Appellate Practice Manual — ABA
1528. Federal Courtroom Evidence — LexisNexis
1529. Federal Court Litigation Forms — West
1530. Federal Pleading Practice Guide — West
1531. Restatement (Second) of Judgments — American Law Institute
1532. Restatement (Second) of Torts — American Law Institute
1533. Restatement (Second) of Contracts — American Law Institute
1534. Restatement (Third) of Agency — American Law Institute
1535. Restatement (Third) of Restitution — American Law Institute
1536. American Jurisprudence (AmJur)
1537. Corpus Juris Secundum (CJS)
1538. Federal Reporter Series — West
1539. United States Reports — Supreme Court
1540. Supreme Court Reporter — West
1541. DOJ Criminal Resource Manual
1542. DOJ Justice Manual
1543. DOJ Federal Prosecution Principles
1544. DOJ Civil Rights Litigation Handbook
1545. DOJ Trial Advocacy Manual
1546. DOJ Appellate Advocacy Manual
1547. DOJ Grand Jury Practice Manual
1548. DOJ Evidence Practice Guide
1549. DOJ Litigation Strategy Guide
1550. DOJ Federal Court Practice Manual
1551. Federal Judicial Center Manual on Complex Litigation
1552. Federal Judicial Center Judicial Writing Manual
1553. Federal Judicial Center Case Management Manual
1554. Federal Judicial Center Evidence Manual
1555. Federal Judicial Center Trial Management Manual
1556. Federal Judicial Center Civil Litigation Guide
1557. Federal Judicial Center Criminal Litigation Guide
1558. Federal Judicial Center Habeas Corpus Guide
1559. Federal Judicial Center Appellate Practice Guide
1560. Federal Judicial Center Judicial Ethics Guide
1561. Section 1983 Litigation — Martin Schwartz
1562. Civil Rights Litigation — Nahmod
1563. Constitutional Law — Chemerinsky
1564. Constitutional Litigation — Chemerinsky
1565. Police Misconduct Litigation — Avery
1566. Federal Civil Rights Acts — Smolla
1567. Civil Rights and Civil Liberties Litigation — Nahmod
1568. Qualified Immunity Doctrine — Federal Judicial Center
1569. Judicial Immunity Doctrine — Federal Judicial Center
1570. Federal Civil Rights Litigation Guide — ABA
1571. Grand Jury Law and Practice — LaFave
1572. Federal Grand Jury Practice — Sara Sun Beale
1573. Criminal Procedure — LaFave
1574. Constitutional Criminal Procedure — Kamisar
1575. Criminal Procedure — Dressler
1576. Search and Seizure — LaFave
1577. Federal Habeas Corpus Practice — Hertz & Liebman
1578. Habeas Corpus Litigation Manual — LexisNexis
1579. Extraordinary Writ Practice Guide — ABA
1580. Mandamus and Prohibition Practice Guide — West
1581. The Federalist Papers — Hamilton, Madison, Jay
1582. Commentaries on the Laws of England — Blackstone
1583. Commentaries on American Law — Kent
1584. The Common Law — Oliver Wendell Holmes
1585. The Path of the Law — Oliver Wendell Holmes
1586. The Nature of the Judicial Process — Cardozo
1587. A Treatise on Constitutional Limitations — Cooley
1588. Law and Revolution — Harold Berman
1589. Judicial Process in America — Carp
1590. Judicial Behavior and Decision Making — Baum
1591. Harvard Law Review
1592. Yale Law Journal
1593. Columbia Law Review
1594. Stanford Law Review
1595. University of Chicago Law Review
1596. Georgetown Law Journal
1597. Michigan Law Review
1598. Virginia Law Review
1599. Cornell Law Review
1600. UCLA Law Review
1601. Northwestern University Law Review
1602. Duke Law Journal
1603. California Law Review
1604. Texas Law Review
1605. Minnesota Law Review
1606. Boston University Law Review
1607. Fordham Law Review
1608. George Washington Law Review
1609. Emory Law Journal
1610. Notre Dame Law Review
1611. Federal Courts Law Review
1612. Journal of Appellate Practice and Process
1613. American Criminal Law Review
1614. Criminal Justice Journal
1615. Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology
1616. Federal Sentencing Reporter
1617. Litigation Journal — ABA
1618. Trial Magazine — American Association for Justice
1619. Judicature — Duke Law
1620. Judicial Conduct Reporter
1621. DOJ Office of Inspector General Reports
1622. FBI Law Enforcement Bulletin
1623. DOJ Civil Rights Division Publications
1624. Federal Judicial Center Publications
1625. Administrative Office of U.S. Courts Publications
1626. Supreme Court Historical Society Publications
1627. National Center for State Courts Publications
1628. Brennan Center for Justice Reports
1629. Cato Institute Legal Studies
1630. Heritage Foundation Legal Studies
1631. American Bar Association Litigation Section Publications
1632. American Bar Association Criminal Justice Section Publications
1633. National Institute of Justice Publications
1634. Federal Public Defender Training Materials
1635. National Association of Criminal Defense Lawyers Publications
1636. Trial Lawyers College Training Materials
1637. National Institute for Trial Advocacy Materials
1638. Advanced Trial Advocacy Workshops — NITA
1639. Federal Defender Habeas Training Materials
1640. DOJ Prosecutor Training Materials
1641. Supreme Court Oral Argument Transcripts
1642. Federal Appellate Oral Argument Transcripts
1643. Federal District Court Trial Transcripts
1644. State Supreme Court Oral Argument Transcripts
1645. Federal Court Docket Filings — PACER
1646. Supreme Court Briefs Archive
1647. Federal Appellate Briefs Archive
1648. Amicus Brief Archives — Supreme Court
1649. DOJ Brief Archive
1650. Solicitor General Brief Archive
1651. Oyez Supreme Court Audio Archive
1652. Supreme Court Historical Audio Archive
1653. Federal Judicial Oral Argument Audio Archive
1654. State Supreme Court Audio Archive
1655. DOJ Litigation Training Videos
1656. Federal Judicial Center Training Videos
1657. ABA Trial Advocacy Video Library
1658. National Institute for Trial Advocacy Video Library
1659. Trial Lawyers College Video Archive
1660. Federal Defender Training Video Archive
1661. Harvard Law School Litigation Training Materials
1662. Yale Law School Litigation Training Materials
1663. Stanford Law School Litigation Training Materials
1664. Columbia Law School Litigation Training Materials
1665. Georgetown Law Litigation Training Materials
1666. University of Chicago Law Litigation Training Materials
1667. NYU Law Litigation Training Materials
1668. Michigan Law Litigation Training Materials
1669. Texas Law Litigation Training Materials
1670. UCLA Law Litigation Training Materials
1671. DOJ Ethics Training Materials
1672. Judicial Ethics Advisory Opinions
1673. Federal Judicial Conduct Decisions
1674. State Judicial Conduct Decisions Archive
1675. Attorney Discipline Case Archive
1676. Bar Disciplinary Proceedings Archive
1677. Judicial Misconduct Investigation Reports
1678. Prosecutorial Misconduct Investigation Reports
1679. Police Misconduct Litigation Archive
1680. Civil Rights Litigation Archive
1681. Federal Habeas Corpus Petition Archive
1682. Section 1983 Litigation Archive
1683. Federal Civil Rights Complaint Archive
1684. Federal Mandamus Petition Archive
1685. Federal Prohibition Petition Archive
1686. Federal Certiorari Petition Archive
1687. Federal Appeal Brief Archive
1688. Federal Trial Motion Archive
1689. Federal Discovery Motion Archive
1690. Federal Suppression Motion Archive
1691. Federal Motion to Dismiss Archive
1692. Federal Motion for Summary Judgment Archive
1693. Federal Motion to Vacate Archive
1694. Federal Motion for New Trial Archive
1695. Federal Motion for Reconsideration Archive
1696. Federal Motion to Recuse Archive
1697. Federal Motion to Disqualify Archive
1698. Federal Motion to Compel Archive
1699. Federal Motion for Sanctions Archive
1700. Federal Motion to Suppress Archive
1701. Supreme Court Certiorari Grant Archive
1702. Supreme Court Certiorari Denial Archive
1703. Supreme Court Reversal Archive
1704. Supreme Court Vacatur Archive
1705. Supreme Court Mandamus Archive
1706. Supreme Court Prohibition Archive
1707. Supreme Court Habeas Archive
1708. Supreme Court Section 1983 Archive
1709. Supreme Court Due Process Archive
1710. Supreme Court Judicial Bias Archive
1711. Federal Appellate Reversal Archive
1712. Federal Appellate Vacatur Archive
1713. Federal Appellate Mandamus Archive
1714. Federal Appellate Habeas Archive
1715. Federal Appellate Judicial Bias Archive
1716. Federal Appellate Due Process Archive
1717. Federal Appellate Jurisdiction Archive
1718. Federal Appellate Immunity Archive
1719. Federal Appellate Civil Rights Archive
1720. Federal Appellate Prosecutorial Misconduct Archive
1721. Federal Trial Court Void Judgment Archive
1722. Federal Trial Court Jurisdiction Archive
1723. Federal Trial Court Habeas Archive
1724. Federal Trial Court Suppression Archive
1725. Federal Trial Court Recusal Archive
1726. Federal Trial Court Disqualification Archive
1727. Federal Trial Court Mandamus Archive
1728. Federal Trial Court Discovery Abuse Archive
1729. Federal Trial Court Due Process Archive
1730. Federal Trial Court Civil Rights Archive
1731. State Supreme Court Reversal Archive
1732. State Supreme Court Mandamus Archive
1733. State Supreme Court Habeas Archive
1734. State Supreme Court Void Judgment Archive
1735. State Supreme Court Jurisdiction Archive
1736. State Supreme Court Recusal Archive
1737. State Supreme Court Judicial Bias Archive
1738. State Supreme Court Civil Rights Archive
1739. State Supreme Court Prosecutorial Misconduct Archive
1740. State Supreme Court Due Process Archive
1741. State Appellate Court Reversal Archive
1742. State Appellate Court Mandamus Archive
1743. State Appellate Court Habeas Archive
1744. State Appellate Court Void Judgment Archive
1745. State Appellate Court Jurisdiction Archive
1746. State Appellate Court Recusal Archive
1747. State Appellate Court Civil Rights Archive
1748. State Appellate Court Judicial Bias Archive
1749. State Appellate Court Due Process Archive
1750. State Appellate Court Prosecutorial Misconduct Archive
1751. Federal Rules Advisory Committee Reports
1752. Judicial Conference of the United States Reports
1753. Congressional Judiciary Committee Reports
1754. Senate Judiciary Committee Reports
1755. House Judiciary Committee Reports
1756. DOJ Office of Legal Counsel Opinions
1757. Solicitor General Opinions
1758. Attorney General Opinions
1759. State Attorney General Opinions Archive
1760. Federal Administrative Agency Legal Opinions Archive
1761. Federal Court Procedural Training Archive
1762. Judicial Clerk Training Manuals
1763. Prosecutor Training Manuals
1764. Federal Defender Training Manuals
1765. Trial Advocacy Seminar Archive
1766. Appellate Advocacy Seminar Archive
1767. Habeas Corpus Seminar Archive
1768. Mandamus Litigation Seminar Archive
1769. Civil Rights Litigation Seminar Archive
1770. Constitutional Litigation Seminar Archive
1771. Federal Court Litigation Audio Archive
1772. Federal Court Litigation Video Archive
1773. Supreme Court Historical Litigation Archive
1774. Federal Judicial Historical Archive
1775. Judicial Discipline Historical Archive
1776. Prosecutorial Discipline Historical Archive
1777. Civil Rights Litigation Historical Archive
1778. Habeas Corpus Historical Archive
1779. Mandamus Historical Archive
1780. Appellate Litigation Historical Archive
1781. Federal Litigation Case Study Archive
1782. Supreme Court Litigation Case Study Archive
1783. Federal Appellate Litigation Case Study Archive
1784. Federal Trial Litigation Case Study Archive
1785. Civil Rights Litigation Case Study Archive
1786. Judicial Misconduct Case Study Archive
1787. Prosecutorial Misconduct Case Study Archive
1788. Habeas Corpus Case Study Archive
1789. Mandamus Case Study Archive
1790. Void Judgment Case Study Archive
1791. Federal Litigation Strategy Case Study Archive
1792. Appellate Litigation Strategy Case Study Archive
1793. Trial Litigation Strategy Case Study Archive
1794. Civil Rights Strategy Case Study Archive
1795. Constitutional Litigation Strategy Case Study Archive
1796. Habeas Corpus Strategy Case Study Archive
1797. Mandamus Strategy Case Study Archive
1798. Jurisdiction Strategy Case Study Archive
1799. Due Process Strategy Case Study Archive
1800. Judicial Accountability Strategy Case Study Archive
2001. Supreme Court of the United States Opinions Archive
2002. United States Courts Opinions Archive
2003. Federal District Court Opinions Archive
2004. Federal Appellate Court Opinions Archive
2005. State Supreme Court Opinions Archive
2006. State Appellate Court Opinions Archive
2007. Federal Habeas Corpus Opinions Archive
2008. Federal Civil Rights Opinions Archive
2009. Federal Mandamus Opinions Archive
2010. Federal Prohibition Opinions Archive
2011. Supreme Court Briefs Archive
2012. Supreme Court Certiorari Petition Archive
2013. Supreme Court Merits Brief Archive
2014. Supreme Court Amicus Brief Archive
2015. Supreme Court Oral Argument Transcript Archive
2016. Supreme Court Oral Argument Audio Archive
2017. Supreme Court Oral Argument Video Archive
2018. Federal Appellate Brief Archive
2019. Federal Appellate Oral Argument Archive
2020. Federal Trial Court Brief Archive
2021. Federal Motion Practice Archive
2022. Federal Motion to Dismiss Archive
2023. Federal Motion for Summary Judgment Archive
2024. Federal Motion to Suppress Archive
2025. Federal Motion to Vacate Archive
2026. Federal Motion for Reconsideration Archive
2027. Federal Motion for New Trial Archive
2028. Federal Motion to Recuse Archive
2029. Federal Motion to Disqualify Archive
2030. Federal Motion for Sanctions Archive
2031. Federal Discovery Motion Archive
2032. Federal Motion to Compel Archive
2033. Federal Motion for Protective Order Archive
2034. Federal Motion in Limine Archive
2035. Federal Motion to Strike Archive
2036. Federal Motion to Quash Archive
2037. Federal Motion for Judgment as Matter of Law Archive
2038. Federal Motion to Amend Judgment Archive
2039. Federal Motion for Relief from Judgment Archive
2040. Federal Rule 60(b) Motion Archive
2041. Federal Rule 12(b) Motion Archive
2042. Federal Rule 50 Motion Archive
2043. Federal Rule 52 Motion Archive
2044. Federal Rule 56 Motion Archive
2045. Federal Rule 59 Motion Archive
2046. Federal Rule 60 Motion Archive
2047. Federal Rule 65 Motion Archive
2048. Federal Rule 41 Motion Archive
2049. Federal Rule 37 Motion Archive
2050. Federal Rule 11 Sanctions Motion Archive
2051. Federal Jurisdiction Challenge Archive
2052. Federal Subject Matter Jurisdiction Archive
2053. Federal Personal Jurisdiction Archive
2054. Federal Venue Challenge Archive
2055. Federal Standing Challenge Archive
2056. Federal Mootness Challenge Archive
2057. Federal Ripeness Challenge Archive
2058. Federal Sovereign Immunity Archive
2059. Federal Qualified Immunity Archive
2060. Federal Absolute Immunity Archive
2061. Federal Judicial Bias Archive
2062. Federal Judicial Recusal Archive
2063. Federal Judicial Disqualification Archive
2064. Federal Judicial Misconduct Archive
2065. Federal Judicial Discipline Archive
2066. Federal Judicial Ethics Archive
2067. Federal Judicial Accountability Archive
2068. Federal Judicial Conduct Complaints Archive
2069. Federal Judicial Discipline Decisions Archive
2070. Federal Judicial Sanctions Archive
2071. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Archive
2072. Federal Brady Violation Archive
2073. Federal Giglio Violation Archive
2074. Federal Prosecutorial Immunity Archive
2075. Federal Prosecutorial Discipline Archive
2076. Federal Prosecutorial Ethics Archive
2077. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Case Archive
2078. Federal Prosecutorial Accountability Archive
2079. Federal Prosecutorial Sanctions Archive
2080. Federal Prosecutorial Conflict of Interest Archive
2081. Federal Grand Jury Indictment Archive
2082. Federal Grand Jury Proceedings Archive
2083. Federal Grand Jury Subpoena Archive
2084. Federal Grand Jury Challenge Archive
2085. Federal Grand Jury Abuse Archive
2086. Federal Grand Jury Misconduct Archive
2087. Federal Grand Jury Access Archive
2088. Federal Grand Jury Accountability Archive
2089. Federal Grand Jury Case Law Archive
2090. Federal Grand Jury Litigation Archive
2091. Federal Civil Rights Complaint Archive
2092. Federal Section 1983 Complaint Archive
2093. Federal Bivens Action Archive
2094. Federal Civil Rights Appeal Archive
2095. Federal Civil Rights Trial Archive
2096. Federal Civil Rights Settlement Archive
2097. Federal Civil Rights Judgment Archive
2098. Federal Civil Rights Reversal Archive
2099. Federal Civil Rights Vacatur Archive
2100. Federal Civil Rights Mandamus Archive
2101. Federal Habeas Corpus Petition Archive
2102. Federal Habeas Corpus Appeal Archive
2103. Federal Habeas Corpus Grant Archive
2104. Federal Habeas Corpus Denial Archive
2105. Federal Habeas Corpus Reversal Archive
2106. Federal Habeas Corpus Vacatur Archive
2107. Federal Habeas Corpus Evidentiary Hearing Archive
2108. Federal Habeas Corpus Procedural Default Archive
2109. Federal Habeas Corpus Jurisdiction Archive
2110. Federal Habeas Corpus Litigation Strategy Archive
2111. Federal Mandamus Petition Archive
2112. Federal Mandamus Grant Archive
2113. Federal Mandamus Denial Archive
2114. Federal Mandamus Appeal Archive
2115. Federal Mandamus Jurisdiction Archive
2116. Federal Mandamus Judicial Accountability Archive
2117. Federal Mandamus Prosecutorial Accountability Archive
2118. Federal Mandamus Administrative Accountability Archive
2119. Federal Mandamus Appellate Court Archive
2120. Federal Mandamus Supreme Court Archive
2121. Federal Void Judgment Archive
2122. Federal Rule 60(b)(4) Void Judgment Archive
2123. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Judgment Archive
2124. Federal Fraud on the Court Archive
2125. Federal Structural Error Archive
2126. Federal Due Process Violation Archive
2127. Federal Jurisdictional Defect Archive
2128. Federal Constitutional Violation Archive
2129. Federal Void Order Archive
2130. Federal Judgment Nullification Archive
2131. Federal Appellate Reversal Archive
2132. Federal Appellate Vacatur Archive
2133. Federal Appellate Remand Archive
2134. Federal Appellate Mandamus Archive
2135. Federal Appellate Habeas Archive
2136. Federal Appellate Civil Rights Archive
2137. Federal Appellate Jurisdiction Archive
2138. Federal Appellate Judicial Bias Archive
2139. Federal Appellate Prosecutorial Misconduct Archive
2140. Federal Appellate Due Process Archive
2141. Federal Trial Court Judgment Archive
2142. Federal Trial Court Motion Archive
2143. Federal Trial Court Appeal Archive
2144. Federal Trial Court Suppression Archive
2145. Federal Trial Court Recusal Archive
2146. Federal Trial Court Jurisdiction Archive
2147. Federal Trial Court Habeas Archive
2148. Federal Trial Court Civil Rights Archive
2149. Federal Trial Court Constitutional Violation Archive
2150. Federal Trial Court Void Judgment Archive
2151. State Supreme Court Litigation Archive
2152. State Supreme Court Mandamus Archive
2153. State Supreme Court Habeas Archive
2154. State Supreme Court Civil Rights Archive
2155. State Supreme Court Jurisdiction Archive
2156. State Supreme Court Judicial Bias Archive
2157. State Supreme Court Prosecutorial Misconduct Archive
2158. State Supreme Court Due Process Archive
2159. State Supreme Court Void Judgment Archive
2160. State Supreme Court Structural Error Archive
2161. State Appellate Court Litigation Archive
2162. State Appellate Court Mandamus Archive
2163. State Appellate Court Habeas Archive
2164. State Appellate Court Civil Rights Archive
2165. State Appellate Court Jurisdiction Archive
2166. State Appellate Court Judicial Bias Archive
2167. State Appellate Court Prosecutorial Misconduct Archive
2168. State Appellate Court Due Process Archive
2169. State Appellate Court Void Judgment Archive
2170. State Appellate Court Structural Error Archive
2171. State Trial Court Litigation Archive
2172. State Trial Court Motion Archive
2173. State Trial Court Habeas Archive
2174. State Trial Court Civil Rights Archive
2175. State Trial Court Jurisdiction Archive
2176. State Trial Court Judicial Bias Archive
2177. State Trial Court Prosecutorial Misconduct Archive
2178. State Trial Court Due Process Archive
2179. State Trial Court Void Judgment Archive
2180. State Trial Court Structural Error Archive
2181. Federal Discovery Abuse Archive
2182. Federal Discovery Sanctions Archive
2183. Federal Discovery Violations Archive
2184. Federal Discovery Enforcement Archive
2185. Federal Discovery Litigation Archive
2186. Federal Discovery Appeals Archive
2187. Federal Discovery Mandamus Archive
2188. Federal Discovery Protective Orders Archive
2189. Federal Discovery Suppression Archive
2190. Federal Discovery Evidence Archive
2191. Federal Evidence Suppression Archive
2192. Federal Exclusionary Rule Archive
2193. Federal Fourth Amendment Suppression Archive
2194. Federal Fifth Amendment Suppression Archive
2195. Federal Sixth Amendment Suppression Archive
2196. Federal Due Process Evidence Suppression Archive
2197. Federal Illegal Search Suppression Archive
2198. Federal Illegal Seizure Suppression Archive
2199. Federal Evidence Exclusion Archive
2200. Federal Evidence Admissibility Archive
2201. Federal Constitutional Litigation Archive
2202. Federal Due Process Litigation Archive
2203. Federal Equal Protection Litigation Archive
2204. Federal Civil Rights Appeals Archive
2205. Federal Structural Error Litigation Archive
2206. Federal Judicial Accountability Litigation Archive
2207. Federal Prosecutorial Accountability Litigation Archive
2208. Federal Government Accountability Litigation Archive
2209. Federal Administrative Law Litigation Archive
2210. Federal Agency Accountability Litigation Archive
2211. Federal Administrative Procedure Act Litigation Archive
2212. Federal Agency Rule Challenge Archive
2213. Federal Agency Abuse of Discretion Archive
2214. Federal Agency Ultra Vires Action Archive
2215. Federal Agency Jurisdiction Challenge Archive
2216. Federal Agency Constitutional Violation Archive
2217. Federal Agency Due Process Violation Archive
2218. Federal Agency Enforcement Challenge Archive
2219. Federal Agency Enforcement Defense Archive
2220. Federal Agency Enforcement Appeal Archive
2221. Federal Declaratory Judgment Archive
2222. Federal Injunction Litigation Archive
2223. Federal Temporary Restraining Order Archive
2224. Federal Preliminary Injunction Archive
2225. Federal Permanent Injunction Archive
2226. Federal Emergency Injunction Archive
2227. Federal Injunction Appeal Archive
2228. Federal Injunction Enforcement Archive
2229. Federal Injunction Modification Archive
2230. Federal Injunction Dissolution Archive
2231. Federal Contempt Litigation Archive
2232. Federal Civil Contempt Archive
2233. Federal Criminal Contempt Archive
2234. Federal Contempt Appeal Archive
2235. Federal Contempt Sanctions Archive
2236. Federal Contempt Defense Archive
2237. Federal Contempt Enforcement Archive
2238. Federal Contempt Jurisdiction Archive
2239. Federal Contempt Habeas Archive
2240. Federal Contempt Mandamus Archive
2241. Federal Sanctions Litigation Archive
2242. Federal Rule 11 Sanctions Archive
2243. Federal Inherent Power Sanctions Archive
2244. Federal Bad Faith Sanctions Archive
2245. Federal Litigation Misconduct Sanctions Archive
2246. Federal Discovery Sanctions Litigation Archive
2247. Federal Judicial Sanctions Litigation Archive
2248. Federal Prosecutorial Sanctions Litigation Archive
2249. Federal Government Sanctions Litigation Archive
2250. Federal Sanctions Appeal Archive
2251. Federal Settlement Litigation Archive
2252. Federal Settlement Enforcement Archive
2253. Federal Settlement Challenge Archive
2254. Federal Settlement Appeal Archive
2255. Federal Settlement Vacatur Archive
2256. Federal Settlement Nullification Archive
2257. Federal Settlement Fraud Challenge Archive
2258. Federal Settlement Constitutional Challenge Archive
2259. Federal Settlement Jurisdiction Challenge Archive
2260. Federal Settlement Enforcement Appeal Archive
2261. Federal Structural Constitutional Litigation Archive
2262. Federal Separation of Powers Litigation Archive
2263. Federal Judicial Power Challenge Archive
2264. Federal Executive Power Challenge Archive
2265. Federal Legislative Power Challenge Archive
2266. Federal Government Authority Challenge Archive
2267. Federal Constitutional Authority Challenge Archive
2268. Federal Constitutional Structural Error Archive
2269. Federal Structural Due Process Archive
2270. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Archive
2271. Federal Judicial Accountability Complaint Archive
2272. Federal Judicial Discipline Complaint Archive
2273. Federal Judicial Removal Litigation Archive
2274. Federal Judicial Misconduct Complaint Archive
2275. Federal Judicial Ethics Enforcement Archive
2276. Federal Judicial Bias Complaint Archive
2277. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Archive
2278. Federal Judicial Impropriety Complaint Archive
2279. Federal Judicial Accountability Appeal Archive
2280. Federal Judicial Accountability Mandamus Archive
2281. Federal Prosecutorial Accountability Complaint Archive
2282. Federal Prosecutorial Discipline Complaint Archive
2283. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Complaint Archive
2284. Federal Prosecutorial Ethics Enforcement Archive
2285. Federal Prosecutorial Bias Complaint Archive
2286. Federal Prosecutorial Conflict of Interest Archive
2287. Federal Prosecutorial Abuse of Power Archive
2288. Federal Prosecutorial Accountability Appeal Archive
2289. Federal Prosecutorial Accountability Mandamus Archive
2290. Federal Prosecutorial Accountability Litigation Archive
2291. Federal Jurisdictional Void Order Archive
2292. Federal Jurisdictional Defect Order Archive
2293. Federal Ultra Vires Judicial Order Archive
2294. Federal Ultra Vires Government Action Archive
2295. Federal Jurisdictional Nullification Archive
2296. Federal Void Judgment Enforcement Challenge Archive
2297. Federal Void Judgment Appeal Archive
2298. Federal Void Judgment Habeas Archive
2299. Federal Void Judgment Mandamus Archive
2300. Federal Void Judgment Litigation Archive
2301. Federal Due Process Violation Appeal Archive
2302. Federal Due Process Violation Habeas Archive
2303. Federal Due Process Violation Mandamus Archive
2304. Federal Due Process Violation Reversal Archive
2305. Federal Due Process Violation Vacatur Archive
2306. Federal Due Process Violation Structural Error Archive
2307. Federal Due Process Violation Nullification Archive
2308. Federal Due Process Violation Litigation Archive
2309. Federal Due Process Violation Complaint Archive
2310. Federal Due Process Violation Enforcement Archive
2311. Federal Structural Error Appeal Archive
2312. Federal Structural Error Habeas Archive
2313. Federal Structural Error Mandamus Archive
2314. Federal Structural Error Reversal Archive
2315. Federal Structural Error Vacatur Archive
2316. Federal Structural Error Nullification Archive
2317. Federal Structural Error Litigation Archive
2318. Federal Structural Error Complaint Archive
2319. Federal Structural Error Enforcement Archive
2320. Federal Structural Error Judicial Accountability Archive
2321. Federal Constitutional Rights Enforcement Archive
2322. Federal Constitutional Rights Litigation Archive
2323. Federal Constitutional Rights Appeal Archive
2324. Federal Constitutional Rights Habeas Archive
2325. Federal Constitutional Rights Mandamus Archive
2326. Federal Constitutional Rights Reversal Archive
2327. Federal Constitutional Rights Vacatur Archive
2328. Federal Constitutional Rights Nullification Archive
2329. Federal Constitutional Rights Structural Error Archive
2330. Federal Constitutional Rights Complaint Archive
2331. Federal Constitutional Violation Litigation Archive
2332. Federal Constitutional Violation Appeal Archive
2333. Federal Constitutional Violation Habeas Archive
2334. Federal Constitutional Violation Mandamus Archive
2335. Federal Constitutional Violation Vacatur Archive
2336. Federal Constitutional Violation Reversal Archive
2337. Federal Constitutional Violation Nullification Archive
2338. Federal Constitutional Violation Structural Error Archive
2339. Federal Constitutional Violation Complaint Archive
2340. Federal Constitutional Violation Enforcement Archive
2341. Federal Equal Protection Litigation Archive
2342. Federal Equal Protection Appeal Archive
2343. Federal Equal Protection Habeas Archive
2344. Federal Equal Protection Mandamus Archive
2345. Federal Equal Protection Vacatur Archive
2346. Federal Equal Protection Reversal Archive
2347. Federal Equal Protection Nullification Archive
2348. Federal Equal Protection Structural Error Archive
2349. Federal Equal Protection Complaint Archive
2350. Federal Equal Protection Enforcement Archive
2351. Federal First Amendment Litigation Archive
2352. Federal First Amendment Appeal Archive
2353. Federal First Amendment Habeas Archive
2354. Federal First Amendment Mandamus Archive
2355. Federal First Amendment Vacatur Archive
2356. Federal First Amendment Reversal Archive
2357. Federal First Amendment Nullification Archive
2358. Federal First Amendment Structural Error Archive
2359. Federal First Amendment Complaint Archive
2360. Federal First Amendment Enforcement Archive
2361. Federal Fourth Amendment Litigation Archive
2362. Federal Fourth Amendment Appeal Archive
2363. Federal Fourth Amendment Habeas Archive
2364. Federal Fourth Amendment Mandamus Archive
2365. Federal Fourth Amendment Vacatur Archive
2366. Federal Fourth Amendment Reversal Archive
2367. Federal Fourth Amendment Nullification Archive
2368. Federal Fourth Amendment Structural Error Archive
2369. Federal Fourth Amendment Complaint Archive
2370. Federal Fourth Amendment Enforcement Archive
2371. Federal Fifth Amendment Litigation Archive
2372. Federal Fifth Amendment Appeal Archive
2373. Federal Fifth Amendment Habeas Archive
2374. Federal Fifth Amendment Mandamus Archive
2375. Federal Fifth Amendment Vacatur Archive
2376. Federal Fifth Amendment Reversal Archive
2377. Federal Fifth Amendment Nullification Archive
2378. Federal Fifth Amendment Structural Error Archive
2379. Federal Fifth Amendment Complaint Archive
2380. Federal Fifth Amendment Enforcement Archive
2381. Federal Sixth Amendment Litigation Archive
2382. Federal Sixth Amendment Appeal Archive
2383. Federal Sixth Amendment Habeas Archive
2384. Federal Sixth Amendment Mandamus Archive
2385. Federal Sixth Amendment Vacatur Archive
2386. Federal Sixth Amendment Reversal Archive
2387. Federal Sixth Amendment Nullification Archive
2388. Federal Sixth Amendment Structural Error Archive
2389. Federal Sixth Amendment Complaint Archive
2390. Federal Sixth Amendment Enforcement Archive
2391. Federal Seventh Amendment Litigation Archive
2392. Federal Seventh Amendment Appeal Archive
2393. Federal Seventh Amendment Habeas Archive
2394. Federal Seventh Amendment Mandamus Archive
2395. Federal Seventh Amendment Vacatur Archive
2396. Federal Seventh Amendment Reversal Archive
2397. Federal Seventh Amendment Nullification Archive
2398. Federal Seventh Amendment Structural Error Archive
2399. Federal Seventh Amendment Complaint Archive
2400. Federal Seventh Amendment Enforcement Archive
2401. Federal Eighth Amendment Litigation Archive
2402. Federal Eighth Amendment Appeal Archive
2403. Federal Eighth Amendment Habeas Archive
2404. Federal Eighth Amendment Mandamus Archive
2405. Federal Eighth Amendment Vacatur Archive
2406. Federal Eighth Amendment Reversal Archive
2407. Federal Eighth Amendment Nullification Archive
2408. Federal Eighth Amendment Structural Error Archive
2409. Federal Eighth Amendment Complaint Archive
2410. Federal Eighth Amendment Enforcement Archive
2411. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Litigation Archive
2412. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Appeal Archive
2413. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Habeas Archive
2414. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Mandamus Archive
2415. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Vacatur Archive
2416. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Reversal Archive
2417. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Nullification Archive
2418. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Structural Error Archive
2419. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Complaint Archive
2420. Federal Fourteenth Amendment Enforcement Archive
2421. Federal Fraud on the Court Litigation Archive
2422. Federal Fraud on the Court Appeal Archive
2423. Federal Fraud on the Court Mandamus Archive
2424. Federal Fraud on the Court Vacatur Archive
2425. Federal Fraud on the Court Nullification Archive
2426. Federal Fraud on the Court Structural Error Archive
2427. Federal Fraud on the Court Complaint Archive
2428. Federal Fraud on the Court Enforcement Archive
2429. Federal Fraud on the Court Habeas Archive
2430. Federal Fraud on the Court Accountability Archive
2431. Federal Ultra Vires Litigation Archive
2432. Federal Ultra Vires Appeal Archive
2433. Federal Ultra Vires Mandamus Archive
2434. Federal Ultra Vires Vacatur Archive
2435. Federal Ultra Vires Nullification Archive
2436. Federal Ultra Vires Structural Error Archive
2437. Federal Ultra Vires Complaint Archive
2438. Federal Ultra Vires Enforcement Archive
2439. Federal Ultra Vires Habeas Archive
2440. Federal Ultra Vires Accountability Archive
2441. Federal Judgment Destruction Litigation Archive
2442. Federal Judgment Nullification Litigation Archive
2443. Federal Judgment Vacatur Litigation Archive
2444. Federal Judgment Reversal Litigation Archive
2445. Federal Judgment Mandamus Litigation Archive
2446. Federal Judgment Habeas Litigation Archive
2447. Federal Judgment Jurisdiction Challenge Archive
2448. Federal Judgment Constitutional Challenge Archive
2449. Federal Judgment Enforcement Challenge Archive
2450. Federal Judgment Structural Error Archive
2451. Federal Procedural Due Process Litigation Archive
2452. Federal Procedural Due Process Appeal Archive
2453. Federal Procedural Due Process Habeas Archive
2454. Federal Procedural Due Process Mandamus Archive
2455. Federal Procedural Due Process Vacatur Archive
2456. Federal Procedural Due Process Reversal Archive
2457. Federal Procedural Due Process Nullification Archive
2458. Federal Procedural Due Process Structural Error Archive
2459. Federal Procedural Due Process Complaint Archive
2460. Federal Procedural Due Process Enforcement Archive
2461. Federal Substantive Due Process Litigation Archive
2462. Federal Substantive Due Process Appeal Archive
2463. Federal Substantive Due Process Habeas Archive
2464. Federal Substantive Due Process Mandamus Archive
2465. Federal Substantive Due Process Vacatur Archive
2466. Federal Substantive Due Process Reversal Archive
2467. Federal Substantive Due Process Nullification Archive
2468. Federal Substantive Due Process Structural Error Archive
2469. Federal Substantive Due Process Complaint Archive
2470. Federal Substantive Due Process Enforcement Archive
2471. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Litigation Archive
2472. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Appeal Archive
2473. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Habeas Archive
2474. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Mandamus Archive
2475. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Vacatur Archive
2476. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Reversal Archive
2477. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Nullification Archive
2478. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Structural Error Archive
2479. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Complaint Archive
2480. Federal Lack of Jurisdiction Enforcement Archive
2481. Federal Void Order Litigation Archive
2482. Federal Void Order Appeal Archive
2483. Federal Void Order Habeas Archive
2484. Federal Void Order Mandamus Archive
2485. Federal Void Order Vacatur Archive
2486. Federal Void Order Reversal Archive
2487. Federal Void Order Nullification Archive
2488. Federal Void Order Structural Error Archive
2489. Federal Void Order Complaint Archive
2490. Federal Void Order Enforcement Archive
2491. Federal Void Judgment Litigation Archive
2492. Federal Void Judgment Appeal Archive
2493. Federal Void Judgment Habeas Archive
2494. Federal Void Judgment Mandamus Archive
2495. Federal Void Judgment Vacatur Archive
2496. Federal Void Judgment Reversal Archive
2497. Federal Void Judgment Nullification Archive
2498. Federal Void Judgment Structural Error Archive
2499. Federal Void Judgment Complaint Archive
2500. Federal Void Judgment Enforcement Archive
2501. Federal Lack of Standing Litigation Archive
2502. Federal Lack of Standing Appeal Archive
2503. Federal Lack of Standing Habeas Archive
2504. Federal Lack of Standing Mandamus Archive
2505. Federal Lack of Standing Vacatur Archive
2506. Federal Lack of Standing Reversal Archive
2507. Federal Lack of Standing Nullification Archive
2508. Federal Lack of Standing Structural Error Archive
2509. Federal Lack of Standing Complaint Archive
2510. Federal Lack of Standing Enforcement Archive
2511. Federal Ripeness Challenge Litigation Archive
2512. Federal Ripeness Challenge Appeal Archive
2513. Federal Ripeness Challenge Habeas Archive
2514. Federal Ripeness Challenge Mandamus Archive
2515. Federal Ripeness Challenge Vacatur Archive
2516. Federal Ripeness Challenge Reversal Archive
2517. Federal Ripeness Challenge Nullification Archive
2518. Federal Ripeness Challenge Structural Error Archive
2519. Federal Ripeness Challenge Complaint Archive
2520. Federal Ripeness Challenge Enforcement Archive
2521. Federal Mootness Doctrine Litigation Archive
2522. Federal Mootness Doctrine Appeal Archive
2523. Federal Mootness Doctrine Habeas Archive
2524. Federal Mootness Doctrine Mandamus Archive
2525. Federal Mootness Doctrine Vacatur Archive
2526. Federal Mootness Doctrine Reversal Archive
2527. Federal Mootness Doctrine Nullification Archive
2528. Federal Mootness Doctrine Structural Error Archive
2529. Federal Mootness Doctrine Complaint Archive
2530. Federal Mootness Doctrine Enforcement Archive
2531. Federal Judicial Bias Litigation Archive
2532. Federal Judicial Bias Appeal Archive
2533. Federal Judicial Bias Habeas Archive
2534. Federal Judicial Bias Mandamus Archive
2535. Federal Judicial Bias Vacatur Archive
2536. Federal Judicial Bias Reversal Archive
2537. Federal Judicial Bias Nullification Archive
2538. Federal Judicial Bias Structural Error Archive
2539. Federal Judicial Bias Complaint Archive
2540. Federal Judicial Bias Enforcement Archive
2541. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Litigation Archive
2542. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Appeal Archive
2543. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Habeas Archive
2544. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Mandamus Archive
2545. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Vacatur Archive
2546. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Reversal Archive
2547. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Nullification Archive
2548. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Structural Error Archive
2549. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Complaint Archive
2550. Federal Judicial Conflict of Interest Enforcement Archive
2551. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Litigation Archive
2552. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Appeal Archive
2553. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Habeas Archive
2554. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Mandamus Archive
2555. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Vacatur Archive
2556. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Reversal Archive
2557. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Nullification Archive
2558. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Structural Error Archive
2559. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Complaint Archive
2560. Federal Prosecutorial Misconduct Enforcement Archive
2561. Federal Brady Violation Litigation Archive
2562. Federal Brady Violation Appeal Archive
2563. Federal Brady Violation Habeas Archive
2564. Federal Brady Violation Mandamus Archive
2565. Federal Brady Violation Vacatur Archive
2566. Federal Brady Violation Reversal Archive
2567. Federal Brady Violation Nullification Archive
2568. Federal Brady Violation Structural Error Archive
2569. Federal Brady Violation Complaint Archive
2570. Federal Brady Violation Enforcement Archive
2571. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Litigation Archive
2572. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Appeal Archive
2573. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Habeas Archive
2574. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Mandamus Archive
2575. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Vacatur Archive
2576. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Reversal Archive
2577. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Nullification Archive
2578. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Structural Error Archive
2579. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Complaint Archive
2580. Federal Exculpatory Evidence Suppression Enforcement Archive
2581. Federal Evidence Suppression Litigation Archive
2582. Federal Evidence Suppression Appeal Archive
2583. Federal Evidence Suppression Habeas Archive
2584. Federal Evidence Suppression Mandamus Archive
2585. Federal Evidence Suppression Vacatur Archive
2586. Federal Evidence Suppression Reversal Archive
2587. Federal Evidence Suppression Nullification Archive
2588. Federal Evidence Suppression Structural Error Archive
2589. Federal Evidence Suppression Complaint Archive
2590. Federal Evidence Suppression Enforcement Archive
2591. Federal Illegal Search Litigation Archive
2592. Federal Illegal Search Appeal Archive
2593. Federal Illegal Search Habeas Archive
2594. Federal Illegal Search Mandamus Archive
2595. Federal Illegal Search Vacatur Archive
2596. Federal Illegal Search Reversal Archive
2597. Federal Illegal Search Nullification Archive
2598. Federal Illegal Search Structural Error Archive
2599. Federal Illegal Search Complaint Archive
2600. Federal Illegal Search Enforcement Archive
2601. Federal Illegal Seizure Litigation Archive
2602. Federal Illegal Seizure Appeal Archive
2603. Federal Illegal Seizure Habeas Archive
2604. Federal Illegal Seizure Mandamus Archive
2605. Federal Illegal Seizure Vacatur Archive
2606. Federal Illegal Seizure Reversal Archive
2607. Federal Illegal Seizure Nullification Archive
2608. Federal Illegal Seizure Structural Error Archive
2609. Federal Illegal Seizure Complaint Archive
2610. Federal Illegal Seizure Enforcement Archive
2611. Federal Warrant Defect Litigation Archive
2612. Federal Warrant Defect Appeal Archive
2613. Federal Warrant Defect Habeas Archive
2614. Federal Warrant Defect Mandamus Archive
2615. Federal Warrant Defect Vacatur Archive
2616. Federal Warrant Defect Reversal Archive
2617. Federal Warrant Defect Nullification Archive
2618. Federal Warrant Defect Structural Error Archive
2619. Federal Warrant Defect Complaint Archive
2620. Federal Warrant Defect Enforcement Archive
2621. Federal False Arrest Litigation Archive
2622. Federal False Arrest Appeal Archive
2623. Federal False Arrest Habeas Archive
2624. Federal False Arrest Mandamus Archive
2625. Federal False Arrest Vacatur Archive
2626. Federal False Arrest Reversal Archive
2627. Federal False Arrest Nullification Archive
2628. Federal False Arrest Structural Error Archive
2629. Federal False Arrest Complaint Archive
2630. Federal False Arrest Enforcement Archive
2631. Federal Malicious Prosecution Litigation Archive
2632. Federal Malicious Prosecution Appeal Archive
2633. Federal Malicious Prosecution Habeas Archive
2634. Federal Malicious Prosecution Mandamus Archive
2635. Federal Malicious Prosecution Vacatur Archive
2636. Federal Malicious Prosecution Reversal Archive
2637. Federal Malicious Prosecution Nullification Archive
2638. Federal Malicious Prosecution Structural Error Archive
2639. Federal Malicious Prosecution Complaint Archive
2640. Federal Malicious Prosecution Enforcement Archive
2641. Federal Selective Prosecution Litigation Archive
2642. Federal Selective Prosecution Appeal Archive
2643. Federal Selective Prosecution Habeas Archive
2644. Federal Selective Prosecution Mandamus Archive
2645. Federal Selective Prosecution Vacatur Archive
2646. Federal Selective Prosecution Reversal Archive
2647. Federal Selective Prosecution Nullification Archive
2648. Federal Selective Prosecution Structural Error Archive
2649. Federal Selective Prosecution Complaint Archive
2650. Federal Selective Prosecution Enforcement Archive
2651. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Litigation Archive
2652. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Appeal Archive
2653. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Habeas Archive
2654. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Mandamus Archive
2655. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Vacatur Archive
2656. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Reversal Archive
2657. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Nullification Archive
2658. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Structural Error Archive
2659. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Complaint Archive
2660. Federal Vindictive Prosecution Enforcement Archive
2661. Federal Judicial Fraud Litigation Archive
2662. Federal Judicial Fraud Appeal Archive
2663. Federal Judicial Fraud Habeas Archive
2664. Federal Judicial Fraud Mandamus Archive
2665. Federal Judicial Fraud Vacatur Archive
2666. Federal Judicial Fraud Reversal Archive
2667. Federal Judicial Fraud Nullification Archive
2668. Federal Judicial Fraud Structural Error Archive
2669. Federal Judicial Fraud Complaint Archive
2670. Federal Judicial Fraud Enforcement Archive
2671. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Litigation Archive
2672. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Appeal Archive
2673. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Habeas Archive
2674. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Mandamus Archive
2675. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Vacatur Archive
2676. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Reversal Archive
2677. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Nullification Archive
2678. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Structural Error Archive
2679. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Complaint Archive
2680. Federal Prosecutorial Fraud Enforcement Archive
2681. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Litigation Archive
2682. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Appeal Archive
2683. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Habeas Archive
2684. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Mandamus Archive
2685. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Vacatur Archive
2686. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Reversal Archive
2687. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Nullification Archive
2688. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Structural Error Archive
2689. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Complaint Archive
2690. Federal Fraudulent Judgment Enforcement Archive
2691. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Litigation Archive
2692. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Appeal Archive
2693. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Habeas Archive
2694. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Mandamus Archive
2695. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Vacatur Archive
2696. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Reversal Archive
2697. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Nullification Archive
2698. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Structural Error Archive
2699. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Complaint Archive
2700. Federal Structural Constitutional Violation Enforcement Archive
2701. Federal Illegal Detention Litigation Archive
2702. Federal Illegal Detention Appeal Archive
2703. Federal Illegal Detention Habeas Archive
2704. Federal Illegal Detention Mandamus Archive
2705. Federal Illegal Detention Vacatur Archive
2706. Federal Illegal Detention Reversal Archive
2707. Federal Illegal Detention Nullification Archive
2708. Federal Illegal Detention Structural Error Archive
2709. Federal Illegal Detention Complaint Archive
2710. Federal Illegal Detention Enforcement Archive
2711. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Litigation Archive
2712. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Appeal Archive
2713. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Habeas Archive
2714. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Mandamus Archive
2715. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Vacatur Archive
2716. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Reversal Archive
2717. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Nullification Archive
2718. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Structural Error Archive
2719. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Complaint Archive
2720. Federal Illegal Imprisonment Enforcement Archive
2721. Federal Case Collapse Litigation Archive
2722. Federal Case Collapse Appeal Archive
2723. Federal Case Collapse Habeas Archive
2724. Federal Case Collapse Mandamus Archive
2725. Federal Case Collapse Vacatur Archive
2726. Federal Case Collapse Reversal Archive
2727. Federal Case Collapse Nullification Archive
2728. Federal Case Collapse Structural Error Archive
2729. Federal Case Collapse Complaint Archive
2730. Federal Case Collapse Enforcement Archive
2731. Federal Judgment Destruction Enforcement Archive
2732. Federal Judgment Collapse Enforcement Archive
2733. Federal Judgment Vacatur Enforcement Archive
2734. Federal Judgment Reversal Enforcement Archive
2735. Federal Judgment Nullification Enforcement Archive
2736. Federal Judgment Jurisdiction Collapse Archive
2737. Federal Judgment Constitutional Collapse Archive
2738. Federal Judgment Procedural Collapse Archive
2739. Federal Judgment Structural Collapse Archive
2740. Federal Judgment Enforcement Destruction Archive
2741. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Litigation Archive
2742. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Appeal Archive
2743. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Habeas Archive
2744. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Mandamus Archive
2745. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Vacatur Archive
2746. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Reversal Archive
2747. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Nullification Archive
2748. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Structural Error Archive
2749. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Complaint Archive
2750. Federal Jurisdiction Collapse Enforcement Archive
2751. Federal Void Judgment Litigation Archive
2752. Federal Void Judgment Appeal Archive
2753. Federal Void Judgment Habeas Archive
2754. Federal Void Judgment Mandamus Archive
2755. Federal Void Judgment Vacatur Archive
2756. Federal Void Judgment Reversal Archive
2757. Federal Void Judgment Nullification Archive
2758. Federal Void Judgment Structural Error Archive
2759. Federal Void Judgment Complaint Archive
2760. Federal Void Judgment Enforcement Archive
2761. Federal Structural Error Litigation Archive
2762. Federal Structural Error Appeal Archive
2763. Federal Structural Error Habeas Archive
2764. Federal Structural Error Mandamus Archive
2765. Federal Structural Error Vacatur Archive
2766. Federal Structural Error Reversal Archive
2767. Federal Structural Error Nullification Archive
2768. Federal Structural Error Structural Error Archive
2769. Federal Structural Error Complaint Archive
2770. Federal Structural Error Enforcement Archive
2771. Federal Due Process Collapse Litigation Archive
2772. Federal Due Process Collapse Appeal Archive
2773. Federal Due Process Collapse Habeas Archive
2774. Federal Due Process Collapse Mandamus Archive
2775. Federal Due Process Collapse Vacatur Archive
2776. Federal Due Process Collapse Reversal Archive
2777. Federal Due Process Collapse Nullification Archive
2778. Federal Due Process Collapse Structural Error Archive
2779. Federal Due Process Collapse Complaint Archive
2780. Federal Due Process Collapse Enforcement Archive
2781. Federal Constitutional Violation Litigation Archive
2782. Federal Constitutional Violation Appeal Archive
2783. Federal Constitutional Violation Habeas Archive
2784. Federal Constitutional Violation Mandamus Archive
2785. Federal Constitutional Violation Vacatur Archive
2786. Federal Constitutional Violation Reversal Archive
2787. Federal Constitutional Violation Nullification Archive
2788. Federal Constitutional Violation Structural Error Archive
2789. Federal Constitutional Violation Complaint Archive
2790. Federal Constitutional Violation Enforcement Archive
2791. Federal Judicial Bias Litigation Archive
2792. Federal Judicial Bias Appeal Archive
2793. Federal Judicial Bias Habeas Archive
2794. Federal Judicial Bias Mandamus Archive
2795. Federal Judicial Bias Vacatur Archive
2796. Federal Judicial Bias Reversal Archive
2797. Federal Judicial Bias Nullification Archive
2798. Federal Judicial Bias Structural Error Archive
2799. Federal Judicial Bias Complaint Archive
2800. Federal Judicial Bias Enforcement Archive
2801. Federal Judicial Corruption Litigation Archive
2802. Federal Judicial Corruption Appeal Archive
2803. Federal Judicial Corruption Habeas Archive
2804. Federal Judicial Corruption Mandamus Archive
2805. Federal Judicial Corruption Vacatur Archive
2806. Federal Judicial Corruption Reversal Archive
2807. Federal Judicial Corruption Nullification Archive
2808. Federal Judicial Corruption Structural Error Archive
2809. Federal Judicial Corruption Complaint Archive
2810. Federal Judicial Corruption Enforcement Archive
2811. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Litigation Archive
2812. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Appeal Archive
2813. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Habeas Archive
2814. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Mandamus Archive
2815. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Vacatur Archive
2816. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Reversal Archive
2817. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Nullification Archive
2818. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Structural Error Archive
2819. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Complaint Archive
2820. Federal Prosecutorial Corruption Enforcement Archive
2821. Federal Fraud on the Court Litigation Archive
2822. Federal Fraud on the Court Appeal Archive
2823. Federal Fraud on the Court Habeas Archive
2824. Federal Fraud on the Court Mandamus Archive
2825. Federal Fraud on the Court Vacatur Archive
2826. Federal Fraud on the Court Reversal Archive
2827. Federal Fraud on the Court Nullification Archive
2828. Federal Fraud on the Court Structural Error Archive
2829. Federal Fraud on the Court Complaint Archive
2830. Federal Fraud on the Court Enforcement Archive
2831. Federal Illegal Conviction Litigation Archive
2832. Federal Illegal Conviction Appeal Archive
2833. Federal Illegal Conviction Habeas Archive
2834. Federal Illegal Conviction Mandamus Archive
2835. Federal Illegal Conviction Vacatur Archive
2836. Federal Illegal Conviction Reversal Archive
2837. Federal Illegal Conviction Nullification Archive
2838. Federal Illegal Conviction Structural Error Archive
2839. Federal Illegal Conviction Complaint Archive
2840. Federal Illegal Conviction Enforcement Archive
2841. Federal Wrongful Conviction Litigation Archive
2842. Federal Wrongful Conviction Appeal Archive
2843. Federal Wrongful Conviction Habeas Archive
2844. Federal Wrongful Conviction Mandamus Archive
2845. Federal Wrongful Conviction Vacatur Archive
2846. Federal Wrongful Conviction Reversal Archive
2847. Federal Wrongful Conviction Nullification Archive
2848. Federal Wrongful Conviction Structural Error Archive
2849. Federal Wrongful Conviction Complaint Archive
2850. Federal Wrongful Conviction Enforcement Archive
2851. Federal Void Proceedings Litigation Archive
2852. Federal Void Proceedings Appeal Archive
2853. Federal Void Proceedings Habeas Archive
2854. Federal Void Proceedings Mandamus Archive
2855. Federal Void Proceedings Vacatur Archive
2856. Federal Void Proceedings Reversal Archive
2857. Federal Void Proceedings Nullification Archive
2858. Federal Void Proceedings Structural Error Archive
2859. Federal Void Proceedings Complaint Archive
2860. Federal Void Proceedings Enforcement Archive
2861. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Litigation Archive
2862. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Appeal Archive
2863. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Habeas Archive
2864. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Mandamus Archive
2865. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Vacatur Archive
2866. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Reversal Archive
2867. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Nullification Archive
2868. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Structural Error Archive
2869. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Complaint Archive
2870. Federal Jurisdiction Defect Enforcement Archive
2871. Federal Illegal Court Action Litigation Archive
2872. Federal Illegal Court Action Appeal Archive
2873. Federal Illegal Court Action Habeas Archive
2874. Federal Illegal Court Action Mandamus Archive
2875. Federal Illegal Court Action Vacatur Archive
2876. Federal Illegal Court Action Reversal Archive
2877. Federal Illegal Court Action Nullification Archive
2878. Federal Illegal Court Action Structural Error Archive
2879. Federal Illegal Court Action Complaint Archive
2880. Federal Illegal Court Action Enforcement Archive
2881. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Litigation Archive
2882. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Appeal Archive
2883. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Habeas Archive
2884. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Mandamus Archive
2885. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Vacatur Archive
2886. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Reversal Archive
2887. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Nullification Archive
2888. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Structural Error Archive
2889. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Complaint Archive
2890. Federal Structural Judicial Violation Enforcement Archive
2891. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Litigation Archive
2892. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Appeal Archive
2893. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Habeas Archive
2894. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Mandamus Archive
2895. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Vacatur Archive
2896. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Reversal Archive
2897. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Nullification Archive
2898. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Structural Error Archive
2899. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Complaint Archive
2900. Federal Constitutional Enforcement Enforcement Archive
2901. Federal Legal Nullification Litigation Archive
2902. Federal Legal Nullification Appeal Archive
2903. Federal Legal Nullification Habeas Archive
2904. Federal Legal Nullification Mandamus Archive
2905. Federal Legal Nullification Vacatur Archive
2906. Federal Legal Nullification Reversal Archive
2907. Federal Legal Nullification Nullification Archive
2908. Federal Legal Nullification Structural Error Archive
2909. Federal Legal Nullification Complaint Archive
2910. Federal Legal Nullification Enforcement Archive
2911. Federal Case Reversal Litigation Archive
2912. Federal Case Reversal Appeal Archive
2913. Federal Case Reversal Habeas Archive
2914. Federal Case Reversal Mandamus Archive
2915. Federal Case Reversal Vacatur Archive
2916. Federal Case Reversal Reversal Archive
2917. Federal Case Reversal Nullification Archive
2918. Federal Case Reversal Structural Error Archive
2919. Federal Case Reversal Complaint Archive
2920. Federal Case Reversal Enforcement Archive
2921. Federal Judgment Vacatur Litigation Archive
2922. Federal Judgment Vacatur Appeal Archive
2923. Federal Judgment Vacatur Habeas Archive
2924. Federal Judgment Vacatur Mandamus Archive
2925. Federal Judgment Vacatur Vacatur Archive
2926. Federal Judgment Vacatur Reversal Archive
2927. Federal Judgment Vacatur Nullification Archive
2928. Federal Judgment Vacatur Structural Error Archive
2929. Federal Judgment Vacatur Complaint Archive
2930. Federal Judgment Vacatur Enforcement Archive
2931. Federal Judgment Nullification Litigation Archive
2932. Federal Judgment Nullification Appeal Archive
2933. Federal Judgment Nullification Habeas Archive
2934. Federal Judgment Nullification Mandamus Archive
2935. Federal Judgment Nullification Vacatur Archive
2936. Federal Judgment Nullification Reversal Archive
2937. Federal Judgment Nullification Nullification Archive
2938. Federal Judgment Nullification Structural Error Archive
2939. Federal Judgment Nullification Complaint Archive
2940. Federal Judgment Nullification Enforcement Archive
2941. Federal Judgment Collapse Litigation Archive
2942. Federal Judgment Collapse Appeal Archive
2943. Federal Judgment Collapse Habeas Archive
2944. Federal Judgment Collapse Mandamus Archive
2945. Federal Judgment Collapse Vacatur Archive
2946. Federal Judgment Collapse Reversal Archive
2947. Federal Judgment Collapse Nullification Archive
2948. Federal Judgment Collapse Structural Error Archive
2949. Federal Judgment Collapse Complaint Archive
2950. Federal Judgment Collapse Enforcement Archive
2951. Federal Legal Warfare Strategic Doctrine Archive
2952. Federal Strategic Litigation Doctrine Archive
2953. Federal Constitutional Litigation Doctrine Archive
2954. Federal Procedural Warfare Doctrine Archive
2955. Federal Structural Litigation Doctrine Archive
2956. Federal Litigation Collapse Doctrine Archive
2957. Federal Litigation Nullification Doctrine Archive
2958. Federal Litigation Enforcement Doctrine Archive
2959. Federal Litigation Defense Doctrine Archive
2960. Federal Litigation Offense Doctrine Archive
2961. Federal Advanced Legal Warfare Doctrine Archive
2962. Federal Elite Litigation Warfare Doctrine Archive
2963. Federal Strategic Case Collapse Doctrine Archive
2964. Federal Structural Case Collapse Doctrine Archive
2965. Federal Constitutional Case Collapse Doctrine Archive
2966. Federal Procedural Case Collapse Doctrine Archive
2967. Federal Jurisdiction Case Collapse Doctrine Archive
2968. Federal Judgment Collapse Warfare Doctrine Archive
2969. Federal Judicial Collapse Warfare Doctrine Archive
2970. Federal Prosecutorial Collapse Warfare Doctrine Archive
2971. Federal Judicial Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2972. Federal Prosecutorial Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2973. Federal Constitutional Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2974. Federal Procedural Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2975. Federal Structural Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2976. Federal Jurisdiction Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2977. Federal Legal Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2978. Federal Case Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2979. Federal Litigation Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2980. Federal Court Accountability Warfare Doctrine Archive
2981. Federal Advanced Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2982. Federal Elite Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2983. Federal Strategic Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2984. Federal Constitutional Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2985. Federal Procedural Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2986. Federal Structural Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2987. Federal Jurisdiction Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2988. Federal Judicial Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2989. Federal Prosecutorial Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2990. Federal Court Litigation Warfare Corpus Archive
2991. Federal Litigation Warfare Master Doctrine Archive
2992. Federal Litigation Warfare Strategic Doctrine Archive
2993. Federal Litigation Warfare Enforcement Doctrine Archive
2994. Federal Litigation Warfare Collapse Doctrine Archive
2995. Federal Litigation Warfare Nullification Doctrine Archive
2996. Federal Litigation Warfare Vacatur Doctrine Archive
2997. Federal Litigation Warfare Reversal Doctrine Archive
2998. Federal Litigation Warfare Accountability Doctrine Archive
2999. Federal Litigation Warfare Constitutional Doctrine Archive
3000. Federal Litigation Warfare Master Corpus Archive
🟨 FAQ
Q: What is Legal AI?
A: Legal AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to analyze legal information, automate drafting, assess evidence, and support legal decision-making while maintaining compliance and accountability.
Q: How does Mega Lawfare Legal AI differ from other legal AI tools?
A: Mega Lawfare Legal AI is institutional-grade enforcement infrastructure, combining education, intake, drafting, evidence analysis, governance, and mass coordination into a single auditable platform.
Q: Can Legal AI be used for civil rights and public accountability?
A: Yes. Mega Lawfare Legal AI is specifically designed to support civil rights enforcement, public accountability, and rule-of-law actions at scale.
Q: Is Mega Lawfare Legal AI compliant and ethical?
A: The platform is compliance-first, non-coercive, auditable, and designed to promote restraint, proportionality, and institutional trust.
